
- Part 1. What is a lithium-ion battery and why discharge depth matters?
- Part 2. What does “fully discharging” really mean?
- Part 3. What happens when a lithium battery is fully discharged?
- Part 4. Optimal lithium battery maintenance: The 20–80% rule
- Part 5. What happens if a 12V rechargeable lithium battery is fully discharged?
- Part 6. Do lithium-ion batteries have a memory effect?
- Part 7. How to recharge a fully discharged lithium-ion battery safely?
- Part 8. Battery Management Systems: Your electronic safeguard
- Part 9. Accident recovery protocol
- Part 10. Quantifying lithium battery longevity
- Part 11. Advanced FAQs about lithium battery discharge
Is it bad to fully discharge a lithium-ion battery? Yes. Allowing a lithium-ion battery to discharge below its safe voltage limit (typically under 3.0V per cell) causes permanent chemical damage, reduces capacity, and may make the battery unsafe or impossible to recharge.
In simple terms: A lithium battery should never be truly discharged to 0%. What devices display as “0%” is only a protective cutoff, not a real full discharge.
This guide explains what fully discharging a lithium battery really means, what happens when it occurs, how to safely recharge a fully discharged lithium-ion battery, and how to prevent long-term damage in real-world applications such as 12V rechargeable batteries, electric vehicles, and energy storage systems.
Part 1. What is a lithium-ion battery and why discharge depth matters?
Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries store and release energy by moving lithium ions between a graphite anode and a metal-oxide cathode such as NMC or LFP. This process operates safely only within a specific voltage window, typically 3.0V–4.2V per cell.
- Below 3.0V: The anode structure destabilizes, and copper current collectors may begin dissolving.
- Above 4.2V: Cathode oxidation accelerates, increasing thermal runaway risk.
Depth of Discharge (DoD) refers to how much of a battery’s total capacity is used in each cycle. Research published in the Journal of Power Sources shows that reducing DoD by just 10% can significantly extend cycle life.
What does fully discharging a lithium battery mean?
Fully discharging a lithium battery means allowing the cell voltage to drop below its minimum safe limit (typically 2.5–3.0V per cell), not simply reaching 0% on a device display.
Once this threshold is crossed, internal chemical damage begins, even if the battery can later be recharged.
Part 2. What does “fully discharging” really mean?
A true full discharge occurs when a lithium-ion cell’s voltage falls below 3.0V — far lower than the shutdown point enforced by most devices and Battery Management Systems (BMS).
This deep-discharge region triggers irreversible damage through multiple mechanisms:
- Copper dissolution: Below ~2.5V, copper from the current collector dissolves and forms internal short circuits.
- SEI layer breakdown: The protective solid electrolyte interface degrades, consuming active lithium.
- Electrolyte decomposition: Organic solvents break down, generating flammable gases.
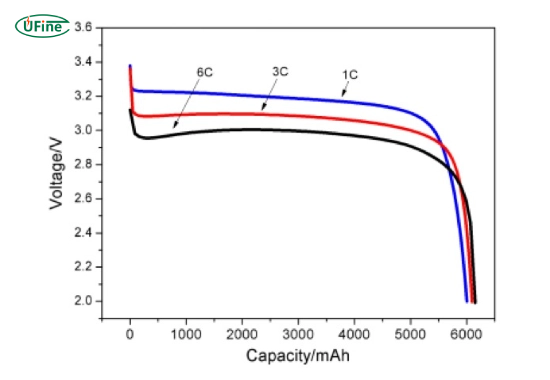
University of Michigan research shows that lithium cells discharged to 2.0V can lose up to 15% of their capacity in a single cycle.
Part 3. What happens when a lithium battery is fully discharged?
When a lithium-ion battery is fully discharged, irreversible chemical reactions occur inside the cell, leading to permanent capacity loss, internal resistance increase, and elevated safety risks.
- Structural collapse: Graphite layers exfoliate below 2.5V, reducing anode capacity by 30–40%.
- Gas generation: Electrolyte decomposition produces CO₂ and C₂H₄, causing swelling.
- BMS stress: Repeated deep discharge accelerates MOSFET wear and protection failure.
If you are seeing frequent battery discharge warnings, the battery may already be operating outside safe limits.
Part 4. Optimal lithium battery maintenance: The 20–80% rule
The 20–80% charging rule is the most effective way to extend lithium-ion battery lifespan in daily use. Instead of fully charging and deeply discharging, the battery operates within a low-stress voltage range.
| Discharge Depth | Typical Cycle Life | Capacity After 2 Years | Degradation Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100% (0–100%) | 300–500 cycles | 60–70% | ~1.8% / month |
| 50% (30–80%) | 1,200–2,000 cycles | 85–90% | ~0.5% / month |
- Temperature control: Keep operating temperature between 15–25°C. Every 8°C above 30°C cuts battery life in half.
