Lithium polymer (LiPo) batteries power everything from high-speed RC cars to cutting-edge drones, offering unmatched energy density and lightweight performance. However, their sensitivity to improper charging and discharging makes them prone to failure—or even catastrophic fires—if not managed correctly. At the heart of LiPo maintenance lies a critical tool: the battery balancer. This comprehensive guide explores why balancing is non-negotiable, how balancers work, and practical steps to ensure your LiPo batteries deliver peak performance safely.
Part 1. Why does lipo battery need to be balanced?
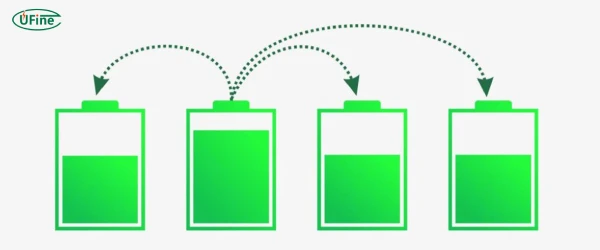
LiPo batteries are constructed from multiple cells connected in series to achieve higher voltages (e.g., a 3S pack has three 3.7V cells for 11.1V total). However, due to manufacturing tolerances, temperature fluctuations, and uneven aging, individual cells inevitably develop voltage disparities during charge/discharge cycles.
The Risks of Unbalanced Cells
-
Overcharging High-Voltage Cells: If one cell reaches its maximum voltage (4.2V) before others, continued charging forces it into an overcharged state. This generates excess heat, accelerates electrolyte decomposition, and can trigger thermal runaway—a chain reaction leading to swelling, venting, or fire.
-
Undercharging Low-Voltage Cells: Weak cells discharge faster, dragging down the entire pack’s capacity. Repeated undercharging causes lithium plating on the anode, permanently reducing efficiency.
-
Capacity Fade: Over time, unbalanced cells degrade at different rates, shrinking the pack’s usable capacity by 20–30% or more.
Balancing mitigates these risks by ensuring all cells charge/discharge uniformly, maximizing lifespan and safety.
Part 2. How they work and types explained
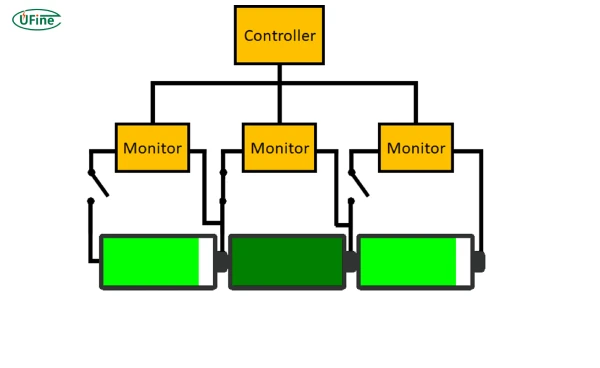
A battery balancer is an electronic system that monitors and equalizes the voltage across each cell in a LiPo pack. It intervenes during charging or discharging to correct imbalances, typically through two primary methods:
Passive Balancing (Resistive)
-
Mechanism: Diverts excess energy from higher-voltage cells through resistors, dissipating it as heat.
-
Pros: Simple, low-cost design.
-
Cons: Energy-wasteful; slower balancing speeds; generates heat, which may stress cells.
-
Use Case: Budget-friendly chargers or low-power applications.
Active Balancing (Energy Transfer)
-
Mechanism: Uses capacitors, inductors, or transformers to redistribute energy from high-voltage cells to low-voltage ones.
-
Pros: Energy-efficient; faster balancing; minimal heat generation.
-
Cons: Complex circuitry; higher cost.
-
Use Case: High-performance RC systems, EVs, and grid storage.
Modern balancers often combine both methods, employing passive balancing for minor corrections and active balancing for large disparities.
Part 3. 3 Methods to charge LiPo batteries with a balancer
Method 1: Integrated Balance Charging (JST-XH Port)
Most LiPo packs include a balance port (e.g., JST-XH) that connects directly to smart chargers like the HOTA D6 Pro or SkyRC Q200.
-
Process:
-
Connect the balance plug to the charger’s corresponding port.
-
Attach the main discharge leads to the charger.
-
Select “Balance Charge” mode, which charges the pack while continuously monitoring and adjusting individual cell voltages.
-
-
Advantage: Seamless, automated balancing with minimal user input.
Method 2: External Standalone Balancers
For packs without balance ports or legacy chargers, standalone balancers like the ISDT BG-8S act as intermediaries:
-
Connect the balancer to the LiPo’s balance leads.
-
Link the balancer to the charger via its output ports.
-
The balancer dynamically adjusts cell voltages during charging.
-
Advantage: Adds balancing capabilities to basic chargers.
