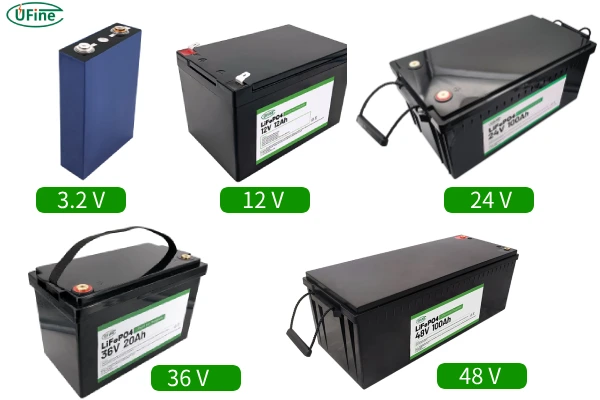
Part 1. What is LiFePO4 battery voltage?
1. What is the lithium battery voltage?
The electrode potential determines the voltage of a lithium battery. Voltage, also known as potential difference or potential difference, is a physical quantity that measures the energy difference between charges in an electrostatic field due to different potentials.
The electrode potential of lithium ions is about 3 V. The voltage of lithium batteries varies with different materials. For example, the rated voltage of a general lithium battery is 3.7 V, and the fully charged voltage is 4.2 V. The rated voltage of a lithium iron phosphate battery is 3.2 V, and the total voltage is 3.65 V. In other words, the potential difference between the positive and negative electrodes of lithium batteries in practice cannot exceed 4.2 V. This requirement is based on material and use safety.
2. What is the voltage of the LiFePO4 battery?
The nominal voltage will vary Depending on the lithium battery pack‘s cathode material. The nominal voltage of a lithium cobalt oxide battery is 3.7 V. The nominal voltage of a lithium manganate battery is 3.8 V. The nominal voltage of lithium batteries made of lithium-nickel-cobalt-manganese ternary material is only 3.5-3.6 V. However, with the continuous improvement of the formula and the improvement of the structure, the nominal voltage of lithium batteries of this material can reach 3.7 V. Lithium iron phosphate battery has the lowest nominal voltage, only 3.2 V.
The nominal voltage of the LiFePO4 battery is 3.2 V, the high-end charging voltage is 3.65 V, and the low-end discharge voltage is 2.0 V. Due to the different quality and process of the positive and negative electrode materials and electrolyte materials used by various battery manufacturers, their performance will be different.
Lithium iron phosphate batteries have the advantages of high safety, long cycle life, rate discharge, and high-temperature resistance. They are considered to be a new generation of lithium batteries. It can be applied to power energy storage, special equipment, robots, AGVs, rail transit, medical equipment, emergency equipment, power communications, etc.
3. LiFePO4 battery features
- Excellent safety performance: No explosion or burning when punctured or overcharged.
- Superior cycle life: LiFePO4 batteries can exceed 2,000 cycles.
- Outstanding high-temperature performance: Operates within -20 °C to 70°C range.
- High tap density and increased capacity in comparable conditions.
- Enables rapid charging at 1C-5C rates, significantly reducing charging time.
A. 3.2 V LiFePO4 battery
3.2V lithium iron phosphate battery refers to the nominal voltage of the battery cell. That is, the average voltage from the beginning to the end of discharge (the voltage we often say is dead) after the battery cell is fully charged.、
B. 3.65 V LiFePO4 battery
As for 3.6 voltage refers to the no-load voltage of the lithium iron phosphate battery when it is fully charged. In other words, these two voltages refer to the voltage of the battery core. The single-cell voltages of similar batteries are the same, but the capacity is different. The battery capacity depends on the cell size, specifications, equipment, and R&D technical strength of the lithium iron phosphate battery manufacturer. Strong lithium battery manufacturers, such as Ufine, can produce lithium iron phosphate batteries of the same size and specifications with higher capacity. Still, of course, the price will be more expensive.
