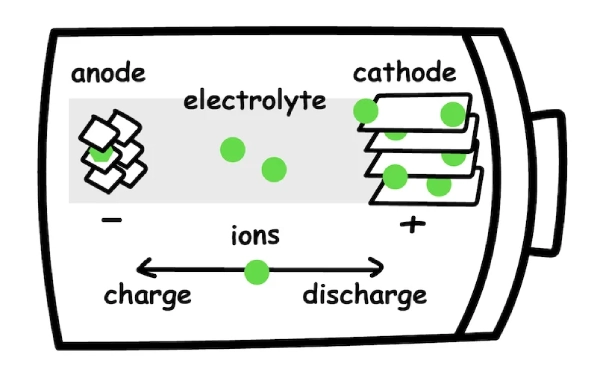
Lithium batteries are currently the most widely used rechargeable batteries. Correctly charging lithium batteries can extend the life of the lithium battery and ensure its performance and safety.
Lithium batteries can be made rectangular, cylindrical, rectangular, and button-type according to the requirements of different electronic devices. Single-cell lithium batteries can be used in low-power devices. Multiple lithium batteries can also be combined in series and parallel to obtain higher voltage and capacity lithium battery packs for use in higher-power electronic equipment.
Part 1. Learn about lithium Battery Charging
Although lithium batteries have the advantages of high capacity and long life, they require special attention when charging and discharging. All rechargeable lithium batteries must be equipped with a “charge and discharge management IC” to limit the charging and discharging voltage to ensure that the safe voltage is not exceeded and the battery explodes. When the battery voltage is lower than 2.5V, the output is cut off to avoid shortening the battery life.
In addition to over-discharge, lithium batteries are not suitable for high-current discharge. The high current discharge will reduce the discharge time. Therefore, lithium battery manufacturers should regulate the maximum discharge current of this product. It should be less than the maximum discharge current during use.
Lithium batteries have very high requirements for charging quality. A sophisticated charging circuit is required to ensure charging safety.
In particular, the accuracy of the termination voltage is required to be within 1% of the rated value (for example, for charging a 4.2V lithium-ion battery, the tolerance is ±0.042V). Overvoltage charging may cause permanent damage to lithium batteries or even cause the battery to explode.
The charging current of a lithium battery should be selected according to the specifications of the lithium battery manufacturer.
In addition, not all lithium battery charging uses constant current charging; it also uses constant voltage mode charging. So, the actual charging time is about 2.5 hours. The charging temperature of a lithium battery is in the range of 0℃~60℃. If the charging current is too high, the temperature will be too high, which will damage the battery and cause an explosion. Therefore, when charging with a high current, the battery’s temperature needs to be detected. To ensure safety, it can stop charging when the set charging temperature is exceeded.
In addition, the lithium battery charger circuit has a set current limiting resistor. This ensures that the charging current does not exceed the set limit current.
Part 2. Lithium-ion battery charging methods
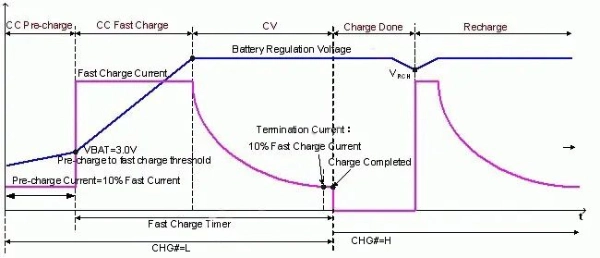
At present, lithium battery chargers often use the three-stage charging method. Namely Pre-Charging Mode, Fast Charging Mode, and Constant Voltage Mode. The terminal discharge voltage of lithium-ion batteries is 2.5V.
1. Pre-Charging Mode
A well-designed lithium battery charger can rescue and repair over-discharged batteries. That is, preprocessing is performed before formal charging.
Check the battery voltage before charging: if the battery voltage is greater than 3V, charge as normal. Suppose the battery voltage is lower than 3V. In that case, it is charged with a small current (about 10% Pre-Charging Mode), called Pre-Charging Mode, so that the passivation film dissolved in a deep discharge state can be restored.
In addition, when the battery is over-discharged, part of the copper metal may be released and cause a short circuit at the anode. At this time, forced charging with a high current will cause the battery to overheat. Pre-Charging Mode can avoid this phenomenon. After charging to 3V, press Fast Charging Mode to charge.
2. Fast Charging Mode
When the battery voltage exceeds 3V, charge according to Fast Charging Mode (as shown in the figure, taking a 4.2V lithium battery as an example). Just start charging in the Fast Charging Mode. At this time, the battery voltage rises at a faster slope.
As battery power storage increases, the battery voltage rise slope gradually decreases. When it rises to close to 4.2V, Fast Charging Mode ends. The charger changes to 4.2 V Constant Voltage Mode for charging.
In Constant Voltage Mode, the voltage is almost unchanged, but the charging current decreases. The timer is activated when the charging current drops to a certain value. After counting time expires, the charging ends, and the charging process is completed.
3. Constant Voltage Mode
Constant Voltage Mode’s output voltage regulation accuracy is important for maximizing lithium battery capacity and extending battery life.
When the battery voltage regulation is lower than 4.2V, the battery may be undercharged. Although it does not affect the life of the battery, it does reduce the battery capacity. For example, as long as insufficient charging reaches 1% of the total voltage, the battery storage capacity will be reduced by 8%.
On the other hand, if the battery voltage regulation is too high, it will cause the battery to be overcharged, shorten its service life, and even cause danger.
To ensure the safety of lithium battery charging, the ambient temperature when starting charging must be between 0°C and 45°C. Charging at lower temperatures results in the formation of more metallic lithium, which can lead to increased battery impedance and degradation. Charging in a high-temperature environment will increase the reaction between lithium ions and electrolytes and accelerate battery degradation.
Part 3. FAQs
-
Should lithium batteries be charged 100%?
It is generally recommended not to charge lithium batteries to 100% capacity regularly for prolonged storage as it may increase stress on the battery. Partial charging between 20-80% is often advised for optimal battery lifespan. -
Can I use an ordinary charger to charge lithium batteries?
Using an ordinary charger to charge lithium batteries is not recommended, as they require specific charging protocols to ensure safety and maximize battery life. -
How long does it take to charge a lithium battery?
The charging time for lithium batteries varies depending on the battery capacity, charger output, and charging method used. -
How to charge lithium batteries in winter?
It is important to keep lithium batteries at a moderate temperature range during charging in winter. Avoid charging in extremely cold conditions, as it can affect battery performance. If possible, charge batteries indoors at room temperature or use a charger with temperature compensation.
Related Tags:
More Articles

How to Choose the Best Floor Scrubber Battery for Commercial Cleaning?
Selecting the ideal floor scrubber battery ensures a long runtime, rapid charging, and minimal maintenance for efficient commercial cleaning operations.
Battery for Blower vs Battery for Leaf Vacuum: Which One Should You Choose?
Battery for blower vs leaf vacuum—learn the key differences in power, fit, and runtime to choose the right battery for your outdoor tool needs.
How to Choose the Right Battery for Blower?
Choosing the right blower battery? Consider voltage, capacity, chemistry & usage. This guide helps match the best battery for peak performance.
How to Choose the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries?
Choosing the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries? Discover key factors such as size, material, and safety for optimal protection and performance.
7 Critical Elements on a Lithium Battery Shipping Label
What must be on a lithium battery shipping label? Learn 7 key elements to ensure safety, legal compliance, and correct handling across all transport modes.