- Part 1. Ideal storage environment for lithium ion batteries
- Part 2. How to store lithium batteries safely at home
- Part 3. How to store lithium batteries safely in warehouses?
- Part 4. How to safely transport lithium batteries?
- Part 5. 10 Best ways to store lithium batteries?
- Part 6. How to deal with dangerous lithium batteries?
Part 1. Ideal storage environment for lithium ion batteries
In addition to warehouse-specific guidelines, lithium-ion batteries also need to be stored properly in other environments. Whether you’re storing them at home, in a factory, or in a smaller facility, here are the essential tips to keep your batteries safe and functional:
1. Choose a Dry, Cool, and Ventilated Location
Lithium-ion batteries should always be stored in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area. Exposure to high temperatures and humidity can degrade the battery and damage its surface, reducing its lifespan.
2. Don’t Overstack Battery Cartons
It’s important to avoid stacking lithium battery cartons higher than the recommended limit. Overstacking can put pressure on the lower cartons, potentially leading to battery deformation and leakage. This not only affects the batteries but can also pose a safety risk.
3. Keep Batteries Away from Direct Sunlight and Rain
Exposure to sunlight or rain can cause significant damage. Sunlight can overheat batteries, while water exposure can reduce insulation resistance and lead to issues like self-discharge or rusting. Always ensure that the batteries are stored in a dry, sheltered place.
4. Don’t Stack Batteries Randomly
Never stack batteries in an unorganized way. Doing so could cause short circuits or even physical damage to the batteries. Proper organization helps prevent accidents and ensures that each battery is easily accessible.
5. Store Potentially Hazardous Materials Separately
If you’re storing items that could potentially combust or explode, make sure they’re kept in isolation from the lithium-ion batteries. Furthermore, materials with different fire-extinguishing requirements should be kept separated to ensure proper safety measures can be taken if necessary.
Part 2. How to store lithium batteries safely at home
Storing lithium-ion batteries at home requires attention to safety and proper conditions. Follow these tips to prevent accidents and maintain battery health:
-
Choose a Cool, Dry Location Store batteries in a well-ventilated, temperature-controlled area (20–25°C). Avoid humid spaces, direct sunlight, and extreme temperature fluctuations.
-
Avoid Flammable Materials Keep batteries away from flammable items like paper, fabric, or cleaning products.
-
Use Original Packaging or Insulation Store batteries in their original packaging or cover terminals with insulating tape to prevent short circuits.
-
Maintain a Partial Charge Keep batteries at 50%-60% charge for long-term storage. Check and recharge every three months if unused.
-
Keep Out of Reach Store batteries in a safe place, away from children and pets, to avoid accidental damage.
-
Inspect Regularly Check batteries for leaks, bulging, or corrosion. Dispose of damaged batteries at a recycling center.
Part 3. How to store lithium batteries safely in warehouses?
When it comes to lithium-ion battery storage, safety is paramount. If you’re responsible for managing a storage facility, there are several critical guidelines you need to follow:
1. Compliance with Safety Standards
Lithium batteries, especially battery packs, are classified as dangerous goods. To ensure safe handling and transportation, all lithium-ion batteries must pass the UN38.3 test, which checks the safety of these batteries during transport.
2. Maintain the Ideal Temperature
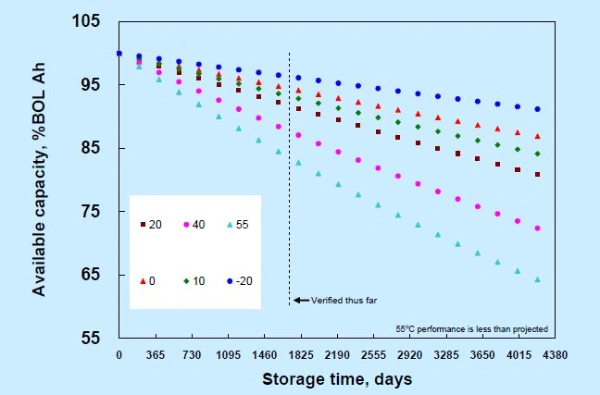
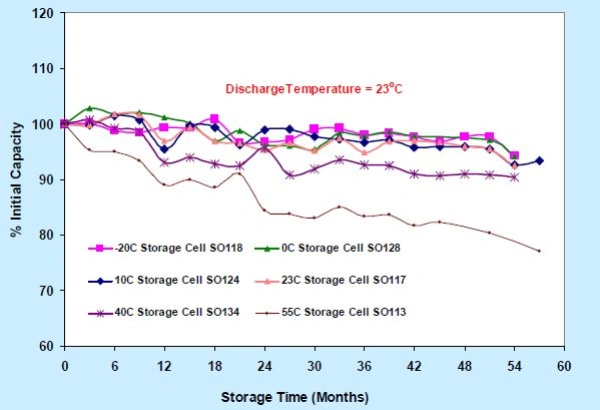
The storage environment for lithium-ion batteries needs to be kept at a temperature between 18°C and 25°C (64°F to 77°F). This is also the ideal temperature range for testing lithium batteries. Higher temperatures can accelerate the decay of battery capacity, leading to a shorter lifespan.
In fact, storing lithium batteries at room temperature or cooler can preserve over 90% of their remaining capacity after 54 months. It’s clear that temperature plays a major role in battery longevity.
3. Control Humidity Levels
Excessive moisture can severely damage lithium-ion batteries. It’s crucial to maintain a relative humidity level between 40% and 90% in the storage area. Humidity levels outside this range can lead to corrosion, rust, or even malfunctioning of the battery cells.
4. Secure the Warehouse Environment
Lithium-ion battery warehouses must be physically separated by brick walls or other fire-resistant materials to minimize risks in case of an incident. Furthermore, warehouses should be equipped with closed, explosion-proof, or otherwise safety-rated electrical lighting systems.
