Part 1. What is the lithium battery electrolyte?
Electrolyte is one of the four key materials of lithium-ion batteries. It is called the “blood” of lithium-ion batteries. Its function is to conduct electrons between the cathode and anode in the battery, and it is also an important guarantee for lithium-ion batteries to obtain the advantages of high voltage and high specific energy.
More simply, electrolytes are like water in a swimming pool, where lithium ions can come and go freely. According to the latest research report, the cost of electrolytes currently accounts for about 15% of the production cost of lithium-ion batteries.
Battery electrolyte is the carrier for ion transport in the battery. Battery electrolytes consist of lithium salts and organic solvents. The electrolyte plays a role in conducting ions between the cathode and anode of lithium batteries, which guarantees lithium-ion batteries obtain the advantages of high voltage and high specific energy.
Part 2. What is the use of lithium battery electrolyte?
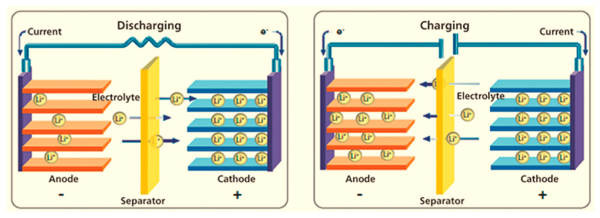
1. Provide ion transmission
Lithium battery electrolyte contains lithium ions (Li+). It can move freely in the electrolyte. Lithium ions are released from the positive electrode and swim in the electrolyte to the negative electrode during charging. Lithium ions move from the negative to the positive electrode during discharge. Lithium ions in the electrolyte move back and forth between the electrodes to complete current transmission.
2. Maintain battery reaction balance
Lithium-ion battery electrolytes also contain solvents and additives, such as organic and salts. These substances play a role in maintaining the balance of battery reactions. This ensures efficient and stable transfer of lithium ions between the electrolyte and the electrode.
3. Maintain battery temperature
The liquid range, low-temperature conductivity, and thermal stability of the electrolyte in the electrolyte determine the operating temperature range of the lithium battery. The solvent in the lithium battery electrolyte can absorb and release heat energy and regulate the battery temperature. When the battery is working, because the reaction process generates heat, the electrolyte can prevent the battery from overheating by absorbing heat and, at the same time, preventing the battery from being too cold by releasing heat.
Part 3. Lithium-ion battery electrolyte types
1. Liquid electrolyte
Liquid electrolytes are the earliest type of electrolytes used in lithium batteries. Its main ingredients include lithium salts, organic solvents, and additives. Among them, lithium salt plays the role of conducting lithium ions, the organic solvent is the carrier for lithium ions to migrate in the battery, and the additives can improve the stability and conductivity of the electrolyte.
2. Gel electrolyte
A gel electrolyte is an electrolyte between liquid and solid state. It is characterized by high ionic conductivity and low risk of liquid leakage. Gel electrolytes mainly comprise the polymer matrix, lithium salt, organic solvent, and additives. By adjusting the ratio of polymer matrix and lithium salt, gelation of the electrolyte can be achieved, thereby improving battery safety and cycle life.
3. Solid electrolyte
Solid electrolytes refer to lithium battery electrolytes that do not contain organic solvents. Its main components are lithium salt, polymer matrix, and additives. Solid electrolytes have higher safety and energy density. However, they still face challenges in ionic conductivity and battery cycle life.
Part 4. Battery electrolyte composition
Battery electrolyte: The general electrolyte electrolytes include lithium salt, organic solvents, additives, and other raw materials, which are prepared in a certain proportion.
Part 5. What is lithium salt?
There are many types of lithium salts. However, commercial lithium-ion batteries contain very little lithium salt. An ideal lithium salt needs to have the following properties.
- It has a small degree of association and is easy to dissolve in organic solvents, ensuring high ionic conductivity of the electrolyte;
- Anions are resistant to oxidation and reduction, and the reduction products are conducive to the formation of a stable low-resistance SEI film;
- It has good chemical stability and does not cause harmful side reactions with electrode materials, electrolytes, separators, etc.;
- The preparation process is simple, low-cost, non-toxic and pollution-free.
Part 6. What are organic solvents for lithium batteries?
The main component of the liquid electrolyte is an organic solvent, which dissolves lithium salts and provides a carrier for lithium ions. The ideal organic solvent for lithium-ion battery electrolytes must meet the following conditions.
- High dielectric constant and strong dissolving ability of lithium salt;
- Low melting point, high boiling point, and remains liquid in a wide temperature range;
- Low viscosity, which facilitates the transmission of lithium ions;
- Good chemical stability, without destroying the cathode and anode structures or dissolving the cathode and anodematerials;
- High lighting efficiency, good safety, low cost, non-toxic, and pollution-free.
Common organic solvents in lithium battery electrolytes are mainly divided into carbonate solvents and organic ether solvents. A mixed solvent containing two or more organic solvents is usually used to obtain a lithium-ion battery electrolyte with better performance. This enables them to learn from each other’s strengths and perform better.
Part 7. What are lithium battery additives?
The additive dosage is small, and the effect is significant. It is an economical and practical method to improve the performance of lithium-ion batteries.
By adding smaller doses of additives to the electrolytes of lithium-ion batteries, certain battery properties can be improved in a targeted manner. For example, reversible capacity, electrode/electrolyte compatibility, cycle performance, rate performance safety performance, etc., play a key role in lithium-ion batteries.
An ideal lithium-ion battery electrolyte additive should have the following characteristics.
- High solubility in organic solvents;
- A small amount of addition can greatly improve one or several properties;
- Does not cause harmful side reactions with other components of the battery and affect battery performance;
- Low-cost, non-toxic, or low toxicity.
The different functions of additives can be divided into conductive additives, overcharge protection additives, flame retardant additives, SEI film-forming additives, cathode material protective agents, LiPF6 stabilizers, and other functional additives.
Part 4. Summary
The electrolyte can affect the lithium battery’s specific capacity by affecting the electrode material’s inverse specific capacity. In addition, the electrolyte is related to the corrosiveness of the current collector, which causes the aging of the electrode material, thus determining the cycle life of the lithium battery. More importantly, the organic solvent in the electrolyte is prone to spontaneous combustion at high temperatures, affecting the safety performance of lithium batteries.
The electrolyte plays a vital role in the battery’s specific capacity, operating temperature range, cycle life, safety performance, etc.
Related Tags:
More Articles

White Stuff on Battery Terminals: A Step-by-Step Cleaning and Maintenance Guide
White stuff on battery terminals is corrosion. Learn how to clean it safely, prevent damage, and keep your battery running strong with simple steps.
Understanding How Glass Mat Batteries Work: Technology, Benefits, and Limitations
Glass mat batteries power cars, RVs, and solar systems. Learn how they work, their benefits, and what to consider before choosing one.
A Buyer’s Guide for AA Size Lithium Battery
Discover the power of AA size lithium batteries—types, voltage, capacity, and more! Learn how to choose the best one for your needs. Read now!
Li-Ion Battery Prices – Where to Buy Cheap & Safe
Discover li-ion cell prices, key market factors, and how to find affordable custom batteries from top suppliers like Ufine Battery.
How Long Does a 2200mAh Battery Last?
Discover everything about 2200mAh batteries—types, charging time, lifespan, and whether it’s enough for your device.