Energy storage plays a key role in the modern power grid. As we transition to renewable energy sources like solar and wind, we need efficient, long-lasting, cost-effective batteries to store excess energy.
One of the most promising solutions is the liquid metal battery. This type of battery differs from traditional batteries because it uses liquid metals instead of solid materials.
But how does a liquid metal battery work? Why is it better for large-scale energy storage? And how does it compare to lithium-ion batteries?
This article will explore everything you need to know about liquid metal batteries, from their working principles to their potential applications.
Part 1. What is a liquid metal battery?
A liquid metal battery is a type of rechargeable battery that uses liquid metal electrodes and a molten salt electrolyte. Unlike lithium-ion batteries with solid components, liquid metal batteries stay in a liquid state when operating.
This unique design gives the battery high efficiency, long lifespan, and low cost, making it a strong candidate for storing renewable energy at a large scale.
Professor Donald Sadoway and his team at MIT first developed liquid metal batteries. Today, companies like Ambri are working to commercialize this technology.
Part 2. How does a liquid metal battery work?
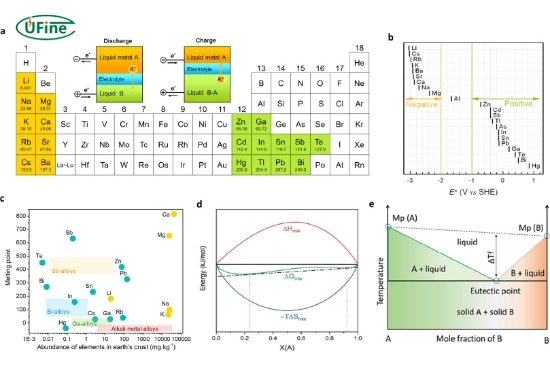
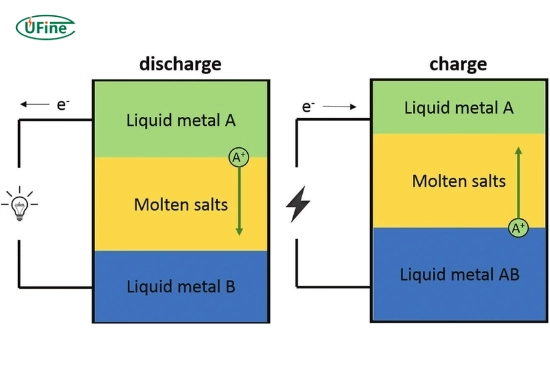
A liquid metal battery has three layers:
- Top layer (positive electrode): A light liquid metal, such as calcium or lithium.
- Middle layer (electrolyte): A molten salt that allows ions to move between the electrodes.
- Bottom layer (negative electrode): A heavier liquid metal, such as antimony or lead.
Charging Process
- When the battery is charged, metal ions move from the bottom layer to the top layer through the molten salt.
- This process stores electrical energy in the form of chemical energy.
Discharging Process
- When the battery is discharged, metal ions return to the bottom layer, generating an electric current.
- This current can then be used to power electrical devices.
Since all the components are liquid, the battery does not suffer from material degradation, making it more durable than traditional batteries.
Part 3. What makes liquid metal batteries different from regular batteries?
Liquid metal batteries are very different from traditional lithium-ion or lead-acid batteries.
Key Differences:
- State of Materials: Traditional batteries use solid electrodes, while liquid metal batteries use liquid electrodes.
- Lifespan: Lithium-ion batteries degrade over time, but liquid metal batteries can last over 10,000 cycles.
- Safety: Liquid metal batteries do not catch fire like lithium-ion batteries, making them safer.
- Cost: Liquid metal batteries use low-cost, abundant materials, while lithium-ion batteries require expensive rare metals.
These differences make liquid metal batteries a great choice for grid-scale energy storage.
Artikel Terkait: Liquid Lithium vs. Solid Lithium: Which One Powers the Future of Battery Tech?
Part 4. What are the advantages of liquid metal batteries?
Liquid metal batteries offer several significant advantages:
- Long lifespan
These batteries last over 10,000 charge cycles, much longer than lithium-ion batteries. - Low cost
They use common and inexpensive materials, such as aluminum, magnesium, and antimony.
This makes them much cheaper than lithium-ion batteries, which require expensive cobalt and nickel. - High efficiency
Liquid metal batteries have an energy efficiency of 90% or more.
