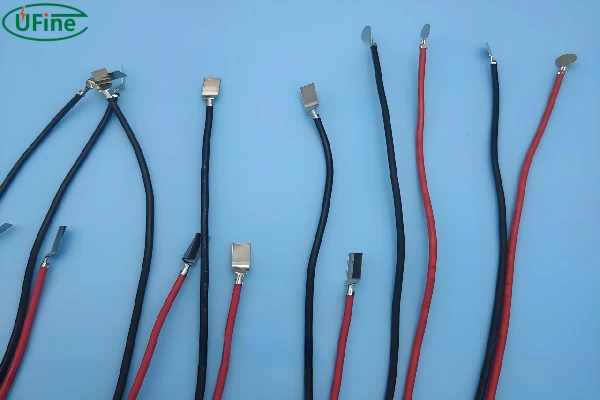
Lithium batteries have become a cornerstone in powering various devices, from everyday electronics like smartphones to advanced applications such as electric vehicles and renewable energy systems. Properly identifying lithium battery terminals is essential to ensure these devices’ safe and efficient operation. This comprehensive guide will walk you through what lithium battery terminals are, the various types available, the significance of correct identification, and how to select the right terminal for your specific needs.
Part 1. What are lithium battery terminals?
Lithium battery terminals are the crucial connection points where electrical current flows into and out of the battery. These terminals are responsible for linking the battery to the device’s electrical system, allowing power to be effectively delivered. Typically, a lithium battery has two terminals: a positive terminal and a negative terminal. The positive terminal is where the current flows out of the battery. In contrast, the negative terminal is where the current returns. Proper identification and connection of these terminals are vital for the battery to function correctly and safely, preventing damage to both the battery and the connected device.
Part 2. Types of lithium battery terminals
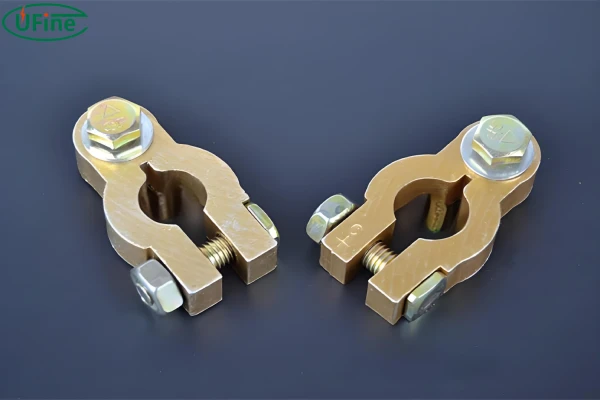
1. Stud Terminals
Stud terminals are threaded posts that protrude from the battery. They are designed to be used with nuts and washers to secure the connection firmly. These terminals are commonly found in larger lithium batteries, such as those used in electric vehicles, marine applications, and solar power systems.
Pros:
- Secure Connection: Provides a tight and stable connection, which is crucial for high-current applications.
- Durability: Ideal for environments that involve vibrations and movement.
Cons:
Tools Required: Installation and removal require tools, which can be inconvenient.
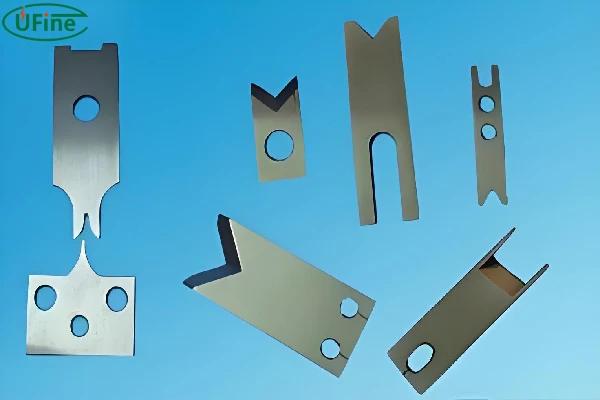
2. Blade Terminals
Blade terminals are flat, thin metal pieces that slide into corresponding connectors or slots. These terminals are typically used in smaller electronics and devices where space is limited.
