Part 1. Structure and principle of lithium LFP battery
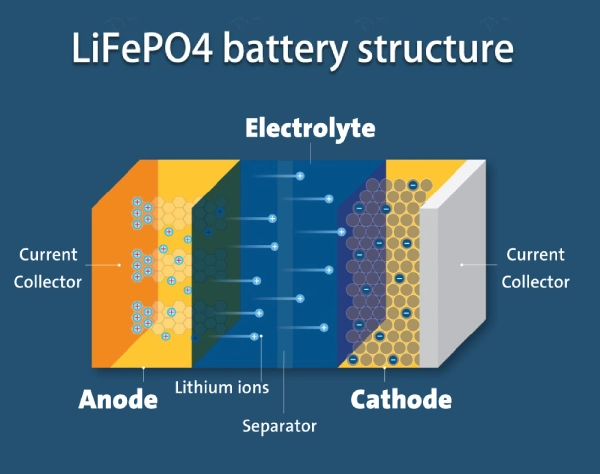
1.LiFePO4 battery structure
The components of a LiFePO4 battery include a positive electrode, negative electrode, electrolyte, diaphragm, positive and negative electrode leads, center terminal, safety valve, sealing ring, shell, etc.
The positive electrode material of lithium iron phosphate batteries is generally called lithium iron phosphate, and the negative electrode material is usually carbon.
- On the left is LiFePO4 with an olivine structure as the battery’s positive electrode, which is connected to the battery’s positive electrode by aluminum foil.
- In the middle is a polymer separator that separates the positive and negative electrodes. Lithium ions Li+ can pass through, but electrons e- cannot.
- On the right is the battery’s negative electrode, composed of carbon (graphite) and connected to the battery’s negative electrode by copper foil.
The structural characteristics of the LFP battery cathode material determine the low conductivity of the material itself, as well as the material’s stability and safety performance.
2. LiFePO4 battery principle
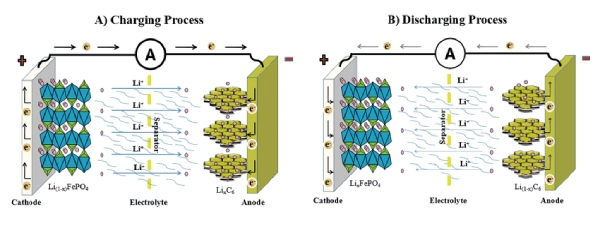
When the LFP battery is charged, lithium ions migrate from the surface of the lithium iron phosphate crystal to the surface of the crystal. Under the action of the electric field force, it enters the electrolyte, passes through the separator, and then migrates to the surface of the graphite crystal through the electrolyte. It is then embedded into a graphite lattice.
At the same time, electrons flow to the aluminum foil collector of the positive electrode through the conductor and to the copper foil current collector of the negative electrode through the tab, battery pole, external circuit, negative pole, and negative tab.
Then, it flows through the conductor to the graphite negative electrode to balance the charge on the negative electrode. After the lithium ions are deintercalated from the lithium iron phosphate, the lithium iron phosphate is converted into iron phosphate.
When the LFP battery is discharged, lithium ions are deintercalated from the graphite crystal, enter the electrolyte, and pass through the separator.
Then, it migrates to the surface of the lithium iron phosphate crystal through the electrolyte, and then is embedded into the crystal lattice of the lithium iron phosphate again through the surface.
At the same time, the battery flows to the copper foil collector of the negative electrode through the conductor. It flows to the aluminum foil current collector of the battery’s positive electrode through the tab, negative battery post, external circuit, positive post, and positive tab. Then, it flows through the conductor to the lithium iron phosphate positive electrode to balance the charge of the positive electrode.
Part 2. How to charge lithium phosphate battery?
It is recommended to use the CCCV charging method for charging lithium iron phosphate battery packs, that is, constant current first and then constant voltage. The constant current recommendation is 0.3C. The constant voltage recommendation is 3.65V.
Are LFP batteries and lithium-ion battery chargers the same?
- The charging method of both batteries is a constant current and then a constant voltage (CCCV), but the constant voltage points are different.
- The nominal voltage of a lithium iron phosphate battery is 3.2V, and the charging cut-off voltage is 3.6V.
- The nominal voltage of ordinary lithium batteries is 3.6V, and the charging cut-off voltage is 4.2V.
Can I charge LiFePO4 batteries with solar?
Solar panels cannot directly charge lithium-iron phosphate batteries. Because the voltage of solar panels is unstable, they cannot directly charge lithium-iron phosphate batteries. A voltage stabilizing circuit and a corresponding lithium iron phosphate battery charging circuit are required to charge it.