5. Fire Safety Measures
For warehouses storing lithium-ion batteries, proper fire safety equipment is essential. Ensure that there are enough fire extinguishers, particularly dry powder extinguishers, and that they are in good working condition. Additionally, store a fire bucket filled with water nearby as a backup.
6. Strict No Smoking or Fireworks Policy
To prevent accidental fires or explosions, smoking and the use of fireworks must be strictly prohibited in and around lithium-ion battery storage areas.
7. Avoid Storing Flammable Materials Nearby
Never store flammable or explosive materials in the same area as lithium batteries. This could lead to disastrous consequences in case of an accident.
Part 4. How to safely transport lithium batteries?
When it comes to transporting lithium-ion batteries, safety is essential. Improper handling or stacking can damage the batteries and pose safety risks. Here are some key guidelines to follow:
1. Handle with Care
Lithium batteries should always be handled carefully to prevent damage. Avoid dropping or mishandling the batteries, as this can cause internal short circuits or physical damage. Be mindful of load directionality when loading or unloading batteries.
2. Proper Stacking
When transporting lithium-ion batteries, make sure they are stacked securely. Follow the rule of heavy first, light last. This ensures that heavier batteries are placed at the bottom, minimizing the risk of damage during transport.
3. Use Safe Loading Equipment
If using a forklift or cart, take extra care when loading and unloading the batteries. Be sure to avoid crushing or causing any impact that could damage the battery’s internal structure or circuitry.
Part 5. 10 Best ways to store lithium batteries?
Proper storage is crucial for maintaining the health and longevity of lithium-ion batteries. Here are 10 tips to ensure safe storage:
1. Maintain a 50%-60% State of Charge
If you’re not using the lithium-ion battery for a while, store it at a 50%-60% charge. This helps preserve the battery’s health. Also, remember to charge the battery every 3 months to keep it from discharging too much. A full charge and discharge cycle every 6 months is ideal.
2. Protect from Moisture and Physical Damage
During transportation and storage, always protect the batteries from moisture, extrusion, and collision. These can cause serious damage to the battery cells.
3. Avoid High Temperatures
Never store or use lithium-ion batteries in extremely high temperatures. Don’t leave them in direct sunlight or in hot cars. Overheating can lead to fire, malfunction, and shortened battery life.
4. Stay Clear of Strong Magnetic Fields and Static Electricity
Storing lithium-ion batteries in places with strong static electricity or magnetic fields can damage the safety protection devices within the battery, posing potential risks.
5. Monitor for Abnormal Behavior
If the battery emits an unusual smell, generates heat, changes color, or deforms during use, storage, or charging, remove the battery immediately from the device or charger. Stop using it and dispose of it safely.
6. Set Up a Designated Storage Area
Lithium battery storage areas should be independent and clearly marked. A “No Fireworks” sign should be visible. Avoid storing flammable or combustible materials near the storage area.
7. Install Safety Monitoring Systems
Ensure that your battery storage facility is equipped with video surveillance and smoke and temperature alarms. These systems should be connected to a 24-hour manned location for quick responses to any emergencies.
8. Store Batteries Neatly and Safely
Always store batteries in an organized manner to avoid stacking them too high. The storage area should be made from non-combustible materials, and anti-static measures should be implemented.
9. Control Temperature and Humidity
Battery storage rooms should be kept at a temperature of 20±5°C (68°F) and relative humidity below 75%. This will help keep the batteries in good condition for long-term storage.
10. Handle Disposed Batteries with Care
Discarded lithium batteries should be wrapped in insulating paper to cover the electrodes. This prevents accidental fire or explosion during disposal.
Part 6. How to deal with dangerous lithium batteries?
It’s essential to know how to handle lithium-ion batteries when things go wrong. Here’s what you should do in case of overheating, fire, or explosion:
1. What to Do If the Lithium Battery Gets Hot
Lithium batteries naturally generate heat during charging or discharging, but the temperature usually stays below 60°C (140°F). However, if a battery experiences an internal or external short circuit, the temperature can rise significantly, potentially reaching dangerous levels.
- Isolate the battery immediately by placing it in sand to absorb the heat.
- Do not touch the battery directly with your hands to avoid burns.
- Once the temperature normalizes, consider disposing of the battery properly.
2. What to Do If the Lithium Battery Burns or Explodes
If a lithium battery catches fire or explodes, the situation can be very dangerous. Here’s how to handle it:
- Stay away from the fire or explosion.
- If only a single or a few batteries are burning, cover the battery with sand to smother the flames.
- In the case of a large fire, first cool it down with water and then use a dry powder fire extinguisher to put out the fire.
Related Tags:
More Articles

고방전 배터리는 높은 전류와 발열로 배터리수명이 줄어듭니다. 구조적 한계, 사용 패턴, 충전 습관 등 실제 수명 단축 요인을 체계적으로 분석했습니다.
Capacitor vs Battery: What is the Difference?
Capacitor vs battery explained in detail. Learn the difference between capacitor and battery in energy storage, charging speed, lifespan, and real applications.
18650 Battery vs AA: Which Is Better for Your Device?
Compare 18650 vs AA batteries in capacity, voltage, rechargeability, and applications. Learn which battery type fits high-drain or everyday devices.
What is the Difference Between Battery Cell, Battery Control Module, and Battery Pack?
Compare battery cells, modules, and packs. Learn functions, design differences, control modules, and selection tips for EV, ESS, and industrial use.
How to Prevent LiPo Battery Explosion?
Can LiPo batteries explode or catch fire? Learn key causes of LiPo battery fires and proven charging, storage, and handling tips to reduce explosion risk.