In our fast-paced world, where everyone is always on the go, waiting for hours to charge a device can be frustrating. Fast charging has emerged as the solution, promising to power up batteries quickly and get us back to using our devices in no time. However, this convenience often raises a key question: is fast charging harmful to lithium batteries? In this article, we’ll dive deep into the science behind lithium battery charging, how fast charging works, the potential impacts on battery health, and whether or not you should worry about using it regularly.
Part 1. Understanding the charging principle of lithium batteries
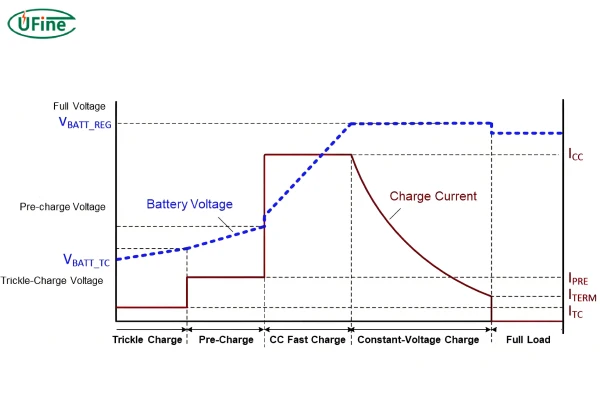
Lithium-ion batteries have revolutionized portable energy, powering everything from smartphones to electric vehicles. To understand the effects of fast charging, we first need to understand how these batteries charge in standard conditions. Charging a lithium-ion battery is a delicate process that involves moving lithium ions from one electrode to another.
How Lithium-Ion Charging Works
-
Basic Structure: A lithium-ion battery consists of two main electrodes—an anode (negative) and a cathode (positive)—separated by an electrolyte that allows ions to move back and forth. During charging, lithium ions move from the cathode to the anode, and during discharging, they return to the cathode, releasing energy to power the device.
-
Constant Current Phase: Charging typically starts with a constant current (CC) phase, where a steady current is applied to the battery, gradually increasing its voltage until it reaches a specific level (usually around 4.2 volts for lithium-ion cells).
-
Constant Voltage Phase: Once the battery reaches this voltage, the charging enters a constant voltage (CV) phase. In this stage, the voltage remains stable, but the current slowly decreases as the battery nears full capacity. This phase is designed to avoid overcharging and to maximize battery safety.
-
Battery Management System (BMS): Most lithium-ion batteries are equipped with a Battery Management System (BMS), which monitors voltage, current, and temperature to optimize safety and efficiency. The BMS prevents the battery from overcharging, which can lead to overheating and potential degradation over time.
Fast Charging Technology and BMS for Lithium Batteries
This two-phase approach helps protect the battery’s structure, ensuring stable performance and extending battery lifespan.
Part 2. What is the fast charging battery?
Now, what exactly do we mean by “fast charging”? Typically, fast charging refers to charging that operates above the standard 1C rate, where “C” represents the battery’s capacity. For example, if a 1,000mAh battery charges at 1C, it takes one hour to charge fully at 1,000mA. Fast charging increases this rate, achieving 50% or even 80% capacity in under an hour.
What does C Mean in Batteries?
How Fast is Considered “Fast Charging”?
Fast charging generally refers to anything that charges a battery significantly faster than standard 1C. Different technologies, such as Qualcomm Quick Charge, USB Power Delivery (PD), and proprietary fast-charging systems from companies like Tesla or OnePlus, can charge batteries at rates from 1.5C to as high as 5C or more. This level of power delivery requires special chargers and a compatible device, and the faster the charging, the more complex the battery management needed to prevent damage.
Part 3. The principle of fast charging batteries
Fast charging a lithium battery works by delivering either higher current, increased voltage, or a combination of both. Let’s look at the main approaches:
High-Current Charging
Increasing the current during charging directly reduces the time required. However, high-current charging generates more heat, putting additional stress on the battery’s materials. Managing this heat is crucial, as excess heat can accelerate chemical reactions that lead to degradation.
Increased Voltage Charging
Another fast-charging approach involves raising the charging voltage, which increases the energy pumped into the battery within a given time. This method is generally controlled by the BMS to prevent over-voltage damage.
Pulse Charging and Dual-Cell Batteries
Some advanced fast-charging systems use pulse charging, where the current pulses on and off rapidly. This method reduces overheating and allows for faster charging with less stress on battery cells. Another design strategy is the use of dual-cell batteries, where two smaller cells charge simultaneously, effectively doubling the charging rate without requiring excessively high voltage or current.
Part 4. What is the impact of fast charging on the battery?
While fast charging is highly convenient, it comes with certain impacts on the battery’s health and lifespan. Here’s how fast charging can affect your battery:
Increased Heat Generation
One of the most significant impacts of fast charging is the extra heat generated. Charging at high currents or voltages creates heat as a byproduct. While batteries are built to handle some level of heat, consistently high temperatures can degrade the battery’s electrolyte and the anode-cathode materials, leading to reduced capacity over time.