Method 3: On-Board Active Balancing Systems
Advanced drones and RC vehicles (e.g., DJI Matrice 300) integrate balancing circuits into their power management systems. These systems balance cells in real-time, even during discharge, to prevent imbalances under high-stress conditions.
-
Advantage: Optimal for mission-critical applications requiring continuous voltage stability.
Part 4. LiPo battery balancing current
Balancing current—the rate at which energy is redistributed between cells—varies by device. Key considerations:
-
Typical Range: 300mA to 2A, depending on balancer capacity.
-
Low Current (300–500mA): Safer for small packs (e.g., 2S 500mAh), but slower balancing.
-
High Current (1–2A): Ideal for large packs (e.g., 6S 10,000mAh), resolving imbalances faster.
Formula for Balancing Time:
Example: A 5000mAh pack with a 1000mAh imbalance using a 500mA balancer takes 2 hours to balance.
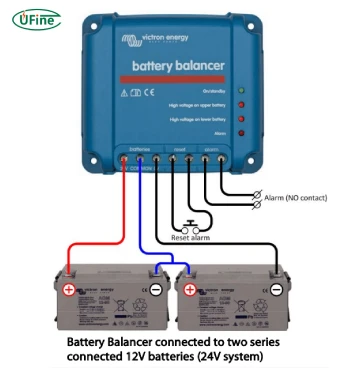
Part 5. Connecting a balancer to LiPo packs
Tools Needed:
-
LiPo battery pack
-
Compatible balancer/charger
-
Fireproof charging bag
-
Multimeter (optional for verification)
Steps:
-
Inspect the Battery: Check for physical damage or swelling.
-
Identify Balance Plug Type: Most packs use JST-XH (3S–6S) or JST-EH (2S).
-
Connect Balance Leads:
-
Align the plug’s negative wire (usually black) with the balancer’s “-” pin.
-
Secure the plug firmly to avoid disconnection.
-
-
Attach Main Discharge Leads: Connect the XT60/XT90/Deans plugs to the charger.
-
Configure Charger Settings:
-
Select cell count (e.g., 4S).
-
Set charge current (1C recommended; e.g., 5A for a 5000mAh pack).
-
Enable “Balance Charge” mode.
-
-
Monitor the Process: Ensure all cells stabilize within 0.01–0.03V of each other.
-
Always charge in a fireproof container.
-
Never leave charging batteries unattended.
-
Use a LiPo voltage checker post-charge to verify balance.
Part 6. How to choose a battery balancer for different types of batteries?
Selecting the right battery balancer isn’t a one-size-fits-all process. Different battery chemistries and applications demand tailored solutions to ensure optimal performance and safety. Below, we break down key considerations for choosing balancers for popular battery types:
A. Lithium Polymer (LiPo) Batteries
Key Requirements:
-
Voltage Range: LiPo cells operate at 3.0–4.2V per cell. Ensure the balancer supports your pack’s configuration (2S–8S).
-
Balancing Current: High-drain applications (e.g., racing drones) benefit from active balancers with 1–2A current to handle rapid imbalances.
-
Compatibility: Verify balance plug type (JST-XH for most RC LiPos).
-
Safety Features: Overvoltage protection and temperature monitoring are critical due to LiPo’s flammability.
Recommended Balancers:
-
HOTA D6 Pro: Supports up to 6S with 1.2A balancing current.
-
ISDT Q8 Max: Active balancing at 2A for large-capacity packs.
B. Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) Batteries
Key Requirements:
-
Lower Voltage Range: LiFePO4 cells operate at 2.5–3.6V. Ensure the balancer’s voltage thresholds match this chemistry.
-
High Cycle Life: Prioritize active balancers to minimize energy loss during frequent cycling (common in solar storage systems).
-
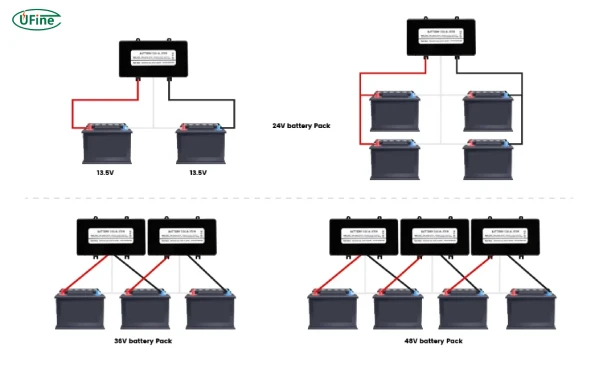
Scalability: For multi-cell setups (e.g., 12V/24V systems), choose balancers with modular designs (e.g., REC BMS).
Recommended Balancers:
-
Daly BMS: Integrates balancing with battery management for 4S–16S LiFePO4 packs.
-
Batrium Watchmon: Advanced balancing with customizable thresholds for industrial applications.
C. Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) Batteries
Key Requirements:
-
Delta V Detection: NiMH cells require balancers that detect voltage drops (ΔV) to prevent overcharging.
