- Part 1. What are lithium manganese batteries?
- Part 2. How do lithium manganese batteries work?
- Part 3. Advantages of lithium manganese batteries
- Part 4. Applications of lithium manganese batteries
- Part 5. Limitations of lithium manganese batteries
- Part 6. How to choose the right lithium manganese battery?
- Part 7. Comparing lithium manganese batteries with other battery technologies
- Part 8. Future of lithium manganese batteries
- Part 9. FAQs
Due to their unique chemistry and remarkable performance characteristics, lithium manganese batteries are revolutionizing energy storage solutions across various industries. As the demand for efficient, safe, and lightweight batteries grows, understanding the intricacies of lithium manganese technology becomes increasingly essential. This comprehensive guide will explore the fundamental aspects of lithium manganese batteries, including their operational mechanisms, advantages, applications, and limitations. Whether you are a consumer seeking reliable energy sources or a professional in the field, this article aims to provide valuable insights into lithium manganese batteries.
Part 1. What are lithium manganese batteries?
Lithium manganese batteries, commonly known as LMO (Lithium Manganese Oxide), utilize manganese oxide as a cathode material. This type of battery is part of the lithium-ion family and is celebrated for its high thermal stability and safety features.
Key Characteristics:
- Composition: The primary components include lithium, manganese oxide, and an electrolyte.
- Voltage Range: Typically operates at a nominal voltage of around 3.7 volts.
- Cycle Life: Known for a longer cycle life than other lithium-ion batteries.
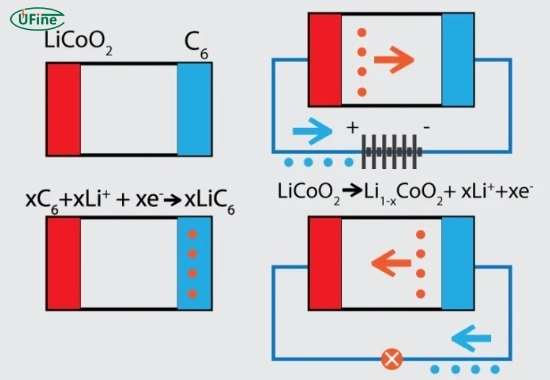
Part 2. How do lithium manganese batteries work?
The operation of lithium manganese batteries revolves around the movement of lithium ions between the anode and cathode during charging and discharging cycles.
Charging Process:
- Lithium ions move from the cathode (manganese oxide) to the anode (usually graphite).
- Electrons flow through an external circuit, creating an electric current.
Discharging Process:
- Lithium ions travel back to the cathode from the anode.
- The stored energy is released as electrical energy.
- An electrolyte facilitates this movement of ions, allowing ionic conductivity while preventing electronic conduction.
Part 3. Advantages of lithium manganese batteries
Lithium manganese batteries offer several benefits that make them appealing for various applications:
- Safety: They have a lower risk of thermal runaway than other lithium-ion chemistries.
- High Discharge Rates: Capable of delivering high current outputs, making them suitable for power-intensive applications.
- Stable Performance: Exhibit consistent performance over a wide temperature range.
- Environmental Impact: Manganese is more abundant and less toxic than cobalt, making these batteries more environmentally friendly.
Part 4. Applications of lithium manganese batteries
Due to their unique properties, lithium manganese batteries are utilized in numerous fields:
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): Their high discharge rates and safety features make them ideal for electric cars.
- Consumer Electronics: Commonly found in laptops, smartphones, and tablets due to their lightweight nature.
- Medical Devices: These are used in portable medical equipment where reliability is critical.
- Energy Storage Systems: Ideal for renewable energy applications like solar power storage.
Part 5. Limitations of lithium manganese batteries
Despite their many advantages, lithium manganese batteries do have some limitations:
- Lower Energy Density: LMO batteries have a lower energy density than other lithium-ion batteries like lithium cobalt oxide (LCO).
- Cost: While generally less expensive than some alternatives, they can still be cost-prohibitive for specific applications.
- Temperature Sensitivity: Although they perform well in various temperatures, extreme conditions can affect their efficiency.
Part 6. How to choose the right lithium manganese battery?
Selecting the appropriate lithium manganese battery involves considering several key factors that align with your specific needs:
Application Requirements:
- Determine what you need the battery for—electric vehicles, consumer electronics, or renewable energy storage.
- Assess the power requirements; higher discharge rates may be necessary for applications like EVs or power tools.
Capacity and Energy Density:
- Look for batteries with adequate capacity (measured in ampere-hours or Ah) to meet your usage demands.
- If space is limited, consider energy density; however, remember that LMO batteries typically have lower energy density than LCO options.
Cycle Life:
- Evaluate how often you charge and discharge the battery; longer cycle life can lead to better long-term value.
- Lithium manganese batteries often provide extended cycle life compared to other chemistries.
Safety Features:
- Prioritize batteries with enhanced safety features, mainly if used in high-temperature environments or applications where overheating could pose risks.
