- Part 1. What is a lithium-ion battery?
- Part 2. Lithium-ion battery advantages and limitations
- Part 3. What is a nickel-cadmium (NiCd) battery?
- Part 4. Nickel-cadmium battery advantages and limitations
- Part 5. Key differences: lithium-ion vs. nickel-cadmium batteries
- Part 6. Recommended uses: Which battery is right for you?
- Part 7. FAQs about nickel-cadmium vs lithium-ion
Lithium-ion (Li-ion) and Nickel-Cadmium (NiCd) batteries are two of the most widely used rechargeable battery types. Li-ion batteries are known for high energy density, lightweight design, and fast charging, making them ideal for portable electronics. NiCd batteries excel in durability, high discharge rates, and wide temperature tolerance, suitable for power tools and industrial equipment. This guide compares nickel cadmium battery vs lithium ion performance, cost, and lifespan, helping you decide which rechargeable battery fits your device or application.
NiCd vs Li-ion battery key difference: Lithium-ion batteries have higher energy density, lighter weight, and no memory effect, making them ideal for portable devices. Nickel-cadmium (NiCd) batteries tolerate extreme temperatures, cost less, and last longer in cycle life, making them suitable for power tools and harsh environments.
- Energy density: Li-ion higher
- Lifespan: NiCd longer cycles
- Memory effect: NiCd yes, Li-ion no
- Best for: Li-ion – electronics; NiCd – industrial tools
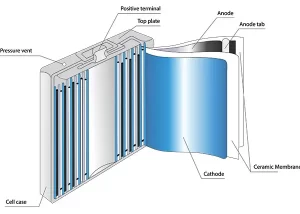
Part 1. What is a lithium-ion battery?
Lithium-ion batteries comprise several vital components, including electrodes, electrolytes, and a separator. The positive electrode, or cathode, typically consists of lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2), lithium nickel manganese cobalt oxide (LiNiMnCoO2), or lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4). The negative electrode, or anode, is usually made of graphite.
During charging, lithium ions move from the cathode to the anode through the electrolyte solution, creating a potential difference. This process is reversed during discharge, as the lithium ions travel back to the cathode, generating electrical energy.
Part 2. Lithium-ion battery advantages and limitations
Advantages
- High Energy Density: Lithium-ion batteries offer a high energy density, meaning they can store a substantial amount of energy in a compact size. This makes them ideal for portable devices where space is limited.
- Lightweight: Li-ion batteries are relatively lightweight compared to other rechargeable battery types, making them suitable for mobile devices.
- No Memory Effect: Unlike other batteries, lithium batteries do not suffer from the memory effect. This means they can be charged and discharged anytime without impacting their overall capacity.
- Fast Charging: Lithium-ion batteries charge quickly, enabling you to minimize downtime and keep your devices powered up.
- Low Self-Discharge: Li-ion batteries have a low rate, meaning they retain their charge for extended periods when not in use.
Limitations
- Limited Lifespan: Li-ion batteries have a limited lifespan, typically lasting between 2 to 3 years before their capacity starts to degrade. Over time, you may notice a decrease in their ability to hold a charge.
- Safety Concerns: While rare, Li-ion batteries can experience thermal runaway, where the battery overheats, potentially leading to fires or explosions. Proper handling, storage, and charging practices mitigate these risks.
- Higher Cost: Li-ion batteries are generally more expensive than other battery types. This is primarily due to the cost of lithium resources and the advanced technology involved in their production.
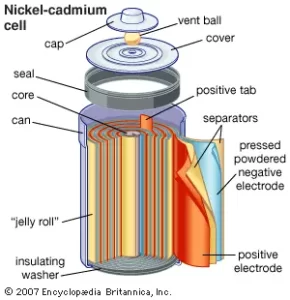
Part 3. What is a nickel-cadmium (NiCd) battery?
A NiCd battery, short for nickel-cadmium battery, is a rechargeable battery type using nickel oxide hydroxide and metallic cadmium as electrodes. Nickel Cadmium batteries consist of a positive electrode (nickel oxide hydroxide), a negative electrode (cadmium), and an alkaline electrolyte (potassium hydroxide). These batteries employ a reversible electrochemical reaction between nickel and cadmium to store and release energy.
