In the evolving world of lithium battery technology, two crucial components often come into focus: the lithium battery PCB (Printed Circuit Board) and the lithium battery BMS (Battery Management System). Both of these elements are essential for ensuring the safety, performance, and longevity of lithium-ion batteries. Understanding the distinctions between them is vital for those designing or selecting battery systems. In this article, we will explore the differences between lithium battery PCBs and BMSs, highlighting their functions, principles, and applications.
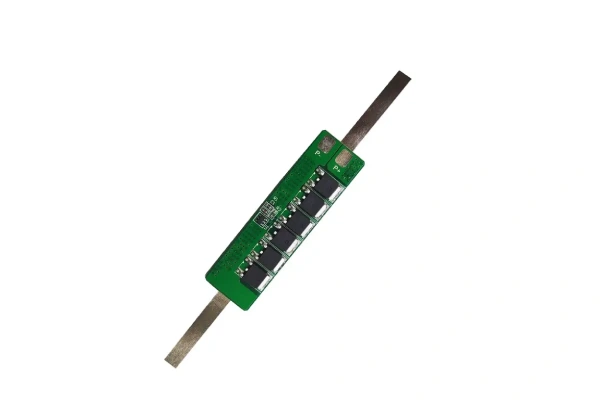
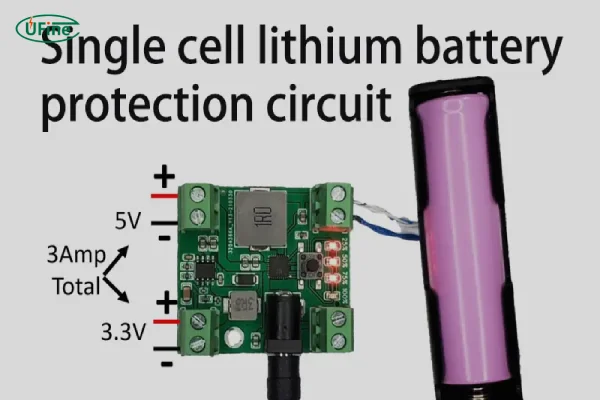
Part 1. What is the lithium battery protection board (PCB)?
Lithium-ion batteries are sensitive to conditions like overcharging and over-discharging, which can compromise their performance or even lead to catastrophic failure. Overcharging occurs when the charging voltage exceeds the battery’s maximum limit, potentially causing the internal pressure to rise, leading to leaks, ruptures, or explosions. Over-discharging happens when the discharge voltage drops too low, resulting in diminished capacity and shortening the battery’s lifespan.
A lithium battery protection board (PCB) serves as a critical safeguard by protecting against both overcharge and over-discharge scenarios. It is an integral part of the battery management system, designed to protect the battery from these harmful conditions and ensure safe operation.
Part 2. How does a lithium battery PCB work?
A lithium battery PCB typically contains components such as microcontrollers, MOSFETs (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors), resistors, and capacitors. The basic working principle involves real-time monitoring of the battery’s voltage, current, and temperature. If the battery exceeds preset thresholds, the microcontroller sends signals to the MOSFETs, turning them on or off to regulate the charge and discharge processes.
The primary goal of a lithium battery PCB is to ensure the safe operation of the battery by preventing conditions that could lead to damage or failure.
Part 3. Key functions of a lithium battery PCB
A well-designed lithium battery PCB includes various safety features to protect the battery from potential hazards. These functions can be classified as basic, enhanced, and extended protections:
1. Basic Protection:- Overcharge Protection
- Over-discharge Protection
- Overcurrent Protection
- Over-temperature Protection
- Low-temperature Protection
- Short Circuit Protection
- Reverse Connection Protection
- Good Consistency
- Minimal Pressure Difference
- Minimal Temperature Difference
These protections are not always required for every battery, but they are essential for ensuring the longevity and safe operation of lithium-ion batteries, especially in more demanding applications.