C. 12 V, 12 V, 24 V, 72 V LiFePO4 battery
So what are the 12 V, 12 V, 24 V, and 72 V of lithium iron phosphate batteries? The statement that the voltage exceeds 3.65 refers to the battery, not the cell. Whether it is 12 V, 24 V, or higher LiFePO4 voltage, it is all achieved through the series connection of battery cells. For example, 12 V requires four 3.2 V battery cells to be connected in series, which is 3.2 V+3.2 V+3.2 V+3.2 V= 12.8 V.
Part 2. LiFePO4 charge voltage vs LiFePO4 float voltage
1. What is lifepo4 charge voltage?
The full charge voltage, also known as the charging voltage, is the maximum voltage that the battery should be charged up to in order to reach a 100% state of charge. Going above this voltage can potentially damage the battery over time.
The typical full charge voltage for a LiFePO4 battery is around 3.65V per cell.
The specific full charge voltage for LiFePO4 batteries can range from around 3.55V to 3.70V per cell, depending on the battery manufacturer, the battery management system design, and the specific application requirements.
Compared to other Li-ion battery chemistries like NMC or LCO which have full charge voltages around 4.2V per cell, the lower full charge voltage of LiFePO4 is another advantage, as it helps improve the overall safety and longevity of the battery pack.
2. What is LiFePO4 float voltage?
The “float voltage” refers to the voltage at which the battery is maintained when it is fully charged and not under load. This float voltage helps to keep the battery in a fully charged state without overcharging it.
The typical float voltage for a LiFePO4 battery is around 3.4V to 3.5V per cell.
The specific float voltage range can vary slightly depending on the battery manufacturer and the battery management system design, but generally LiFePO4 batteries have a lower float voltage compared to other Li-ion battery chemistries like NMC or LCO, which typically have float voltages around 4.2V per cell.
The lower float voltage is one of the advantages of LiFePO4 batteries, as it helps to improve the overall safety and longevity of the battery pack.
3. LiFePO4 Charge Voltage and LiFePO4 Float Voltage
Let’s go through the key points regarding LiFePO4 charge voltage, float voltage, and the difference between them:
1) LiFePO4 Charge Voltage:
- The typical full charge voltage is around 3.65V per cell
- Charge voltage range is typically 3.55V to 3.70V per cell
- This is the maximum voltage the battery should be charged up to for 100% state of charge
2) LiFePO4 Float Voltage:
- Typical float voltage is around 3.40V to 3.50V per cell
- The float voltage is the voltage at which the battery is maintained when fully charged and not under load
- This helps keep the battery in a fully charged state without overcharging
3) The difference:
- The charge voltage is higher than the float voltage
- The charge voltage is the maximum voltage reached during the charging process
- The float voltage is the maintenance voltage once the battery is fully charged
- The difference between the charge voltage and float voltage is what allows the battery management system to properly charge and maintain the LiFePO4 battery
- Keeping the battery at the lower float voltage when fully charged helps extend the overall battery life and prevent damage from overcharging
In summary, the charge voltage charges the battery to 100% state of charge, while the lower float voltage maintains the fully charged state without overcharging the cells.
Part 3. LiFePO4 battery voltage chart
This table provides a comprehensive overview of the key voltage parameters for LiFePO4 batteries.
| Voltage Characteristic | Typical Voltage Range | Key Points |
|---|---|---|
| Nominal Voltage | 3.3V per cell | The average voltage of a LiFePO4 cell during normal operation. |
| Open Circuit Voltage (OCV) | 3.2V to 3.6V | The voltage of the cell when it’s not under load. |
| Charge Voltage | 3.50V to 3.70V | The voltage range used to charge the LiFePO4 cell to 100% state of charge. |
| – Full Charge Voltage | 3.65V per cell | The maximum voltage the cell should be charged to. |
| Float Voltage | 3.40V to 3.50V | The maintenance voltage is when the cell is fully charged and not under load. |
| Discharge Voltage | 2.5V to 3.6V | The voltage range during discharge from full to minimum safe level. |
| – Minimum Discharge | ~2.8V per cell | The lowest recommended voltage to avoid over discharge and potential damage. |
Part 4. LiFePO4 battery voltage and capacity
LiFePO4 Battery Voltage
As mentioned, the nominal voltage of a single lithium iron phosphate battery is 3.2 V, the charging voltage is 3.6 V, and the discharge cut-off voltage is 2.0 V. The lithium iron phosphate battery pack reaches the voltage the equipment requires through the series combination of cells. The battery pack voltage = N * the number of series connections.