- Storage best practice: Store lithium batteries at ~50% state of charge (SOC) at 10–20°C to minimize calendar aging.
Part 5. What happens if a 12V rechargeable lithium battery is fully discharged?
A 12V rechargeable lithium battery typically consists of three or four lithium-ion cells connected in series. When such a battery is fully discharged, damage risk increases significantly compared to a single cell.
- One weaker cell may drop below 2.0V and suffer permanent failure
- Cell imbalance increases, making the pack unsafe to recharge
- The Battery Management System (BMS) may enter permanent protection mode
This issue commonly occurs in applications such as:
- RV and camper power systems
- Solar energy storage and off-grid setups
- Backup power supplies and UPS systems
- Industrial and marine equipment
To avoid failure, a 12V lithium battery should never be stored or operated below 20% state of charge for extended periods.
How to prevent full discharge in 12V lithium battery systems
- Use batteries with built-in low-voltage BMS protection
- Install low-voltage disconnect (LVD) modules in solar and RV systems
- Monitor individual cell voltage in multi-cell battery packs
- Recharge immediately if voltage drops near cutoff level
Part 6. Do lithium-ion batteries have a memory effect?
Short answer: No. Lithium-ion batteries do not have a memory effect.
Unlike nickel-cadmium (NiCd) or nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries, lithium-ion chemistry does not “remember” partial charge cycles. Regular partial charging does not reduce usable capacity.
However, many users confuse battery calibration issues with memory effect.
Why does my battery percentage become inaccurate?
Lithium batteries rely on a Battery Management System (BMS) to estimate remaining charge. Over time, this estimation can drift due to:
- Partial charging patterns
- Temperature variation
- Battery aging and increased internal resistance
How to calibrate a lithium-ion battery safely
Calibration improves percentage accuracy, not battery health.
- Discharge the battery until the device shuts down at its built-in cutoff (usually ~3.0V per cell)
- Recharge immediately to 100% using a standard charger (≤0.5C preferred)
- Repeat no more than once every 2–3 months
Important: This process does not mean deep discharging the battery to true 0%. Stop at the device or BMS cutoff.
Part 7. How to recharge a fully discharged lithium-ion battery safely?
If your lithium-ion battery is fully discharged, follow these steps to recharge it safely:
Step 1: Check battery voltage
Use a digital multimeter to check the open-circuit voltage (OCV). If the voltage is below 2.5V, it likely indicates permanent damage, and recovery is unlikely.
Step 2: Apply low-current recovery charge
If the battery voltage is between 2.5V and 3.0V, apply a constant-voltage charge at a very low current (<0.05C) for 12–24 hours to bring the voltage back to a safe range.
Step 3: Monitor temperature and swelling
During charging, keep an eye on the battery’s temperature. If it exceeds 45°C or begins to swell, immediately stop charging and safely dispose of the battery.
Step 4: Switch to normal charging
If the voltage stabilizes above 3.0V and the battery does not exhibit swelling or excessive heat, you can switch to normal charging (0.5C or ≤1C).
Safety warning:
- Never attempt to charge a battery if it shows visible signs of damage, such as cracks, bulging, or leaking.
- If the battery exhibits any of these symptoms, safely dispose of it according to local hazardous waste regulations.
Part 8. Battery Management Systems: Your electronic safeguard
Modern lithium-ion batteries are equipped with Battery Management Systems (BMS) that provide crucial safety and performance protection. These systems monitor and protect each cell, preventing overcharge, deep discharge, and temperature extremes.
Key functions of a BMS:
- Voltage Monitoring: The BMS tracks the voltage of each cell, ensuring it stays within a safe range (typically 2.8V–4.2V per cell).
- Discharge Cutoff: If a cell’s voltage drops below the minimum threshold (~2.8V), the BMS automatically cuts off discharge to prevent damage.
- Charge Cutoff: When voltage exceeds 4.25V, the BMS prevents overcharging, which can lead to thermal runaway and fires.
- Balancing Systems: Passive or active balancing is employed to ensure all cells in the pack charge and discharge at the same rate, preventing imbalance.
Redundancy in EV Batteries:
In electric vehicles (EVs), BMS systems are often designed with redundancy. Multiple controllers and separate power supplies ensure that even if one system fails, another can step in to keep the battery safe.
Tip: A well-functioning BMS significantly extends the lifespan of your battery by preventing over-discharge, overcharge, and excessive heating.
Part 9. Accident recovery protocol
If your lithium battery has been discharged below safe voltage limits, it is crucial to follow proper recovery protocols to assess its condition and prevent further damage.
Step-by-step recovery process:
Step 1: Initial Assessment
Use precision calipers to check for swelling. Any increase in volume greater than 1mm indicates the battery is unsafe and should be discarded.