Cost Considerations:
- Compare prices among different brands and models; while LMO batteries are generally more affordable than LCO options, costs vary significantly based on capacity and manufacturer reputation.
Manufacturer Reputation:
- Research manufacturers are known for quality and reliability in battery production.
- Look for warranties or guarantees that indicate confidence in their product’s longevity and performance.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can choose a lithium manganese battery that best suits your needs while ensuring optimal performance and safety.
Part 7. Comparing lithium manganese batteries with other battery technologies
When evaluating battery options, it’s essential to understand how lithium manganese batteries compare with other technologies, such as lithium cobalt oxide (LCO) and nickel-metal hydride (NiMH).
Key Differences
Energy Density
- Lithium cobalt oxide (LCO) has a higher energy density at approximately 200 Wh/kg, making it suitable for limited-space applications.
- Lithium manganese oxide (LMO) offers moderate energy density around 150 Wh/kg but excels in safety and thermal stability.
- Nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) provides lower energy density at about 100 Wh/kg but is often used in hybrid vehicles due to its durability.
Safety
- LMO batteries are known for their enhanced safety features due to lower thermal runaway risks.
- LCO has a higher risk associated with overheating.
- NiMH batteries are relatively safe but can still pose risks under certain conditions.
Cycle Life
- LMO typically has a longer cycle life exceeding 2000 cycles compared to LCO’s lifespan of about 500–1000 cycles.
- NiMH batteries have a moderate cycle life but may degrade faster under heavy use.
Cost
- LMO is generally more affordable than LCO but can be more expensive than NiMH, depending on market conditions.
Comparison Table:
| Feature | Lithium Manganese (LMO) | Lithium Cobalt (LCO) | Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | ~150 Wh/kg | ~200 Wh/kg | ~100 Wh/kg |
| Safety | High | Moderate | High |
| Cycle Life | 2000+ cycles | 500-1000 cycles | 500-1000 cycles |
| Cost | Moderate | High | Low |
| Temperature Range | -20°C to 60°C | 0°C to 40°C | -20°C to 60°C |
This comparison illustrates how lithium manganese batteries stand out in terms of safety and cycle life while having moderate energy density compared to other technologies.
Part 8. Future of lithium manganese batteries
The future looks promising for lithium manganese batteries as advancements in technology continue to emerge:
Innovative Materials:
Researchers are exploring new materials that enhance performance metrics, such as energy density and charge/discharge rates.
Recent studies have focused on nanostructured LiMnO₂, which shows potential for improved stability without voltage decay.
Sustainability Focus:
With growing concerns over the environmental impact of mining nickel and cobalt, manganese, due to its abundance, presents a more sustainable alternative.
Market Growth in EVs:
As electric vehicle adoption increases globally, the demand for efficient battery technologies will drive further investment in manganese-based solutions.
Research Collaboration:
Researchers’ collaborative efforts address challenges like capacity loss and dissolution associated with traditional manganese materials.
Commercialization Potential:
Commercializing advanced manganese-based battery technologies could significantly reduce costs while maintaining high performance.
Lithium manganese batteries are poised to play a crucial role in shaping the future of energy storage solutions across various sectors by addressing current limitations and capitalizing on advancements in research.
Part 9. FAQs
-
What is the lifespan of lithium manganese batteries?
Lithium manganese batteries typically range from 2 to 10 years, depending on usage and environmental conditions. -
Are lithium manganese batteries safe?
Yes, they are considered safe due to their thermal stability and lower risk of overheating compared to other lithium-ion chemistries. -
Can lithium manganese batteries be recycled?
Yes, they can be recycled; however, proper recycling facilities must handle them to recover valuable materials safely. -
How do I maintain my lithium manganese battery?
Store your battery’s health in a relaxed environment, avoid deep discharges, and follow manufacturer guidelines for charging cycles. -
What are the main disadvantages of using lithium manganese batteries?
The main disadvantages include lower energy density compared to other types and potential cost issues depending on application needs.
Related Tags:
More Articles
What is the Difference Between Silver Zinc Battery vs. Lithium-ion Rechargeable?
Compare silver zinc and lithium-ion rechargeable batteries: energy density, cycle life, safety, cost, and uses in drones, medical devices, EVs, and electronics.
What are Watts and Watt Hours in Battery?
Understand watt vs watt-hour in batteries: key differences, how to calculate capacity, and why they matter. Includes free comparison table.
Best 10 Blood Pressure Monitor Battery Review: Finding the Most Reliable
Are you looking for a reliable Blood Pressure Monitor battery? Here is a complete guide with the top 10 best blood pressure monitor batteries.
Bluetooth Headphone Battery Guide: All You Need to Know
Maximize headphone battery life with expert tips! Learn how to charge, check, troubleshoot, and choose the best bluetooth headphone battery in 2025.
LiFePO4 Battery VS. Lithium-ion Polymer Battery: Which One Is Best?
Comprehensive comparison of LiFePO4 vs Lithium Ion Polymer batteries: energy density, safety, lifespan, cost. Find out which battery suits your needs in 2025.