Commonly used lithium iron phosphate battery pack voltages are as follows:
- 12 V LiFePO4 Battery
- 24 V LiFePO4 Battery
- 36 V LiFePO4 Battery
- 48 V LiFePO4 Battery
- 72 V LiFePO4 Battery
LiFePO4 Battery Capacity
The capacity of the lithium iron phosphate battery pack is determined based on the capacity and number of cells connected in parallel. It is generally determined based on the specific requirements of the electrical equipment. The more LiFePO4 cells connected in parallel, the greater the capacity. Common LiFePO4 battery pack capacities include 10ah, 20ah, 40ah, 50ah, 100ah, 200ah, 400ah, etc.
Part 5. LiFePO4 voltages and battery life
1. Charge and discharge
When choosing a battery charger, it is best to use a charger with a correct termination device to cut off the charge to avoid shortening the service life of the lithium iron phosphate battery due to overcharging. Generally speaking, slow charging can extend the battery’s life better than fast charging.
2. Discharge depth
The depth of discharge is the main factor affecting the life of lithium iron phosphate batteries. The higher the depth of discharge, the shorter the life of the lithium iron phosphate battery. In other words, as long as the depth of discharge is reduced, the service life of lithium iron phosphate batteries can be greatly extended. Therefore, over-discharging lithium battery UPS to extremely low voltages should be avoided.
3. Working environment
Suppose lithium iron phosphate batteries are used at high temperatures for a long time. In that case, their electrode activity will decay, and their service life will be shortened. Therefore, maintaining a suitable operating temperature is a good way to extend the life of lithium iron phosphate batteries.
Part 6. Final thoughts
There are many kinds of LiFePO4 battery voltages. The capacity of a LiFePO4 battery or battery pack is ever-changing, and batteries with corresponding capacity can be made according to electrical equipment needs. Of course, the capacity of cells of a certain size is also limited. You must connect cells or batteries in parallel to increase the battery capacity. This also has a quantity limit.
Part 7. FAQs
-
What voltage should my LiFePO4 battery be?
The voltage of a LiFePO4 battery should typically be around 3.2 to 3.3 volts per cell. -
What is the safe float voltage for LiFePO4?
The safe float voltage for LiFePO4 batteries is around 3.4 to 3.45 volts per cell. -
What is the nominal voltage of a LFP battery?
The nominal voltage of an LFP (LiFePO4) battery is typically 3.2 volts per cell. -
What is the voltage variation of a LiFePO4 cell?
The voltage variation of a LiFePO4 cell can be around 3.0 to 3.6 volts, depending on the state of charge. -
What is the voltage range of LiFePO4 batteries?
The voltage range of LiFePO4 batteries is generally between 2.5 and 3.6 volts per cell, covering the discharged and fully charged states.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Paper Battery vs. Flexible Battery: What’s the Difference and Which Is Better?
Paper vs. flexible batteries: learn the key differences, benefits, and which power source fits best for wearables, sensors, and smart tech.
What to Know Before Buying a Tiny LiPo Battery for Your Project
Tiny LiPo batteries are powerful and compact. Learn how to choose the right one for your project with specs, safety, and charging tips.
Bloated LiPo Battery: Will It Explode?
Will a bloated LiPo battery explode? Discover the causes, risks, safety steps, and expert tips to avoid disaster and protect your gear. Must-read safety guide!
12V 100Ah Lithium Ion Battery Price: Full Guide
Learn about 12V 100Ah lithium-ion battery price, from cost ranges to best brands, hidden fees, and how to get the best deal. A must-read for smart buyers!
Resistance and Conductivity: What It Means for Your Lithium Batteries
Resistance and conductivity impact lithium battery performance, lifespan, and safety—learn how they work and why they matter.