- Part 1. What is liquid lithium?
- Part 2. What is solid lithium?
- Part 3. Key differences between liquid lithium and solid lithium batteries
- Part 4. Advantages of liquid lithium batteries
- Part 5. Advantages of solid lithium batteries
- Part 6. Challenges of liquid lithium batteries
- Part 7. Challenges of solid lithium batteries
- Part 8. Applications of liquid lithium batteries
- Part 9. Applications of solid lithium batteries
- Part 10. Which one powers the future?
- Part 11. FAQs
The world is rushing toward a future powered by renewable energy, and batteries sit at the heart of this transformation. Batteries are the backbone of sustainable energy systems, from powering electric vehicles (EVs) to storing energy from solar panels. Lithium-based batteries have taken center stage among the many advancements in battery technology. However, a debate continues growing in the scientific and industrial communities: liquid lithium versus solid lithium—which is the key to the future of battery technology?
In this article, we’ll explore liquid and solid lithium battery technologies, breaking down their working mechanisms, benefits, drawbacks, and potential to shape the future. Let’s explore this fascinating topic step by step.
Part 1. What is liquid lithium?
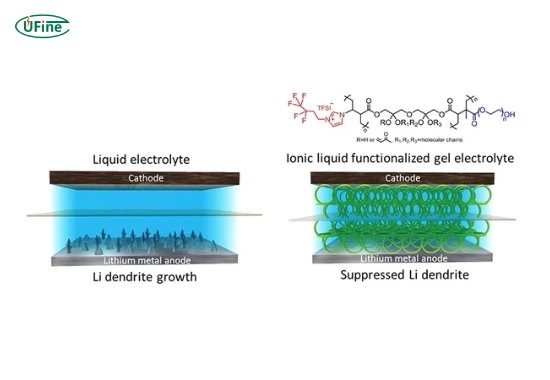
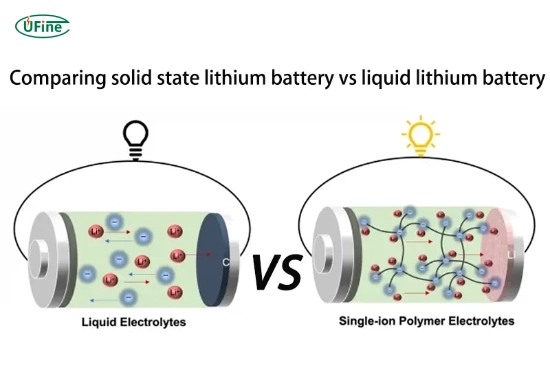
Liquid lithium batteries are lithium-ion batteries that use a liquid electrolyte to transport ions between the anode and cathode. Manufacturers typically dissolve the liquid electrolyte from a lithium salt in a solvent. This design has been the foundation of modern rechargeable batteries for decades, powering everything from smartphones to electric cars.
How do liquid lithium batteries work?
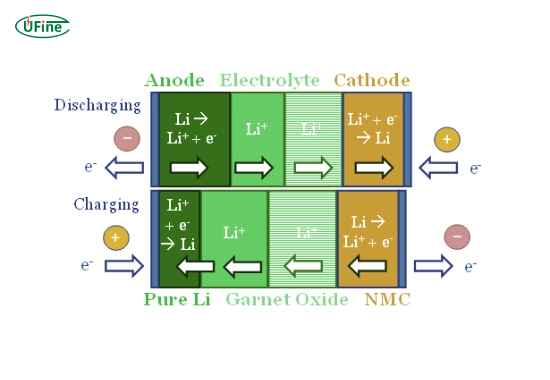
Liquid lithium batteries operate by moving lithium ions. Lithium ions flow from the anode to the cathode through the liquid electrolyte when the battery discharges, creating an electric current. During charging, the process reverses.
Companies widely use this technology due to its high energy density, proven reliability, and cost-effectiveness compared to other types of batteries.
What is Liquid Lithium and How Does It Relate to Lithium-Ion Batteries?
Part 2. What is solid lithium?
Solid lithium batteries are a newer innovation in battery technology. Unlike liquid lithium batteries, they replace the liquid electrolyte with a solid-state electrolyte. This solid material can be ceramic, glass, or some other polymer that allows lithium ions to flow between the anode and cathode.
How do solid lithium batteries work?
Solid lithium batteries work similarly to their liquid counterparts, but the key difference lies in the electrolyte. The solid-state electrolyte facilitates ion transfer without requiring a liquid medium. This change in design opens up opportunities for safer and more energy-dense batteries.
Part 3. Key differences between liquid lithium and solid lithium batteries
When comparing liquid lithium and solid lithium batteries, several vital distinctions emerge. Here’s a breakdown of the most critical differences:
1. Electrolyte Composition
Liquid lithium batteries use a liquid electrolyte, while solid lithium batteries use a solid-state electrolyte.
2. Energy Density
Solid lithium batteries have the potential for higher energy density, meaning they can store more energy in a smaller space.
3. Safety
Solid lithium batteries are generally safer because they are less prone to thermal runaway and electrolyte leakage, which are common risks with liquid lithium batteries.
4. Longevity
Solid lithium batteries typically exhibit better cycle life, meaning they can endure more charge/discharge cycles without significant degradation.
5. Cost
Given the well-established production infrastructure, liquid lithium batteries are currently cheaper. On the other hand, solid lithium batteries are more expensive due to their emerging nature and complex manufacturing process.