Pros:
- Ease of Use: Simple to connect and disconnect without the need for tools.
- Compact Design: Suitable for devices with limited space.
Cons:
Less Secure: Not as secure as stud terminals, making them less ideal for high-current or high-vibration applications.
3. Post Terminals
Post terminals are cylindrical and protrude from the battery, designed to be connected using clamps. Commonly used in automotive batteries and other medium to large-scale batteries.
Pros:
- Ease of Connection: Simple to connect and disconnect, making them user-friendly.
- Versatility: Suitable for medium to high-current applications.
Cons:
Maintenance: Can corrode over time if not properly maintained, requiring periodic cleaning.
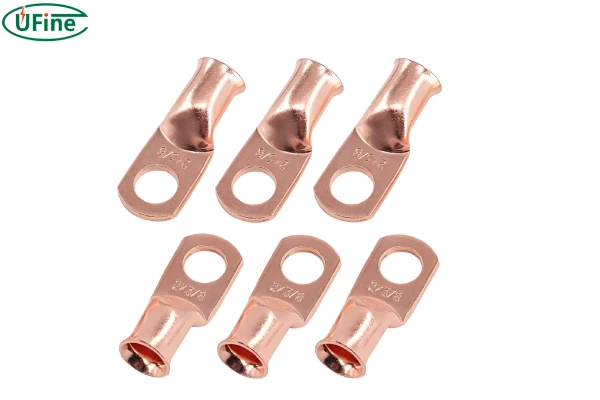
4. Ring Terminals
Ring terminals are circular connectors that fit over a stud or bolt, providing a secure connection. Versatile, used in a wide range of applications from small electronics to large power systems.
Pros:
- Secure Connection: Provides a reliable and stable connection.
- Durability: Suitable for high-vibration environments.
Cons:
Tools Required: Installation and removal require tools.
Part 3. Lithium battery connector and terminals
The lithium battery connector and lithium battery terminals. While they work together, they are distinct parts with different functions. Here’s a breakdown of their differences and connections:
Lithium Battery Terminals:
- What they are: These are the conductive points on the battery itself, usually made of metal, where the electrical connection is made. They are typically small posts, tabs, or flat surfaces.
- Function: They serve as the direct interface for the flow of electricity in and out of the battery.
- Types: Lithium battery terminals come in various forms, including:
- Stud terminals: Threaded posts for secure connections with nuts and washers.
- Blade terminals: Flat, thin metal pieces that slide into connectors.
- Post terminals: Cylindrical posts for clamp connections.
- Button/flat terminals: Simple flat contacts for small batteries.
- Location: They are directly attached to the battery casing.
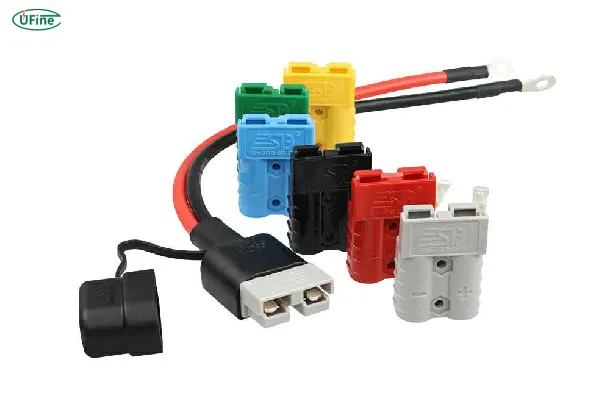
Lithium Battery Connectors:
- What they are: These are separate components that attach to the battery terminals to facilitate a connection with a device or charger. They often involve a housing (usually plastic) and conductive parts.
- Function: They provide a safe, convenient, and often detachable way to link the battery to the external circuit.