Part 4. Nickel-cadmium battery advantages and limitations
Advantages
- Wide Operating Temperature Range: NiCd batteries can function in extreme temperatures, making them suitable for applications in harsh environments where other batteries might struggle.
- High Discharge Rate: NiCd batteries can deliver a high discharge rate, making them suitable for devices that require a sudden burst of power, such as power tools or emergency equipment.
- Long Cycle Life: Nickel Cadmium batteries have a long cycle life, meaning they can withstand many charge and discharge cycles before showing significant degradation in performance.
- Low Internal Resistance: NiCd batteries have a low internal resistance, allowing them to deliver a consistent power output even under heavy loads.
- Relatively Lower Cost: Nickel Cadmium batteries are generally less expensive than Li-ion batteries, making them more cost-effective for specific applications.
Limitations
- Memory Effect: Nickel Cadmium batteries can suffer from the memory effect. You can reduce their overall capacity if you don’t fully discharge them before recharging. However, modern NiCd batteries and other battery chemistries, such as lithium-ion, have been designed to minimize or eliminate the memory effect.
- Toxic Materials: NiCd batteries contain harmful materials, such as cadmium, which raises environmental concerns during the production, use, and disposal of these batteries.
- Lower Energy Density: Nickel Cadmium batteries have a lower energy density than lithium-ion batteries. This means that, for the same capacity, NiCd batteries would be larger and heavier than their Li-ion counterparts.
- Self-Discharge: NiCd batteries have a higher self-discharge rate compared to Li-ion batteries. They tend to lose their charge more quickly when not in use, which can disadvantage applications requiring extended standby periods.
Part 5. Key differences: lithium-ion vs. nickel-cadmium batteries
When deciding between Lithium-ion and Nickel-cadmium batteries, understanding the key differences is crucial. Each has unique strengths and weaknesses that make them suitable for different applications. Let’s explore how these two battery types compare across critical aspects like energy density, lifespan, and environmental impact.
| Aspect | Lithium-ion Battery (Li-ion) | Nickel-Cadmium Battery (NiCd) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemistry | Lithium ions; common cathodes: LiCoO₂, LiFePO₄, LiNiMnCoO₂ | Nickel oxide hydroxide and cadmium; alkaline electrolyte |
| Energy Density | High — stores more energy in smaller, lighter package | Moderate — heavier and larger for same capacity |
| Weight | Lightweight — ideal for portable electronics | Relatively heavy — suitable for power tools and industrial use |
| Cycle Life | Long, but capacity degrades over 2–3 years | Very long — withstands many charge/discharge cycles |
| Charging Speed | Fast — supports quick charging | Moderate — slower charging |
| Self-Discharge Rate | Low — retains charge for long periods | Higher — loses charge faster when not in use |
| Memory Effect | None — can recharge anytime without impact | Present — requires full discharge to maintain capacity |
| Performance in Extreme Temperatures | Good — may degrade in very low temperatures | Excellent — tolerates wide temperature range |
| Environmental Impact | Lower — no cadmium, recyclable | Higher — contains toxic cadmium, requires careful disposal |
| Suitability | Portable devices, smartphones, laptops, EVs | Power tools, emergency backup systems, industrial equipment |
| Cost | Moderate to high — higher upfront cost | Lower — cost-effective for industrial applications |
- Chemistry: Li-ion batteries use lithium ions as charge carriers, while NiCd batteries use nickel oxide hydroxide and metallic cadmium.
- Energy Density: Li-ion batteries have a higher energy density than NiCd batteries. This means they can store more energy in a smaller and lighter package.
- Memory Effect: NiCd batteries can experience the memory effect, which can reduce their overall capacity over time if not fully discharged before recharging. Li-ion batteries do not suffer from this effect.
- Lifespan: Li-ion batteries generally have a shorter lifespan compared to NiCd batteries. NiCd batteries can withstand more charge and discharge cycles before significant degradation occurs.