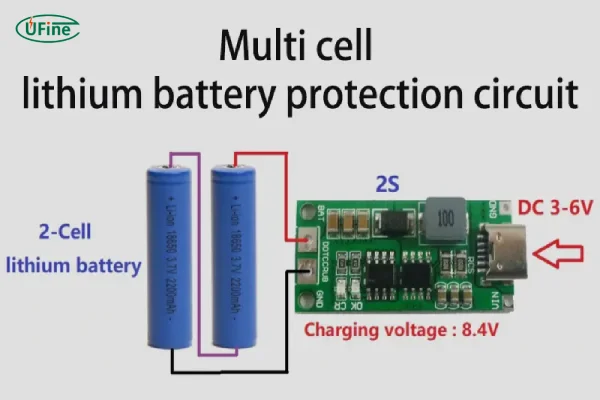
Part 4. Types of lithium battery PCB
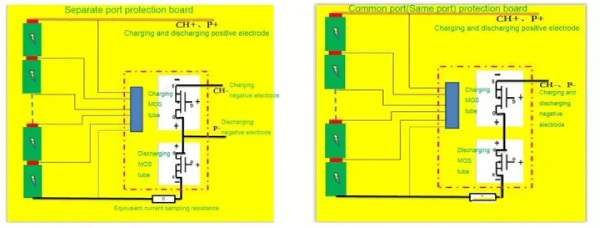
Hardware-type lithium battery PCB can be divided into an independent port protection circuit board and a common port (same port) protection circuit board.
Independent port protection circuit board:
There are three ports in total (charging port, discharge port, common terminal); that is, the charging and discharging ports are separate. (Refer to the picture on the left) There are two ports, CH+ and CH-, for charging and two ports, P+ and P-, for discharging.
Public port (same port) protection circuit board:
There are two ports (positive and negative ports), one for charging and discharging. (Refer to the picture on the right) There are two ports for charging, CH+ (P+) and CH- (P-), and two ports for discharging, CH+ (P+) and CH- (P-).
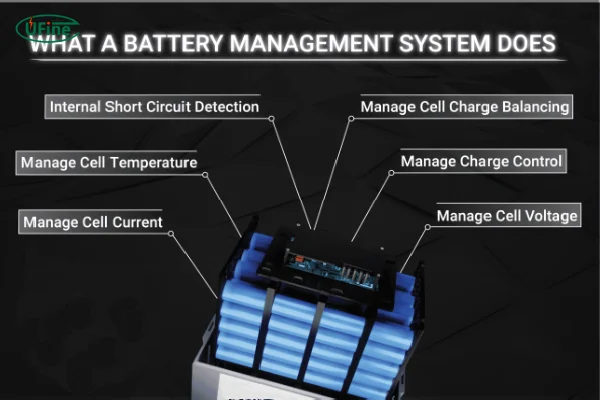
Part 5. What is a lithium battery BMS (battery Management System)?
The lithium battery BMS is an advanced system designed to manage and optimize the performance of an entire battery pack. It prevents overcharging and over-discharging, extends the battery’s lifespan, and ensures that the battery operates within safe parameters.
While a PCB protects individual cells, the BMS has broader functionality, including monitoring, data collection, and fault detection. Additionally, the BMS plays a vital role in managing communication between the battery and external devices, providing real-time data and alerts.
Part 6. Lithium battery BMS principle
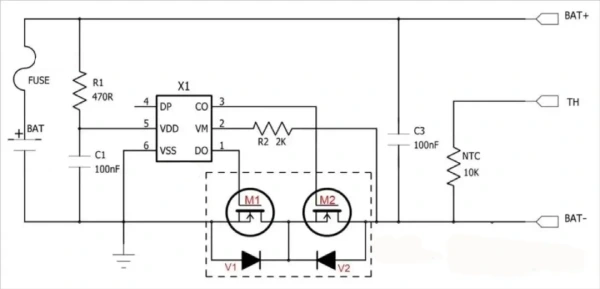
Lithium battery BMS includes control IC, MOS switch, fuse Fuse, NTC thermistor, TVS transient voltage suppressor, capacitor and memory, etc.