-
Pulse Balancing: Some NiMH balancers use pulse charging to equalize cells without generating excess heat.
-
Low Maintenance: NiMH is less prone to severe imbalance, so basic passive balancers often suffice.
Recommended Balancers:
-
Tenergy TB6B: Budget-friendly option with NiMH/NiCd support.
-
SkyRC MC3000: Advanced analyzer with NiMH balancing algorithms.
D. Lead-Acid Batteries
Key Requirements:
-
Equalization Charging: Lead-acid batteries require periodic overcharging (controlled) to balance cells.
-
Voltage Limits: Ensure the balancer prevents overvoltage (above 14.4V for 12V flooded lead-acid).
-
Desulfation Support: Some balancers include pulse desulfation to revive sulfated cells.
Recommended Balancers:
-
NOCO Genius Gen5: Automatic equalization mode for 12V lead-acid batteries.
-
CTEK MXS 5.0: Combines balancing with desulfation for automotive applications.
E. High-Voltage Lithium-Ion Packs (EVs/Grid Storage)
Key Requirements:
-
Modular Design: Balancers must scale for 48V+ systems (e.g., Tesla Powerwall-style setups).
-
Active Balancing: Energy transfer between cells is critical for large packs to avoid efficiency losses.
-
Communication Protocols: CAN bus or Bluetooth integration for real-time monitoring.
Recommended Balancers:
-
Texas Instruments BQ76952: Supports up to 16S configurations with active balancing.
-
Orion BMS 2: Industrial-grade solution for EV battery packs.
F. Specialty Batteries (Li-SOCl₂, Zinc-Air)
Key Requirements:
-
Chemistry-Specific Algorithms: Zinc-air or lithium-thionyl chloride (Li-SOCl₂) batteries have unique discharge curves.
-
Low Self-Discharge Management: Some balancers include trickle charging to maintain balance in low-drain applications.
-
Custom Thresholds: Work with manufacturers for bespoke solutions (common in medical or IoT devices).
Example:
-
EaglePicher BAL-1000: Designed for aerospace-grade lithium primary cells.
General Selection Checklist
-
Chemistry Compatibility: Ensure the balancer matches your battery type (LiPo, LiFePO4, etc.).
-
Cell Count: Verify support for your pack’s configuration (e.g., 4S, 8S).
-
Balancing Speed: Match balancing current to pack size (higher mAh = higher current needed).
-
Safety Certifications: Look for UL, CE, or RoHS certifications for reliability.
-
Integration: Choose standalone balancers or BMS-integrated systems based on your use case.
Part 8. RC LiPo balance plug types
JST-XH
-
Pins: 2.5mm pitch; 4 pins for 3S, 5 pins for 4S, etc.
-
Usage: The industry standard for most hobby-grade LiPos.
JST-EH
-
Pins: 2.0mm pitch; compact design for micro LiPos (e.g., 1S–2S).
XT30/XT60/XT90 with Balance Ports
-
Hybrid Design: Some XT-series connectors (e.g., Amass XT60-S) integrate balance pins for streamlined charging.
EC5/EC3
-
Legacy Use: Found in Traxxas and some Airsoft LiPos; less common today.
Part 9. The hidden costs of skipping a balancer
Neglecting balancing shortens LiPo lifespan by up to 50% and increases failure risks:
-
A 2022 study by Battery University found unbalanced 4S LiPo packs lost 35% capacity after 50 cycles, versus 12% loss in balanced packs.
-
Thermal runaway incidents in RC hobbies are frequently traced to unbalanced charging.
Part 10. Expert tips for long-term LiPo care
-
Storage Voltage: Maintain cells at 3.8–3.85V using “Storage Mode” on chargers.
-
Cycle Testing: Periodically discharge/charge packs to identify weak cells.
-
Temperature Management: Avoid charging below 0°C (32°F) or above 45°C (113°F).
Related Tags:
More Articles

Understanding 9 Volt Battery Capacity: What Do mAh and Voltage Mean?
9V battery capacity affects performance and lifespan. This guide covers mAh, voltage, and key factors to help you choose the best battery.
The Ultimate Guide to Lithium Ion Battery Generators
Lithium-ion battery generators offer lightweight, efficient, quiet power for camping, emergencies, and daily use. Learn how they work and their benefits.
How to Test Battery Capacity for True Ampere-Hours (mAh)?
Learn how to test battery mAh capacity accurately, avoid common mistakes, and understand why real-world results differ from claims. Expert guide inside.
Charging Batteries in Parallel: Safety & Efficiency Guide
Learn if charging batteries in parallel is safe. Discover the right way to do it. Get tips for safe parallel charging to avoid damage!
The Ultimate Guide to a Molten Salt Battery
Molten salt batteries use liquid salts as electrolytes, offering high efficiency, long lifespan, and low cost. Explore their working, benefits, and uses.