Charging lithium iron phosphate batteries with a generator
The generator cannot directly charge the LiFePO4 battery because the power generated by the generator is alternating or pulsed direct current. The LiFePO4 battery must be charged with regulated direct current.
Part 3. How to discharge the LiFePO4 battery?
Here are the steps to properly discharge a LiFePO4 (LFP) battery:
1. Determine the safe discharge rate:
- LiFePO4 batteries have a recommended maximum discharge rate, typically between 1C to 3C. Avoid exceeding this rate to prevent damage.
- 1C means the battery can be discharged at a rate that will fully deplete it in 1 hour. 3C means it can be discharged in 1/3 of an hour.
2. Connect the load:
- Connect the LiFePO4 battery to the device or load you want to discharge it with.
- Make sure the connections are secure and the polarity is correct (positive to positive, negative to negative).
3. Monitor the voltage:
- Use a voltmeter to continuously monitor the battery’s voltage during the discharge process.
- LiFePO4 batteries should not be discharged below 2.5V per cell to avoid overdischarge, which can damage the battery.
4. Discharge at the appropriate rate:
- Discharge the battery at the recommended safe rate (1C to 3C). Do not exceed this rate.
- If the battery gets hot during discharge, reduce the discharge rate.
5. Stop the discharge at the right time:
- Stop the discharge when the battery voltage reaches the recommended minimum of 2.5V per cell.
- Going below 2.5V per cell can cause permanent damage to the LiFePO4 battery.
6. Store the battery properly:
- After discharging, store the LiFePO4 battery in a cool, dry place.
- Avoid storing the battery at full charge or fully discharged. The ideal storage state is around 50% state of charge.
Part 4. How to extend the life of the LiFePO4 battery?
Power batteries are composed of batteries in groups, which are realized by connecting single cells in series and parallel. Due to its characteristics, lithium-ion phosphate battery packs have high requirements for the consistency of single cells. As long as one battery in a group of batteries differs from the others, the effectiveness of the entire battery pack will be greatly reduced.
Moreover, the cycle life of the LFP battery is related to the quality, specifications, frequency of use, charging and discharging methods, and other factors of the battery. Therefore, when using lithium iron batteries, pay attention to usage and maintenance to minimize unnecessary losses and extend the battery’s cycle life.
1. Avoid overcharging and discharging
Lithium-ion batteries are particularly sensitive to overcharging and discharging, so avoid charging more than 100% or discharging less than 20%. Charging when the battery power drops to about 30% is recommended. Keeping battery power between 40-80% can slow down the battery’s cycle age.
2. Control charging time
The charging time should not be too long. It is recommended to use the original charger or a brand charger that meets the standards for charging and cuts off the power in time after it is fully charged.
3. Keep the battery clean
Clean the dust and dirt on the battery surface frequently to prevent dust and debris from entering the battery and affecting battery life.
4. Avoid high and low-temperature environments
High and low-temperature environments have a certain impact on lithium-ion batteries. Temperatures that are too high or too low will shorten the battery life. You should avoid exposing the battery to high or low temperatures and keep the battery temperature between 5-35 degrees Celsius.
5. Avoid being crushed by heavy objects
The casing of lithium iron batteries is generally thin. It should be protected from being crushed or squeezed by heavy objects to prevent battery deformation or internal short circuits.
6. Regular maintenance
Regular maintenance and upkeep of the battery, such as checking the tightening of battery connectors, cleaning battery terminals, checking battery connection lines, etc., can keep the battery in good condition and extend its service life.
7. Lithium iron phosphate battery charger
Use a dedicated charger. Suppose the current and voltage of the LFP battery and the charger do not match. In that case, the battery is likely to be damaged, and the battery life will be affected. Therefore, be sure to use a regular dedicated supporting charger for charging. Do not mix new and old lithium batteries or different types of lithium battery chargers.
Part 5. What is the LiFePO4 charging current?
The recommended charging current for a LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate) battery can vary depending on the specific battery size and application, but here are some general guidelines:
1. Standard Charging Current:
- The standard or recommended charging current for LiFePO4 batteries is usually between 0.2C to 1C.
- For example, a 100Ah LiFePO4 battery would have a standard charging current range of 20A (0.2C) to 100A (1C).
2. Fast Charging Current:
- LiFePO4 batteries can handle higher charging currents compared to other lithium-ion battery chemistries.
- The fast charging current for LiFePO4 batteries is typically between 1C to 3C.
- So, the same 100Ah LiFePO4 battery could be charged at a current of 100A (1C) to 300A (3C) for faster charging.
3. Balancing Charging:
- LiFePO4 batteries require balancing during the charging process to ensure all cells are charged equally.