- Environmental Impact: NiCd batteries contain toxic materials, such as cadmium, which raises environmental concerns during production, use, and disposal. Li-ion batteries have a lower environmental impact in this regard.
- Cost: NiCd batteries are generally less expensive than Li-ion batteries, making them more cost-effective for specific applications.
Part 6. Recommended uses: Which battery is right for you?
Choosing the right battery depends on your specific needs and applications. Below are common scenarios where Lithium-ion and Nickel-Cadmium batteries excel:
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: Best for smartphones, laptops, electric vehicles, and portable devices due to their high energy density, lightweight design, and fast charging.
- Nickel-Cadmium Batteries: Ideal for power tools, emergency backup systems, and harsh environments requiring wide temperature tolerance and high discharge rates.
By assessing your priorities—whether it’s longevity, cost, or performance in extreme conditions—you can make an informed decision.
Summary: For portable devices, Li-ion batteries are superior due to light weight, fast charging, and high energy density. For power tools or harsh environments, NiCd batteries are preferred because of their durability, wide temperature tolerance, and long cycle life. Choosing the right battery depends on device type, usage frequency, and environmental conditions.
Explore Ufine Li-ion batteries
Part 7. FAQs about nickel-cadmium vs lithium-ion
Are NiCd batteries better than Li-ion?
It depends on the application. NiCd batteries excel in durability, high discharge rates, and extreme temperature tolerance, making them ideal for power tools and industrial equipment. Li-ion batteries offer higher energy density, lighter weight, and fast charging, making them better for portable devices like smartphones and laptops.
What is the difference between NiCd and Li-ion batteries?
NiCd batteries have a longer cycle life, handle extreme temperatures, and are cost-effective, but they are heavier and suffer from the memory effect. Li-ion batteries are lighter, store more energy per unit, charge faster, and do not have a memory effect.
Can I replace a NiCd battery with a Li-ion battery?
Yes, replacement is possible if the device supports the voltage and charging requirements. Some modifications may be needed for older devices to function properly with Li-ion batteries.
Which battery is better for power tools?
NiCd batteries are generally preferred for power tools in harsh environments due to their robustness and high discharge capability. Li-ion batteries can be used but may require more careful handling to avoid overheating under heavy load.
How long do NiCd batteries last?
With proper use and maintenance, NiCd batteries can last several years or even decades. Their lifespan depends on usage patterns, storage conditions, and the number of charge-discharge cycles.
Are NiCd batteries safe and legal?
NiCd batteries are legal, but they contain cadmium, a toxic metal, which raises environmental concerns. Some countries restrict its use and require proper disposal and recycling. Li-ion batteries are generally safer regarding toxicity but still require proper handling to avoid thermal runaway.
Why choose Li-ion batteries for portable devices?
Li-ion batteries are lightweight, high in energy density, charge quickly, and have no memory effect. This makes them ideal for smartphones, laptops, and other portable electronics.
Which devices benefit most from NiCd batteries?
NiCd batteries are suited for power tools, emergency backup systems, and equipment used in extreme conditions, thanks to their long cycle life and ability to deliver sudden bursts of power.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Top 10 Lithium Motorcycle Batteries for Optimal Performance
Compare the best lithium motorcycle batteries for 2026, including LiFePO4 vs lead-acid, lifespan, CCA ratings, cold-start performance, and expert buying tips.
Group 35 Battery Size, Type & Best Options for Your Car (2026 Guide)
Discover the complete group 35 battery guide with detailed size charts, battery types, pricing, applications, and recommended brands for your car in 2026.
Understanding D Battery: A Quick Guide
Discover D battery types, voltage, capacity, and lifespan. Learn how to choose the best D battery for flashlights, tools, and emergency gear.
Tracker Lithium Batteries: A Comprehensive Guide
Learn about tracker lithium battery types, applications, advantages, and how to choose the right manufacturer for GPS and IoT tracking devices.
8 Volt Golf Cart Batteries: Tips, Types & Lifespan
Explore 8 volt golf cart batteries, types, lifespan, and maintenance tips. Find out which battery suits your cart best in 2026.