Lithium Polymer (LiPo) batteries power everything from drones to RC cars, but their performance hinges on one critical factor: storage voltage. Storing these batteries incorrectly can lead to irreversible damage, reduced capacity, or even fire hazards. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore not only the what and how of LiPo storage voltage but also the why—delving into the chemistry, external influences, and human errors that shape battery health. Let’s begin.
Part 1. What is storage voltage?
Imagine leaving a carton of milk on the kitchen counter for weeks. Just as milk spoils without refrigeration, a LiPo battery deteriorates if stored at the wrong voltage. Storage voltage refers to the specific charge level (measured in volts per cell) that keeps LiPo batteries chemically stable during inactivity.
The Chemistry Behind the Magic
LiPo batteries rely on lithium ions shuttling between a graphite anode and a lithium-cobalt oxide cathode. When stored fully charged (4.2V/cell), the anode holds excess lithium ions, creating stress that accelerates chemical side reactions. Over time, this leads to:
-
Lithium plating (metallic lithium buildup, reducing capacity).
-
Electrolyte decomposition (gas formation, causing swelling).
-
Cathode oxidation (permanent voltage drop).
Storing at 3.7V–3.85V per cell keeps the ions in a “neutral” state, minimizing wear. Think of it as putting the battery into a deep, peaceful sleep instead of an overworked frenzy.
Need a Custom Solution?
Ufine Battery crafts bespoke LiPo batteries for drones, medical devices, and industrial tools. With 17 years of expertise, we guarantee voltages tailored to your needs. Get a free quote today!
Part 2. How liPo battery voltage changes?
Voltage isn’t static—it’s a dynamic reflection of the battery’s chemical activity.
Discharge Characteristics
During discharge, Li⁺ ions migrate from the anode to the cathode, driven by redox reactions. The voltage curve follows three phases:
-
Initial Drop (4.2V → 3.9V): Rapid voltage decline due to ohmic resistance.
-
Plateau Phase (3.9V → 3.6V): Stable energy delivery, ideal for operational use.
-
Tail-End Decline (<3.6V): Accelerated voltage drop, risking lithium plating.
Self-Discharge Mechanisms
Even during storage, LiPo batteries experience 0.5–2% monthly self-discharge due to:
-
Ionic Leakage: Li⁺ ions bypassing the SEI layer.
-
Parasitic Reactions: Electrolyte decomposition at electrode interfaces.
Storing at 3.8V/cell reduces these losses by 40% compared to 4.2V.
Part 3. LiPo storage voltage chart
Different cell configurations (1S, 2S, etc.) require tailored storage voltages. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
| Battery Type | Total Voltage Range | Per-Cell Voltage |
|---|---|---|
| 1S LiPo | 3.7V – 3.85V | 3.7V – 3.85V |
| 2S LiPo | 7.4V – 7.7V | 3.7V – 3.85V x 2 |
| 3S LiPo | 11.1V – 11.55V | 3.7V – 3.85V x 3 |
| 4S LiPo | 14.8V – 15.4V | 3.7V – 3.85V x 4 |
Note: For multi-cell packs, cell balancing is critical. Imbalanced cells (>0.05V deviation) risk overcharging/over-discharging during storage.
Part 4. What affects LiPo battery storage voltage?
Even if you set the perfect storage voltage, external factors can sabotage your efforts. Let’s dissect the biggest culprits:
A. Temperature: The Stealthy Saboteur
Heat accelerates chemical reactions. Storing a LiPo at 30°C (86°F) degrades it twice as fast as at 20°C (68°F). Cold isn’t safe either—below 0°C (32°F), electrolytes thicken, increasing internal resistance.
Solution: Store batteries in a cool, dry place (15°C–25°C). Avoid garages or cars!
B. Time: The Invisible Thief
LiPo batteries age even when unused. After 6 months at full charge, capacity can drop by 20%. At 3.8V, degradation slows to <5% per year.
Solution: Check voltage every 3 months. Rebalance if needed.
C. Charge Cycles: The Wear-and-Tear Factor
Each charge/discharge cycle strains the battery. A heavily cycled LiPo may lose capacity faster, even at ideal storage voltage.
Solution: Track cycle counts. Replace batteries after 200–300 cycles.
D. Manufacturing Quality: The Hidden Variable
Cheap cells often have impurities or uneven coatings, leading to voltage instability. Premium brands like Ufine Battery use aerospace-grade materials for consistent performance.