- The balancing charging current is usually around 0.1C to 0.2C.
- For the 100Ah LiFePO4 battery, the balancing charging current would be 10A (0.1C) to 20A (0.2C).
4. Trickle Charging:
- Once the LiFePO4 battery is fully charged, a trickle charging current of 0.01C to 0.05C can be used to maintain the battery’s charge level.
- For the 100Ah LiFePO4 battery, the trickle charging current would be 1A (0.01C) to 5A (0.05C).
Part 6. Lithium ion phosphate battery pack charging ways
1. Constant voltage charging
During the charging process, the output voltage of the charging power source remains constant. As the state of charge of the lithium-ion phosphate battery pack changes, the charging current is automatically adjusted. Suppose the specified voltage constant value is appropriate. In that case, it can not only ensure the full charging of the power battery but also minimize gas evolution and water loss.
This charging method only considers changes in a single state of battery voltage. It cannot effectively reflect the overall charging status of the battery. Its initial charging current is too large, which often causes damage to the power battery. Given this shortcoming, constant voltage charging is rarely used.
2. Constant current charging
During the charging process, the charging current is kept constant by adjusting the output voltage. Keeping the charging current constant, the charging rate is relatively low.
The constant current charging control method is simple.
However, since the acceptable current capability of the lithium battery pack gradually decreases as the charging process proceeds, in the later stages of charging, the power battery’s ability to receive electricity decreases and the charging current utilization rate is greatly reduced.
The advantages of this method are simple operation, convenience, easy implementation, and easy calculation of charging capacity.
3. Constant current and constant voltage charging
This charging method is a simple combination of the two mentioned above.
The first stage adopts the constant current charging method to avoid excessive charging current at the beginning of constant voltage charging.
The second stage uses a constant voltage charging method to avoid overcharging caused by constant current charging.
The lithium-ion phosphate battery pack is the same as any other sealed rechargeable battery. Charging must be controlled, and overcharging is not allowed. Otherwise, the battery may be easily damaged.
LFP batteries generally use a charging method of constant current first and then voltage limiting.
4. Chopping charge
Charging is done using the chopper method.
Under this method, the current of the constant current source remains unchanged, and the switch tube is controlled to be turned on for some time and then turned off for some time, and the cycle repeats.
The advantage of this method is that when the battery is charged through an external circuit, the ion generation inside the battery requires a certain response time, and if it is continuously charged, it may reduce its capacity potential.
After charging for a period of time, adding a shutdown time allows the ions generated at the two poles of the battery to diffuse, giving the battery a “digestion” time. This will greatly increase the utilization rate of the lithium-ion phosphate battery pack and improve the charging effect.
Part 7. FAQs
-
What is the best way to charge a LiFePO4 battery?
The best way to charge a LiFePO4 battery is to use a charger specifically designed for LiFePO4 batteries, which provides the appropriate voltage and charging algorithm for optimal performance and safety. -
Should I charge LiFePO4 100%?
Charging LiFePO4 batteries to around 80-90% of their capacity for regular use is generally recommended. Charging them to 100% occasionally can help balance the cells, but frequent full charges may reduce their lifespan. -
Do I need a special charger for the LiFePO4 battery?
Yes, using a charger specifically designed for LiFePO4 batteries is important. LiFePO4 batteries require a different charging algorithm than other battery chemistries, and using a charger with the correct voltage and charging profile ensures safe and efficient charging. -
How do I know if my LiFePO4 battery is fully charged?
By monitoring the charging voltage and current, you can determine if a LiFePO4 battery is fully charged. When the battery reaches its maximum voltage and the charging current drops to a very low level (usually below 5% of the battery’s capacity), it is an indication that the battery is fully charged.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Paper Battery vs. Flexible Battery: What’s the Difference and Which Is Better?
Paper vs. flexible batteries: learn the key differences, benefits, and which power source fits best for wearables, sensors, and smart tech.
What to Know Before Buying a Tiny LiPo Battery for Your Project
Tiny LiPo batteries are powerful and compact. Learn how to choose the right one for your project with specs, safety, and charging tips.
Bloated LiPo Battery: Will It Explode?
Will a bloated LiPo battery explode? Discover the causes, risks, safety steps, and expert tips to avoid disaster and protect your gear. Must-read safety guide!
12V 100Ah Lithium Ion Battery Price: Full Guide
Learn about 12V 100Ah lithium-ion battery price, from cost ranges to best brands, hidden fees, and how to get the best deal. A must-read for smart buyers!
Resistance and Conductivity: What It Means for Your Lithium Batteries
Resistance and conductivity impact lithium battery performance, lifespan, and safety—learn how they work and why they matter.