Many people debate inverters vs. generators when providing power when electricity is inverters generators. Both devices serve the purpose of generating electricity, but they do so in very different ways. Understanding these differences is essential for making the best choice for your needs. This article will explore what inverters and generators are, how they work, and their advantages and disadvantages, and ultimately help you decide which one is right for you.
Part 1. What is an inverter?
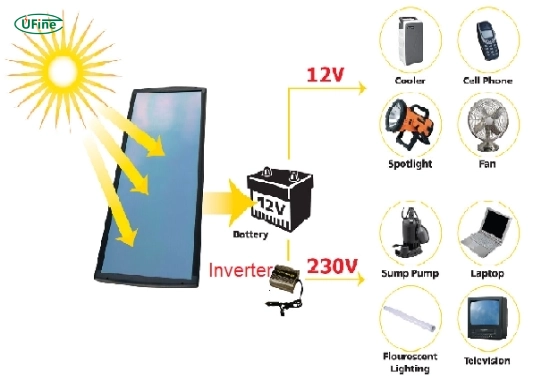
An inverter is a device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC). This conversion allows you to use power from batteries or solar panels to run household appliances and electronic devices that require AC power. Inverters are commonly used in off-grid systems, recreational vehicles (RVs), and backup power setups.
How does an inverter work?
Inverters operate by using electronic circuits to switch the current’s direction rapidly. This switching action creates an AC waveform that standard electrical devices can use. There are different types of inverters, including:
- Pure sine wave inverters: These produce a smooth, consistent waveform similar to the power supplied by utility companies. They are ideal for sensitive electronics like computers and medical equipment.
- Modified sine wave inverters: These generate a less smooth waveform that can still power most devices. They are typically more affordable than pure sine wave inverters but may only be suitable for some electronics.
Inverters can vary widely in size and capacity. Smaller models can power essential devices like lights and phones, while larger models can handle more demanding appliances like refrigerators and microwaves.
All You Need To Know About Battery Inverter
Part 2. What is a generator?
A generator is a machine that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. It typically runs on fuel such as gasoline, diesel, or propane and can provide a reliable power source for various applications, including construction sites, outdoor events, and emergency backup.
How does a generator work?
Generators operate on the principle of electromagnetic induction. When a conductor moves through a magnetic field, it generates electricity. The key components of a generator include:
- Engine: The engine provides the mechanical energy required to turn the rotor.
- Alternator: The alternator converts the mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy.
- Fuel system: This supplies fuel to the engine to keep it running.
We can classify generators into two main types:
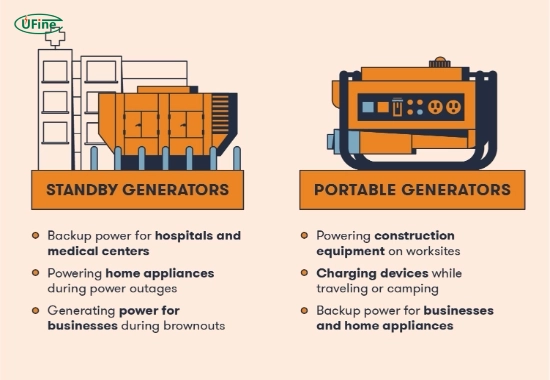
- Portable generators: These smaller units are designed for temporary use, and users can transport them easily. They are great for camping trips or emergency power at home.
- Standby generators: These are larger units installed permanently and automatically provide power during outages. They can run on natural gas or propane and are connected directly to your home’s electrical system.
Part 3. Key differences between inverters and generators
Understanding the differences between inverters and generators can help you choose the right option. Here are some key distinctions:
- Power Source: Inverters rely on batteries or solar panels for their power supply, while generators use gasoline or diesel.
- Output Type: Inverters convert DC to AC power, whereas generators produce AC power directly from mechanical energy.
- Portability: Inverters are lighter and more compact than generators, making them easier to transport.
- Noise Level: Inverters operate quietly compared to generators, which can be loud during operation.
- Fuel Efficiency: Inverters are generally more efficient since they use stored energy without needing fuel when idle; generators consume fuel continuously while running.
- Cost: High-quality inverters can be more expensive than essential generators but may save money over time due to lower operational costs.
Here’s a comparison table summarizing these differences:
| Feature | Inverter | Generator |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Batteries/Solar Panels | Fuel (gasoline/diesel) |
| Output Type | AC from DC | AC from mechanical energy |
| Portability | Generally lightweight | Heavier and bulkier |
| Noise Level | Quiet operation | Noisy during operation |
| Fuel Efficiency | Very efficient | Less efficient |
| Cost | Typically more expensive | Generally cheaper |
Part 4. Advantages of using an inverter
Inverters offer several benefits that make them appealing for specific applications:
- Quiet operation: Inverters operate quietly compared to generators. This makes them suitable for residential areas or camping trips where noise is a concern.
- Fuel efficiency: Since inverters use stored energy from batteries or solar panels, they do not consume fuel while idle, leading to lower operational costs over time.