Step 2: Controlled Recharge
For batteries with voltage between 2.5V and 3.0V, apply a constant-voltage charge at a current-limited supply (max 0.1C). Monitor temperature and voltage closely during the process.
Step 3: Capacity Testing
After the recovery charge, perform a full cycle charge/discharge test. If the capacity drops by more than 20%, it’s best to replace the battery.
Critical Safety Note:
- Do not attempt recovery if the battery shows swelling, excessive heat, or visible damage.
- If the battery exceeds 45°C during charging, stop immediately and safely dispose of it.
Professional recovery services often use sealed environments, such as argon-filled glove boxes, to handle critically damaged cells safely.
Part 10. Quantifying lithium battery longevity
The lifespan of a lithium-ion battery depends on multiple interacting factors, including depth of discharge (DoD), temperature, charging rate, and application scenario. Fully discharging the battery consistently is one of the fastest ways to shorten its usable life.
| Application | Typical Cycle Life | Optimized Cycle Life | Expected Calendar Life |
|---|---|---|---|
| Smartphones & Consumer Electronics | ~500 cycles (80% DoD) | ~1,200 cycles (50% DoD) | 2–3 years |
| 12V Rechargeable Lithium Batteries | ~800 cycles (100% DoD) | 2,000–3,000 cycles (70% DoD) | 5–8 years |
| Electric Vehicles (EVs) | ~1,000 cycles (100% DoD) | 3,000–3,500 cycles (70% DoD) | 8–12 years |
| Grid & Solar Energy Storage | 4,000 cycles (80% DoD) | 10,000–15,000 cycles (50% DoD) | 15–20 years |
Studies from MIT and other research institutions show that proper voltage management and avoiding deep discharge can extend EV battery life beyond 500,000 miles.
Why shallow discharge dramatically increases battery life
- Reduces mechanical stress on electrode materials
- Minimizes SEI layer thickening
- Prevents copper dissolution at the anode
- Maintains stable internal resistance over time
For users operating 12V lithium batteries in solar, RV, or backup systems, limiting discharge depth is the single most effective strategy to maximize return on investment.
Part 11. Advanced FAQs about lithium battery discharge
Is fully discharging a lithium battery bad?
Yes. Fully discharging a lithium battery below its safe voltage limit causes irreversible chemical damage such as copper dissolution, SEI layer breakdown, gas generation, and permanent capacity loss.
Does 0% on my device mean the battery is fully discharged?
No. When a device shows 0%, the Battery Management System has already cut off power to prevent true full discharge.
Can a fully discharged lithium battery be recharged?
Sometimes. If the voltage remains above approximately 2.5V and there is no swelling or overheating, low-current recovery charging may restore partial functionality.
How do I recharge a fully discharged lithium-ion battery safely?
First, measure voltage. If above 2.5V, apply a low-current recovery charge (≤0.05C) until voltage exceeds 3.0V, then resume normal charging while monitoring temperature.
Do lithium batteries need to be fully discharged occasionally?
No. Lithium-ion batteries do not require full discharge. Some manufacturers suggest occasional full discharge only to recalibrate battery percentage estimation, not to improve battery health.
Are 12V rechargeable lithium batteries more sensitive to deep discharge?
Yes. Multi-cell 12V lithium battery packs are more vulnerable because one weak cell can drop below safe voltage, causing pack imbalance and permanent failure.
How can I prevent lithium batteries from fully discharging?
Avoid dropping below 20% state of charge, use batteries with built-in BMS protection, and recharge promptly after low-voltage warnings.
Does temperature affect discharge safety?
Yes. At low temperatures, deep discharge increases lithium plating risk, while high temperatures accelerate degradation and gas generation.
Related Tags:
More Articles

18650 Battery vs AA: Which Is Better for Your Device?
Compare 18650 vs AA batteries in capacity, voltage, rechargeability, and applications. Learn which battery type fits high-drain or everyday devices.
What is the Difference Between Battery Cell, Battery Control Module, and Battery Pack?
Compare battery cells, modules, and packs. Learn functions, design differences, control modules, and selection tips for EV, ESS, and industrial use.
How to Prevent LiPo Battery Explosion?
Can LiPo batteries explode or catch fire? Learn key causes of LiPo battery fires and proven charging, storage, and handling tips to reduce explosion risk.
Aluminium Ion Battery vs Lithium-Ion: A Detailed Comparison
Compare aluminium ion battery vs lithium-ion battery in energy density, charging speed, safety, cost, and uses. A practical guide for engineers and buyers.
C vs D vs AA Battery: Size, Voltage, Capacity & Key Differences Explained
Compare AA, C, and D batteries by size, voltage, capacity, and lifespan. Learn the real difference between C and D batteries and which one you should use.