- Types: Connectors vary widely depending on the application and the type of terminal they are designed to mate with. Some common examples include:
- Plug-and-socket connectors: These are widely used for their ease of connection and disconnection.
- Automotive battery connectors: Heavy-duty connectors designed for the high currents in car batteries.
- Specialized connectors: Unique designs for specific applications, like those in drones or medical devices.
- Connection: The connector is designed to physically and electrically mate with the battery terminal.
Connection between Terminals and Connectors:
- Physical connection: The connector is designed to fit securely onto the battery terminal, ensuring good physical contact. This might involve sliding, clamping, or screwing the connector onto the terminal.
- Electrical connection: The conductive parts of the connector make electrical contact with the terminal, allowing current to flow between the battery and the device.
- Secure and reliable: The connection needs to be secure to prevent accidental disconnections and to ensure reliable power delivery.
Key Differences Summarized:
In essence: The terminal is the point of contact on the battery, while the connector is what you use to actually connect the battery to something. They are both essential for a functioning circuit, but they are distinct components with different roles.
Part 4. Why does correct identification matter?
Correctly identifying lithium battery terminals is critical for several reasons:
- Safety: Connecting the wrong terminals can lead to short circuits, resulting in sparks, fires, or even explosions. This not only endangers the device but also poses a significant risk to the user.
- Performance: Incorrect connections can degrade the performance of the battery and the device it powers. This can lead to inefficiencies, reduced battery life, and potential damage to the device’s electrical components.
- Longevity: Properly connecting the terminals helps maintain the battery’s lifespan. Ensuring the correct flow of current prevents undue stress on the battery, allowing it to operate as intended and last longer.
Part 5. 3 Ways to identify positive and negative lithium battery terminals
1. Visual Indicators
- Color Coding: The most common method of identification is color coding. The positive terminal is typically marked in red, while the negative terminal is marked in black or blue.
- Symbols: Another common indicator is the use of symbols. The positive terminal is often marked with a “+” symbol, and the negative terminal with a “-” symbol.
2. Physical Difference
- Size: In some batteries, the positive terminal is slightly larger than the negative terminal, making it easier to identify.
- Shape: The shape of the terminals can also differ. For example, the positive terminal might be round, while the negative terminal is flat or vice versa. This physical distinction helps identify the terminals even when color coding or symbols are not clear.
3. Multimeter Testing
If visual indicators are unclear, you can use a multimeter to accurately identify the terminals. Here’s how:
- Set the Multimeter: Adjust your multimeter to measure DC voltage.
- Connect the Probes: Touch the multimeter’s red probe to one terminal and the black probe to the other terminal.
- Read the Display: If the reading is a positive number, the red probe is on the positive terminal, and the black probe is on the negative terminal. If the reading is negative, you have the probes reversed.
Part 6. Which terminal is right for your lithium battery?
1. Assess Your Needs
Start by determining the specific requirements of your application. Consider factors such as the current load, the type of connection, and the environmental conditions in which the battery will operate. For instance, high-current applications like electric vehicles will need more robust and secure terminals, while smaller electronic devices may require compact terminals.
Refer to the battery’s manual or the manufacturer’s specifications. Manufacturers often provide detailed information about the recommended terminal types and configurations for their batteries. This guidance ensures compatibility and optimal performance.
3. Consider Compatibility
Ensure that the terminal type matches the connectors in your device or system. Using an incompatible terminal can lead to poor connections, which can cause intermittent power issues or even damage the battery and device. For instance, if your device uses blade connectors, make sure your battery has compatible blade terminals.
4. Evaluate the Environment
The operating environment plays a crucial role in terminal selection. For example:
High-Vibration Settings: Choose terminals that provide a secure and stable connection, such as ring or stud terminals, to prevent disconnection due to vibration.
Corrosive Environments: Opt for terminals with corrosion-resistant coatings or materials to ensure longevity and reliability.
