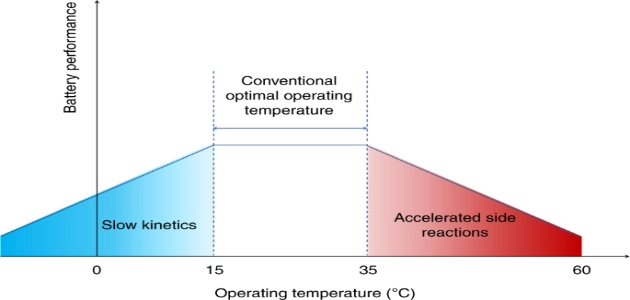
What is the Optimal Lithium Battery Temperature Range? The optimal operating temperature range for lithium batteries is 15°C to 35°C (59°F to 95°F). For storage, a temperature range of -20°C to 25°C (-4°F to 77°F) is recommended. Extreme temperatures can severely impact performance, safety, and lifespan. This guide explains how temperature affects lithium batteries and provides strategies to optimize performance.
Part 1. Why temperature ranges matter for lithium battery performance?
Maintaining the appropriate temperature range is vital for maximizing the efficiency and lifespan of lithium batteries. Operating lithium batteries outside their recommended temperature range can lead to reduced capacity, diminished performance, accelerated aging, and even safety hazards.
Part 2. Best temperature range for lithium battery operation
Optimal Temperature Range
- Lithium batteries work best between 15°C to 35°C (59°F to 95°F).
- This range ensures peak performance and longer battery life.
- Battery performance drops below 15°C (59°F) due to slower chemical reactions.
- Overheating can occur above 35°C (95°F), harming battery health.
Effects of Extreme Temperatures
- Freezing temperatures (below 0°C or 32°F) can freeze the battery’s electrolyte, causing permanent damage.
- High temperatures (above 60°C or 140°F) can speed up battery aging and pose safety risks.
- Extreme temperatures shorten battery lifespan and reduce efficiency.
- Controlled environments and thermal management systems help maintain safe battery temperatures.
- Regular temperature monitoring prevents damage and ensures battery safety.
Lithium Battery Temperature Effects:
| Temperature Range | Performance Impact | Recommendations |
|---|---|---|
| -20°C to 0°C (-4°F to 32°F) | Electrolyte freezing, significant capacity loss | Avoid usage; consider insulation or warming. |
| 15°C to 35°C (59°F to 95°F) | Optimal performance, maximum efficiency | Best for usage and charging. |
| 35°C to 60°C (95°F to 140°F) | Overheating, reduced lifespan, risk of thermal runaway | Use cooling systems to manage temperature. |
| Above 60°C (140°F) | Severe degradation, high safety risk | Avoid at all costs; ensure proper ventilation. |
Part 3. How extreme temperatures affect lithium battery performance?
Performance at Low Temperatures
- In cold temperatures, like below 15°C (59°F), lithium batteries experience reduced performance.
- Chemical reactions within the battery slow down, causing decreased power output.
- Shorter battery life and diminished capacity result from these conditions.
- Devices may shut down unexpectedly in extreme cold due to reduced battery efficiency.
Performance at High Temperatures
- High temperatures above 35°C (95°F) also impact lithium battery performance.
- Excessive heat accelerates chemical reactions, causing the battery to degrade faster.
- Overheating can lead to thermal runaway, a dangerous condition where the battery can catch fire or explode.
- Prolonged exposure to high temperatures shortens battery lifespan and increases safety risks.
- Devices may experience performance issues or even failure in extreme heat.
Part 4. Recommended storage temperatures for lithium batteries
Recommended Storage Temperature Range
Proper storage of lithium batteries is crucial for preserving their performance and extending their lifespan. When not in use, experts recommend storing lithium batteries within a temperature range of -20°C to 25°C (-4°F to 77°F). Storing batteries within this range helps maintain their capacity and minimizes self-discharge rates. Storing batteries at temperatures above 25°C (77°F) can accelerate the aging process, while storing them below -20°C (-4°F) may cause irreversible damage.
Storage Considerations in Extreme Climates
- Insulation or heated storage areas can prevent batteries from freezing in freezing climates.
- Storing batteries in cool, shaded areas or climate-controlled environments is recommended for scorching climates.
- Avoid leaving batteries in vehicles exposed to direct sunlight, as temperatures inside can exceed safe limits.
- During transport in extreme climates, insulated packaging or temperature-controlled containers can protect batteries from temperature fluctuations.