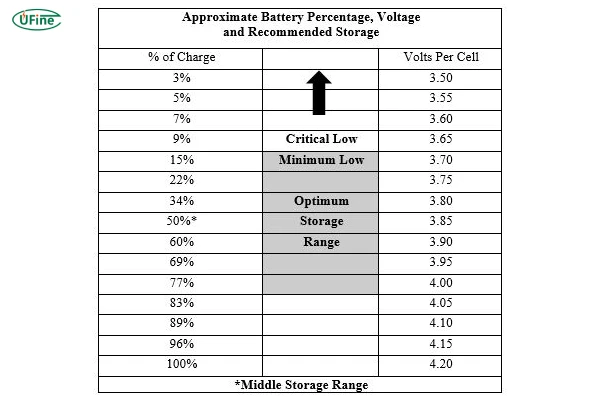
Part 5. LiPo battery storage percentage
Many hobbyists swear by the “50% charge rule,” but let’s clarify:
-
100% Charge (4.2V/cell): High risk of swelling. Only safe for <24 hours.
-
50–60% Charge (3.8V/cell): Ideal for 1–6 months.
-
20% Charge (3.5V/cell): Risky—self-discharge could push it below 3.0V.
Takeaway: Aim for 3.8V/cell (≈60%) for long-term storage.
Part 6. LiPo minimum voltage:
Dropping below 3.0V/cell triggers a death spiral:
-
Copper in the anode dissolves, contaminating the electrolyte.
-
The cathode’s structure collapses, reducing capacity.
-
The battery may refuse to charge—a phenomenon called “voltage lockout.”
Emergency Fix: If caught early, a slow charge at 0.1C might revive the battery.
Part 7. LiPo maximum voltage
Exceeding 4.2V/cell during charging causes:
-
Thermal runaway (rapid overheating).
-
Gas buildup, leading to swelling or explosions.
Safety First: Always use a charger with over-voltage protection.
Part 8. Do you need a LiPo storage box?
Even perfectly stored batteries can fail. A fireproof LiPo storage box (50) contains flames and toxic fumes. For extra safety, add:
-
Silica gel packets (to control humidity).
-
Non-conductive foam (to prevent short circuits).
Part 9. FAQs
1. What happens if I store my LiPo battery at too high a voltage for a long time?
Storing a LiPo battery at full charge (4.2V per cell) for extended periods stresses the chemical structure inside the battery. This can lead to increased internal resistance, reduced capacity, swelling, and even potential failure over time.
2. Can I store my LiPo battery in a refrigerator to extend its lifespan?
While cooler temperatures slow down chemical degradation, refrigerators are not ideal due to moisture and condensation risks. Instead, store your LiPo batteries in a dry, cool place at around 15-25°C (59-77°F).
3. Can I store multiple LiPo batteries together?
Yes, but with caution. Keep LiPo batteries in individual fireproof bags or containers to prevent accidental short circuits. Never store damaged batteries with healthy ones, as they could cause thermal runaway.
4. What’s the safest way to transport LiPo batteries in storage mode?
Use LiPo-safe storage bags or hard cases and avoid metallic objects or conductive materials in the storage area. If traveling by air, check airline regulations, as some require LiPos to be carried in carry-on luggage and stored at a safe voltage.
5. Can I charge a LiPo directly to storage voltage instead of full charge?
Yes! Most LiPo balance chargers have a “Storage Mode” setting that charges or discharges the battery to the correct 3.7V – 3.85V per cell for safe storage.
6. Can I store LiPo batteries inside my drone or RC car?
It’s not recommended. Keeping a LiPo inside a device can lead to parasitic drain, where small amounts of energy are slowly lost. This could drop the voltage below safe levels, causing permanent damage. Always remove LiPos and store them separately at proper storage voltage.
7. How do I know if my LiPo battery is no longer holding storage voltage properly?
If a LiPo battery rapidly loses charge while in storage, shows unbalanced cell voltages, or drops below 3.7V per cell even after balancing, it may be aging or damaged. In such cases, consider replacing it to prevent safety risks.
Related Tags:
More Articles

How to Choose the Best Floor Scrubber Battery for Commercial Cleaning?
Selecting the ideal floor scrubber battery ensures a long runtime, rapid charging, and minimal maintenance for efficient commercial cleaning operations.
Battery for Blower vs Battery for Leaf Vacuum: Which One Should You Choose?
Battery for blower vs leaf vacuum—learn the key differences in power, fit, and runtime to choose the right battery for your outdoor tool needs.
How to Choose the Right Battery for Blower?
Choosing the right blower battery? Consider voltage, capacity, chemistry & usage. This guide helps match the best battery for peak performance.
How to Choose the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries?
Choosing the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries? Discover key factors such as size, material, and safety for optimal protection and performance.
7 Critical Elements on a Lithium Battery Shipping Label
What must be on a lithium battery shipping label? Learn 7 key elements to ensure safety, legal compliance, and correct handling across all transport modes.