5. Seek Professional Advice
If you’re unsure about which terminal to choose, consulting with a professional can be very helpful. Mobility equipment suppliers, electricians, or battery specialists can provide tailored advice based on your specific needs. This can help you avoid common pitfalls and ensure you select the right terminal for your lithium battery.
Part 7. How to match lithium battery connectors and terminals?
Matching lithium battery connectors and terminals is crucial for safety and performance. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you get it right:
1. Identify the Terminal Type:
- Visual inspection: Carefully examine the terminals on your lithium battery. Are they studs, blades, posts, or flat contacts? Note their size, shape, and arrangement.
- Manufacturer’s specifications: If available, consult the battery’s datasheet or the manufacturer’s website. They often provide detailed information about the terminal type and recommended connectors.
2. Consider the Application:
- Current and voltage: Determine the current and voltage requirements of your device. The connector must be able to handle these levels without overheating or causing voltage drops.
- Space constraints: Evaluate the available space in your device for the connector. Choose a connector that fits comfortably without causing any interference.
- Durability and environment: Consider the operating environment. If the battery will be subjected to vibration, moisture, or extreme temperatures, select a connector that is designed to withstand these conditions.
3. Choose the Connector:
- Compatibility: The connector must be compatible with the terminal type on your battery. It should fit securely and provide a reliable electrical connection.
- Connector type: Select a connector type that is appropriate for your application. Some common types include:
- Plug-and-socket connectors: Versatile and easy to use.
- Automotive battery connectors: Heavy-duty connectors for high-current applications.
- Specialized connectors: Unique designs for specific needs.
- Quality: Choose a high-quality connector from a reputable supplier. This will ensure durability and reliable performance.
4. Matching Process:
- Consult resources: Refer to connector catalogs, datasheets, or online resources to find connectors that match your battery terminals and application requirements.
- Seek expert advice: If you are unsure about which connector to choose, consult with an electronics specialist or battery supplier. They can provide guidance based on your specific needs.
- Consider samples: If possible, obtain samples of potential connectors to test their fit and compatibility with your battery terminals.
5. Safety Precautions:
- Polarity: Always ensure that you connect the positive terminal of the battery to the positive terminal of the device, and the negative terminal to the negative terminal. Incorrect polarity can damage the device or even cause a fire.
- Secure connection: Make sure the connector is securely attached to the battery terminal. A loose connection can cause intermittent power issues or even a complete disconnection.
- Insulation: Ensure that the connector is properly insulated to prevent short circuits.
Tips for Success:
- Take measurements: If you are unsure about the size of the terminals, take accurate measurements to ensure a proper fit.
- Consider the locking mechanism: If your application requires a secure connection, choose a connector with a locking mechanism.
- Use the right tools: Use the appropriate tools for installing the connector to avoid damaging the terminals or the connector.
By following these steps, you can effectively match lithium battery connectors and terminals, ensuring safe and reliable power for your devices.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Paper Battery vs. Flexible Battery: What’s the Difference and Which Is Better?
Paper vs. flexible batteries: learn the key differences, benefits, and which power source fits best for wearables, sensors, and smart tech.
What to Know Before Buying a Tiny LiPo Battery for Your Project
Tiny LiPo batteries are powerful and compact. Learn how to choose the right one for your project with specs, safety, and charging tips.
Bloated LiPo Battery: Will It Explode?
Will a bloated LiPo battery explode? Discover the causes, risks, safety steps, and expert tips to avoid disaster and protect your gear. Must-read safety guide!
12V 100Ah Lithium Ion Battery Price: Full Guide
Learn about 12V 100Ah lithium-ion battery price, from cost ranges to best brands, hidden fees, and how to get the best deal. A must-read for smart buyers!
Resistance and Conductivity: What It Means for Your Lithium Batteries
Resistance and conductivity impact lithium battery performance, lifespan, and safety—learn how they work and why they matter.