In the picture above, the control IC turns the circuit on and off by controlling the MOS switch to protect it. FUSE implements secondary protection on this basis. TH is temperature detection, and there is a 10K NTC inside. NTC mainly implements temperature detection. TVS mainly suppresses surges.
Part 7. Functions of a lithium battery BMS
The BMS performs several essential functions to ensure that the battery operates optimally:
Sensing and Measuring:
The BMS continuously monitors parameters like voltage, current, temperature, and the state of charge (SOC). This data helps ensure the battery stays within safe operating limits.
Alarm and Protection:
If an anomaly is detected—such as overcharge, over-discharge, or temperature extremes—the BMS triggers an alarm and takes protective measures, such as disconnecting the battery or adjusting the charge/discharge rates.
Balanced Management:
Battery cells often have slight differences in voltage, resistance, and capacity. The BMS ensures these variations are minimized through active and passive balancing, ensuring uniform charging and discharging across all cells in the pack.
Communication and Positioning:
The BMS can transmit data to external platforms, enabling real-time monitoring of the battery’s health and performance. This data is crucial for applications where battery reliability is critical, such as in electric vehicles or renewable energy systems.
Part 8. Lithium battery PCB vs. BMS: key differences
Both the lithium battery protection board (PCB) and the battery management system (BMS) serve important protective roles, but they differ significantly in terms of functionality and complexity:
1. Lithium Battery PCB:
Typically, a PCB focuses on protecting individual battery cells. It provides basic protections, such as overcharge, over-discharge, overcurrent, and thermal protections, but it lacks the advanced management and communication capabilities of a BMS. It is a simpler, more direct component, primarily found in consumer-grade batteries.
2. Lithium Battery BMS:
A BMS, on the other hand, is far more sophisticated, offering full-scale battery management across an entire battery pack. It handles more complex functions, such as state-of-charge (SOC) calculations, fault diagnostics, balancing management, and communication with external devices. BMS is typically used in more demanding applications, such as electric vehicles (EVs) or energy storage systems.
3. Performance in Low Temperatures:
One notable difference is that while the PCB offers stable performance in most conditions, the performance of the BMS can degrade in extreme temperatures, especially in very cold environments.
Part 9. Conclusion
In summary, the lithium battery PCB and BMS each play essential roles in ensuring the safety, performance, and longevity of lithium-ion batteries. While the PCB focuses on protecting individual cells from overcharge and over-discharge, the BMS offers a comprehensive suite of functions, including battery monitoring, balancing, and fault detection. Understanding the differences between these two components is crucial for selecting the right battery management solution, whether you are designing a battery pack for a consumer device or a more complex application like an electric vehicle.
By choosing the appropriate protection and management system, designers and users can achieve the right balance of performance, safety, and reliability for their specific needs.
Related Tags:
More Articles

What You Need to Know About AA 3.6V Lithium Battery
Learn all about AA 3.6V lithium batteries—voltage, size, capacity, uses, and the best replacements. Discover why they’re powerful, and highly reliable.
What Are Lithium Salts and Why They Matter in Battery Electrolytes
Lithium salts in electrolytes are key to battery performance, powering everything from phones to EVs and shaping the future of clean energy.
Lithium AAA Battery Guide: Power, Performance & Chargers
Explore lithium AAA batteries—voltage, capacity, weight, top brands, and more. Learn how to choose the best battery for your device and why it really matters.
How to Calculate Watts, Volts, and Amps (With Simple Formulas and Examples)
Learn how to calculate watts, volts, and amps for lithium batteries with simple formulas and examples, ideal for EVs, solar, and energy systems.
Comprehensive Analysis of U.S. Tariffs on Chinese Lithium Batteries
U.S. tariffs on Chinese lithium batteries in 2025 impact costs, supply chains, and EV, energy storage, and electronics industries globally.