- Clean power output: Pure sine wave inverters provide clean electricity safe for sensitive electronics like laptops and medical equipment.
- Lightweight and portable: Many inverters are designed to be compact and easy to transport, making them ideal for RVs or outdoor activities where space is limited.
- Low maintenance: Inverters typically require less maintenance than generators since they have fewer moving parts and do not need regular oil changes or fuel refills.
Part 5. Advantages of using a generator
Generators also have their own set of advantages that make them suitable for specific situations:
- High power output: Generators can provide significant power, making them ideal for running multiple appliances simultaneously during outages or at job sites where heavy machinery is used.
- Longer run time: Generators can run continuously as long as they have fuel, allowing you to maintain power for extended periods without needing to recharge or worry about battery life.
- Cost-effective for high demand: Generators may be more cost-effective than investing in large battery systems that require frequent recharging for users who need substantial power regularly—such as construction sites or significant outdoor events.
- Versatility: Generators can be used for various purposes beyond just home backup; they are often employed at events, job sites, or anywhere temporary power is needed.
Part 6. Disadvantages of using an inverter
While inverters have many advantages, they also come with some drawbacks:
- Limited power output: Inverters may need help to supply enough power for high-demand appliances like air conditioners or extensive tools that require significant wattage.
- Dependency on battery charge: An inverter’s performance depends on the state of its battery charge; if the batteries are depleted, it cannot provide power until recharged.
- Higher initial cost: Quality pure sine wave inverters can be more expensive upfront than essential generators, which might deter some buyers looking for immediate affordability.
Part 7. Disadvantages of using a generator
It would help if you considered the limitations of generators:
- Noise pollution: Generators can be pretty loud during operation; this noise may not be suitable for residential areas or quiet environments where peace is desired.
- Fuel dependency: Generators require fuel to operate; this means ongoing costs associated with fuel purchases and potential issues with fuel storage and availability during emergencies.
- Emissions: Running a generator produces emissions that harm health and the environment; proper ventilation is necessary indoors or near living spaces.
Part 8. When should you choose an inverter?
Choosing an inverter might be ideal if you need:
- A quiet solution for camping or RVing where noise could disturb others.
- Clean power for sensitive electronics such as laptops or medical devices that require stable voltage.
- A lightweight option that’s easy to transport without taking up much space.
- A system powered by renewable energy sources like solar panels that align with eco-friendly practices.
- Low-maintenance equipment that doesn’t require frequent servicing or refueling.
Part 9. When should you choose a generator?
Opting for a generator may be better suited if you require:
- High power output capable of running multiple devices simultaneously during outages.
- A reliable source of energy during extended outages when long-term usage is necessary.
- A cost-effective solution for temporary job sites or events where heavy-duty appliances need constant power.
- The ability to run heavy-duty appliances without concern over battery life running out unexpectedly.
- A versatile unit that can serve various purposes beyond home backup needs—like powering tools at construction sites or providing electricity at outdoor events.
Part 10. FAQs
-
Can I use an inverter with my car battery?
Yes, you can use an inverter with your car battery if the inverter’s wattage does not exceed the battery’s capacity. However, prolonged use may drain your car battery quickly if not monitored carefully. -
Are generators safe to use indoors?
Generators should never be indoors due to the risk of carbon monoxide poisoning from exhaust fumes produced during operation. Continuously operate them outdoors in well-ventilated areas away from windows and doors. -
How long can an inverter run on batteries?
The runtime of an inverter depends on both the capacity of its batteries and the total load being powered at any given time. Smaller loads will allow longer runtimes than larger ones, which draw more current from the batteries faster than smaller devices, which would consume it over time. -
Do I need special wiring for a generator?
Yes, if you plan to connect a generator directly to your home’s electrical system, a transfer switch installed by a qualified electrician is essential to prevent the generator from back-feeding into the grid. -
Can I charge my inverter while using it?
Some inverters allow simultaneous charging while powering devices; however, this depends on their design and specifications. Always check the manufacturer’s guidelines before attempting this.
Related Tags:
More Articles
10000mAh Battery Explained: How Long It Lasts, How It Works
A full guide on 10000mAh li-ion batteries, voltage, usage time, and tips. Discover how a 10000mAh battery works, how long it lasts, and how to choose.
10440 Battery Guide: Size, Voltage, Capacity, Uses & More
Understand 10440 batteries better—size, voltage, safety, and how they compare to AAA. Find the best fit for your high-performance devices.
White Stuff on Battery Terminals: A Step-by-Step Cleaning and Maintenance Guide
White stuff on battery terminals is corrosion. Learn how to clean it safely, prevent damage, and keep your battery running strong with simple steps.
Understanding How Glass Mat Batteries Work: Technology, Benefits, and Limitations
Glass mat batteries power cars, RVs, and solar systems. Learn how they work, their benefits, and what to consider before choosing one.
A Buyer’s Guide for AA Size Lithium Battery
Discover the power of AA size lithium batteries—types, voltage, capacity, and more! Learn how to choose the best one for your needs. Read now!