This means very little energy is lost when charging and discharging. - Safety and stability
Unlike lithium-ion batteries, they do not overheat or catch fire.
This makes them a safer option for large-scale energy storage. - Scalability
These batteries can be built any size, making them ideal for storing renewable energy at power plants.
Part 5. What are the limitations of liquid metal batteries?
Despite their many advantages, liquid metal batteries also have some challenges:
- High operating temperature
They require temperatures of 300–500°C to keep the metals liquid.
This means they need constant heating, which consumes energy. - Not suitable for small devices
Liquid metal batteries cannot be used in smartphones or electric vehicles because of their large size and high temperature.
They are mainly for stationary energy storage. - Slow startup time
Since they require heating, they cannot provide instant power like lithium-ion batteries.
This makes them unsuitable for applications that require sudden bursts of energy.
Despite these challenges, researchers are improving the technology to make liquid metal batteries more efficient and practical.
Part 6. How do liquid metal batteries compare to lithium-ion batteries?
Lithium-ion batteries are the most common type of battery used today. They are found in smartphones, laptops, and electric cars. However, they have some significant drawbacks regarding large-scale energy storage.
Key Differences:
- Lifespan: Lithium-ion batteries degrade over time, while liquid metal batteries last much longer.
- Cost: Lithium-ion batteries use expensive materials like cobalt and lithium, while liquid metal batteries use cheaper, more abundant materials.
- Safety: Lithium-ion batteries can overheat and catch fire, but liquid metal batteries are much safer.
- Efficiency: Liquid metal batteries have an efficiency of over 90%, while lithium-ion batteries range between 85% and 95%.
- Scalability: Liquid metal batteries are better suited for large-scale energy storage. In contrast, lithium-ion batteries are best for portable devices.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Liquid Metal Battery | Lithium-Ion Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Lifespan | 10,000+ cycles | 2,000–3,000 cycles |
| Material Cost | Low | High (rare metals) |
| Efficiency | 90%+ | 85–95% |
| Safety | No risk of fire | Risk of thermal runaway |
| Scalability | High | Limited |
| Operating Temperature | High (300–500°C) | Room temperature |
Part 7. Where are liquid metal batteries used?
Liquid metal batteries are mainly used for stationary energy storage, including:
- Renewable energy storage: Storing excess power from solar and wind farms.
- Grid stability: Balancing electricity supply and demand to prevent blackouts.
- Industrial power management: Helping factories and businesses store electricity for later use.
These applications make liquid metal batteries essential to the future energy grid.
Part 8. What is the future of liquid metal batteries?
The future of liquid metal batteries is auspicious. As the world approaches renewable energy, we need better ways to store electricity.
Researchers are working on the following:
- Lowering the operating temperature to make them more efficient.
- Scaling up production to reduce costs.
- Expanding commercial adoption for grid storage and industrial use.
With continued improvements, liquid metal batteries could replace fossil fuel-based power plants and become a key technology in the clean energy revolution.
Part 9. FAQs about liquid metal battery
Are liquid metal batteries safe?
Yes. Unlike lithium-ion batteries, liquid metal batteries do not catch fire or explode.
Can liquid metal batteries be used in electric vehicles?
No. Because they require high temperatures, they are only suitable for stationary storage.
How long do liquid metal batteries last?
They can last over 10,000 charge cycles, much longer than lithium-ion batteries.
Why are liquid metal batteries essential for renewable energy?
They store excess solar and wind energy, making power grids more stable.
When will liquid metal batteries be widely available?
Companies like Ambri are working on commercial production, which may become more common within the next decade.
Related Tags:
More Articles

How to Choose the Best Floor Scrubber Battery for Commercial Cleaning?
Selecting the ideal floor scrubber battery ensures a long runtime, rapid charging, and minimal maintenance for efficient commercial cleaning operations.
Battery for Blower vs Battery for Leaf Vacuum: Which One Should You Choose?
Battery for blower vs leaf vacuum—learn the key differences in power, fit, and runtime to choose the right battery for your outdoor tool needs.
How to Choose the Right Battery for Blower?
Choosing the right blower battery? Consider voltage, capacity, chemistry & usage. This guide helps match the best battery for peak performance.
How to Choose the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries?
Choosing the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries? Discover key factors such as size, material, and safety for optimal protection and performance.
7 Critical Elements on a Lithium Battery Shipping Label
What must be on a lithium battery shipping label? Learn 7 key elements to ensure safety, legal compliance, and correct handling across all transport modes.