- Regularly monitor storage conditions and take appropriate measures to store batteries within recommended temperature ranges.
Part 5. Lithium battery charging and discharging at extreme temperatures
Charging at Extreme Temperatures
- Charging lithium batteries at extreme temperatures can harm their health and performance.
- At low temperatures, charging efficiency decreases, leading to slower charging times and reduced capacity.
- High temperatures during charging can cause the battery to overheat, leading to thermal runaway and safety hazards.
- It’s best to charge lithium batteries at temperatures within the recommended range of 0°C to 45°C (32°F to 113°F) to ensure optimal performance and safety.
Discharging at Extreme Temperatures
- Discharging lithium batteries at extreme temperatures also affects their performance and lifespan.
- The battery’s internal resistance increases at low temperatures, reducing power output and capacity.
- High temperatures during discharge can accelerate chemical reactions, leading to faster degradation and capacity loss.
- Operating devices powered by lithium batteries in extreme temperatures can result in reduced runtime and potential damage to the battery.
- Avoid discharging lithium batteries in temperatures below -20°C (-4°F) or above 60°C (140°F) whenever possible to maintain battery health and prolong lifespan.
Part 6. Strategy for managing lithium battery temperatures
Thermal Management Systems
- Thermal management systems help regulate the temperature of lithium batteries during operation.
- Typical systems include heat sinks, cooling fans, thermal pads, and temperature sensors.
- Heat sinks dissipate excess heat from the battery to prevent overheating.
- Cooling fans improve airflow around the battery, aiding in heat dissipation.
- Thermal pads provide insulation to maintain stable temperatures within the battery.
- Temperature sensors monitor the battery’s temperature, allowing for real-time adjustments to thermal management systems.
Environmental Control Measures
- Environmental control measures involve controlling the temperature of the surroundings where lithium batteries are used or stored.
- This includes maintaining ambient temperatures within the optimal range of 15°C to 35°C (59°F to 95°F).
- Avoid exposing batteries to extreme temperatures, such as in hot cars or direct sunlight.
- Store batteries in cool, shaded areas to prevent overheating.
- Use climate-controlled environments or insulated storage solutions to maintain stable temperatures in extreme climates.
- Regularly monitor temperature conditions using temperature sensors to keep batteries within the recommended range for optimal performance and safety.
Part 7. In summary
Maintaining the recommended temperature range is essential for maximizing the performance and longevity of lithium batteries. Operating within 15°C to 35°C (59°F to 95°F) for usage and -20°C to 25°C (-4°F to 77°F) for storage minimizes degradation and safety risks. By implementing proper temperature management strategies, lithium batteries can deliver optimal performance and reliability in diverse applications.
Explore More:
How to Store 18650 Batteries Safely?
Part 8. FAQs
-
What is the safe operating temperature for lithium batteries?
Lithium batteries operate best between 15°C to 35°C (59°F to 95°F). Temperatures outside this range can degrade performance and safety. -
Can lithium batteries work in freezing temperatures?
Operating lithium batteries below 0°C (32°F) can cause electrolyte freezing, leading to permanent damage. Pre-heating or insulation can mitigate this. -
How do I store lithium batteries in extreme climates?
Use insulated or climate-controlled storage solutions to maintain temperatures between -20°C to 25°C (-4°F to 77°F). Avoid direct sunlight and freezing environments. -
Why do lithium batteries overheat?
Overheating occurs due to excessive chemical reactions, poor ventilation, or charging/discharging at high temperatures. Implement cooling systems to prevent overheating.
Related Tags:
More Articles

What You Need to Know About AA 3.6V Lithium Battery
Learn all about AA 3.6V lithium batteries—voltage, size, capacity, uses, and the best replacements. Discover why they’re powerful, and highly reliable.
What Are Lithium Salts and Why They Matter in Battery Electrolytes
Lithium salts in electrolytes are key to battery performance, powering everything from phones to EVs and shaping the future of clean energy.
Lithium AAA Battery Guide: Power, Performance & Chargers
Explore lithium AAA batteries—voltage, capacity, weight, top brands, and more. Learn how to choose the best battery for your device and why it really matters.
How to Calculate Watts, Volts, and Amps (With Simple Formulas and Examples)
Learn how to calculate watts, volts, and amps for lithium batteries with simple formulas and examples, ideal for EVs, solar, and energy systems.
Comprehensive Analysis of U.S. Tariffs on Chinese Lithium Batteries
U.S. tariffs on Chinese lithium batteries in 2025 impact costs, supply chains, and EV, energy storage, and electronics industries globally.