Lithium Plating
At high charging speeds, there is a risk of lithium plating, where lithium ions accumulate on the anode’s surface instead of embedding properly. This phenomenon can cause a reduction in battery capacity and increase the risk of short circuits, impacting battery life and even posing safety risks in extreme cases.
Reduced Battery Capacity Over Time
Lithium-ion batteries have a finite number of charge cycles, usually between 300 to 500 full charges. Fast charging, due to its more intense current and temperature, may shorten the effective life of a battery by accelerating the wear on battery cells, leading to a faster loss of capacity.
Part 5. Does fast charging harm the battery?
Yes, fast charging can harm the battery, especially when done frequently. However, the extent of the harm depends on various factors:
-
Battery Design: Batteries designed for fast charging (e.g., in electric vehicles or high-end smartphones) have safeguards in place, such as more advanced BMS and temperature management systems.
-
Usage Patterns: Consistent, daily fast charging can have a cumulative effect on battery health. However, occasional fast charging is less likely to cause significant harm.
To mitigate the potential harm from fast charging, it’s best to use it sparingly and only when necessary.
Part 6. What is the impact of frequent charging on the life of lithium batteries?
Frequent charging, especially if done with fast chargers, can add strain to the battery. Here’s why:
-
More Frequent Cycles: Every time a battery charges, it completes a partial cycle. Frequent partial charging, especially when done at high speed, can accelerate wear, reducing overall lifespan.
-
Shallow Cycles vs. Deep Cycles: Lithium-ion batteries tend to perform best with moderate discharge cycles. Constantly topping off the battery without allowing it to discharge to a lower level can lead to reduced battery capacity over time.
Frequent charging with a fast charger amplifies these issues, potentially reducing the total lifespan of the battery. Balancing fast charging with regular charging can help maintain battery health over time.
Part 7. Does slow charging affect battery life?
Slow charging is less likely to harm battery health and can, in fact, benefit it. Charging at lower speeds allows the battery’s internal chemical reactions to proceed at a more controlled pace, generating less heat and reducing stress on the battery. As a result, slow charging is often considered a “gentler” option for lithium-ion batteries, helping to prolong their lifespan by preventing thermal and chemical stress.
Part 8. Should I avoid using fast charging batteries?
So, with all these potential downsides, should you avoid fast charging altogether? The answer depends on your specific needs and how you use your devices. Here are some best practices to help you use fast charging responsibly:
-
Use Fast Charging Sparingly: Limit fast charging to occasions when you genuinely need a quick power-up. Rely on slower charging when you have more time to extend your battery’s lifespan.
-
Avoid Fast Charging in Hot Conditions: Heat amplifies the wear and tear on your battery. Fast charge in cooler environments and avoid using the device heavily while it’s charging, as this adds to the heat load.
-
Choose High-Quality Chargers: Always use chargers and cables recommended by your device’s manufacturer. Cheap or off-brand fast chargers may not have adequate safeguards, potentially damaging the battery with inconsistent voltage or current levels.
-
Don’t Leave Devices Plugged in for Long: Try not to leave devices plugged into a fast charger for extended periods, as this could overcharge and stress the battery.
By balancing fast charging with regular, slow charging, you can get the best of both worlds—convenience and longer battery health.
Part 9. Final words
Fast charging has transformed the way we use and charge our devices, but it’s important to understand its trade-offs. Regularly using fast charging can speed up wear and reduce a lithium battery’s capacity over time, but if used responsibly, its impact can be minimized. By following some simple guidelines—using fast charging only when necessary, keeping devices cool, and avoiding low-quality chargers—you can enjoy the convenience of fast charging without significantly harming your battery.
In the end, whether fast charging is “bad” depends largely on how often and in what situations you use it. By striking the right balance, you can keep your battery healthy and ready for whatever you need.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Paper Battery vs. Flexible Battery: What’s the Difference and Which Is Better?
Paper vs. flexible batteries: learn the key differences, benefits, and which power source fits best for wearables, sensors, and smart tech.
What to Know Before Buying a Tiny LiPo Battery for Your Project
Tiny LiPo batteries are powerful and compact. Learn how to choose the right one for your project with specs, safety, and charging tips.
Bloated LiPo Battery: Will It Explode?
Will a bloated LiPo battery explode? Discover the causes, risks, safety steps, and expert tips to avoid disaster and protect your gear. Must-read safety guide!
12V 100Ah Lithium Ion Battery Price: Full Guide
Learn about 12V 100Ah lithium-ion battery price, from cost ranges to best brands, hidden fees, and how to get the best deal. A must-read for smart buyers!
Resistance and Conductivity: What It Means for Your Lithium Batteries
Resistance and conductivity impact lithium battery performance, lifespan, and safety—learn how they work and why they matter.