Part 4. Advantages of liquid lithium batteries
Liquid lithium batteries have powered the tech revolution for decades, and their benefits are well-documented:
- Proven Technology: Engineers have extensively tested and refined them, making them reliable for everyday use.
- High Energy Density: They offer a good balance of energy density and weight, which is ideal for portable electronics and EVs.
- Lower Cost: Liquid lithium batteries are widely available and affordable compared to cutting-edge alternatives.
- Scalability: The existing production infrastructure makes it easy to scale manufacturing.
Part 5. Advantages of solid lithium batteries
Solid lithium batteries bring a host of exciting benefits that could revolutionize the battery industry:
- Improved Safety: Solid electrolytes eliminate the risk of leaks and are less likely to catch fire.
- Higher Energy Density: Their compact design allows them to store more power in the same space.
- Better Durability: Solid-state batteries are less prone to degradation, promising a longer lifespan.
- Faster Charging: Their unique structure allows for quicker ion transfer, enabling faster charging times.
- Wide Temperature Range: They can operate more efficiently across extreme temperatures.
Part 6. Challenges of liquid lithium batteries
Despite their popularity, liquid lithium batteries face a range of challenges:
- Safety Concerns: Liquid electrolytes are flammable and prone to thermal runaway.
- Limited Longevity: The liquid electrolyte can degrade over time, reducing battery efficiency.
- Energy Density Ceiling: Liquid lithium batteries can only store limited energy.
- Environmental Impact: The production of liquid lithium batteries is resource-intensive and environmentally taxing.
Part 7. Challenges of solid lithium batteries
While solid lithium batteries hold immense promise, they are not without their own set of hurdles:
- High Production Costs: Manufacturing solid-state batteries is expensive due to the need for advanced materials and processes.
- Material Limitations: Finding a solid electrolyte that is both efficient and economical remains a challenge.
- Scaling Issues: Mass production of solid-state batteries is still in its infancy, making it difficult to meet global demand.
- Interface Problems: Ensuring seamless contact between the solid electrolyte and electrodes can be tricky.
Part 8. Applications of liquid lithium batteries
Liquid lithium batteries are a cornerstone of modern technology, powering:
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): EVs rely heavily on liquid lithium batteries from Tesla to Nissan.
- Consumer Electronics: Smartphones, laptops, and tablets use liquid lithium batteries for portability and power.
- Renewable Energy Storage: They store energy from solar panels and wind turbines.
- Medical Devices: Devices like pacemakers and hearing aids rely on these batteries for extended operation.
Part 9. Applications of solid lithium batteries
Solid lithium batteries are gaining traction in industries that demand high performance and safety:
- Next-Gen Electric Vehicles: Automakers are exploring solid-state batteries for their superior energy density and safety.
- Aerospace: Lightweight and durable, they are ideal for spacecraft and drones.
- Wearable Technology: Their compact design makes them perfect for smartwatches and fitness trackers.
- Grid Storage: They promise greater efficiency for large-scale energy storage systems.
Part 10. Which one powers the future?
The future of battery technology may not rest on a single solution. Liquid lithium batteries will likely remain dominant in the short term due to their established infrastructure and affordability. However, solid lithium batteries represent the future, with their potential for higher energy density, improved safety, and longer lifespan. As production costs decrease and technology advances, solid lithium batteries become the new standard.
Part 11. FAQs
-
What is the main difference between liquid lithium and solid lithium batteries?
The main difference lies in the electrolyte. Liquid lithium batteries use a liquid electrolyte, while solid lithium batteries use a solid-state electrolyte, which makes them safer and more energy-dense. -
Are solid lithium batteries safer than liquid lithium batteries?
Solid lithium batteries are generally safer because they eliminate the risk of leaks and thermal runaway associated with liquid electrolytes. -
Why are solid lithium batteries more expensive?
Solid lithium batteries are more expensive due to their complex manufacturing process and the use of advanced materials for the solid-state electrolyte. -
Can solid lithium batteries replace liquid lithium batteries entirely?
While solid lithium batteries hold great promise, overcoming production and cost barriers will take time. Both technologies are likely to coexist shortly. -
Which battery is better for electric vehicles?
For now, liquid lithium batteries dominate the EV market due to their affordability and established infrastructure. However, solid lithium batteries could become the preferred choice as their production scales up.
Related Tags:
More Articles
Capacitor vs Battery: What is the Difference?
Capacitor vs battery explained in detail. Learn the difference between capacitor and battery in energy storage, charging speed, lifespan, and real applications.
18650 Battery vs AA: Which Is Better for Your Device?
Compare 18650 vs AA batteries in capacity, voltage, rechargeability, and applications. Learn which battery type fits high-drain or everyday devices.
What is the Difference Between Battery Cell, Battery Control Module, and Battery Pack?
Compare battery cells, modules, and packs. Learn functions, design differences, control modules, and selection tips for EV, ESS, and industrial use.
How to Prevent LiPo Battery Explosion?
Can LiPo batteries explode or catch fire? Learn key causes of LiPo battery fires and proven charging, storage, and handling tips to reduce explosion risk.
Aluminium Ion Battery vs Lithium-Ion: A Detailed Comparison
Compare aluminium ion battery vs lithium-ion battery in energy density, charging speed, safety, cost, and uses. A practical guide for engineers and buyers.