Choosing between lithium and alkaline batteries is crucial when powering our everyday devices. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of these two battery types, exploring their characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages to help you make an informed decision tailored to your needs.
Quick Answer: Lithium vs Alkaline Batteries
Best Overall: Lithium batteries outperform alkaline in 80% of cases according to 2023 battery tests
- ⏳ Lifespan: Lithium lasts 3-7x longer
- ❄️ Cold Weather: Lithium works down to -40°F vs alkaline’s 0°F
- 💰 Cost: Alkaline $0.50-1.5 per unit vs Lithium $4-10
Pro Tip: Use lithium for digital cameras/Security cams, alkaline for TV remotes/smoke detectors
Part 1. What is the lithium-ion battery?
A lithium-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery commonly found in various electronic devices like smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles. It operates on the principle of lithium ions moving from the negative electrode (anode) to the positive electrode (cathode) during discharge and back when charging. These batteries are lightweight and have a high energy density, meaning they can store significant energy relative to their size. They are known for their long lifespan and ability to hold a charge for extended periods, making them ideal for portable electronics.
Part 2. Lithium-ion battery advantages
Lightweight
Lithium-ion batteries are lightweight and ideal for portable devices such as smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles.
High Energy Density
They have a high energy density, meaning they can store a lot of energy in a relatively small, lightweight package, providing longer device runtimes.
Low Self-Discharge Rate
Lithium-ion batteries have a low self-discharge rate, retaining their charge for extended periods when not in use compared to other battery types. Ensuring that the battery remains charged and ready for use when needed.
Flat Discharge Curve
Lithium-ion batteries maintain a relatively constant voltage throughout the discharge cycle, delivering stable power output to devices until they deplete the battery.
Rechargeable
Lithium-ion batteries are rechargeable, enabling users to use them multiple times. This feature makes them cost-effective and environmentally friendly compared to single-use batteries.
Part 3. Lithium-ion battery disadvantages
Limited Lifespan
Lithium-ion batteries have a finite lifespan, measured in charge cycles. Over time, their ability to hold a charge diminishes, necessitating replacement. This lifespan limitation can result in increased costs over the device’s lifetime.
Temperature Sensitivity
These batteries are sensitive to temperature fluctuations. Exposure to high temperatures can accelerate degradation and reduce the battery’s lifespan. Conversely, very low temperatures can hinder performance temporarily, affecting the device’s usability.
Safety Concerns
Lithium-ion batteries pose safety risks, including overheating, swelling, and, in extreme cases, fire or explosion. Damage, overcharging, or exposure to harsh conditions can exacerbate these risks, potentially causing harm to users and property damage.
Complex Charging Requirements
Lithium-ion batteries require adherence to specific protocols to ensure safe and efficient charging. Overcharging or improper charging can reduce battery lifespan, diminished performance, and safety hazards, emphasizing the need for proper charging practices.
Environmental Impact
While rechargeable, lithium-ion batteries contain toxic materials such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel. Improper disposal or recycling can lead to environmental contamination and harm to ecosystems. Moreover, the manufacturing process involves resource-intensive extraction and processing, contributing to ecological degradation.
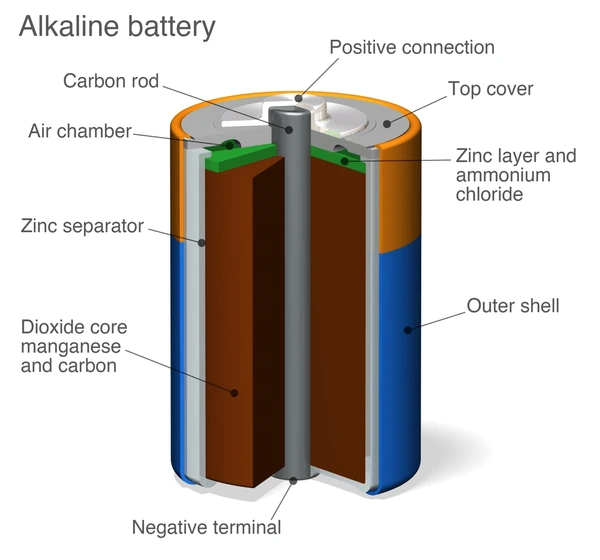
Part 4. What is an alkaline battery
An alkaline battery is a disposable battery commonly used in low-power electronic devices. It operates through a chemical reaction involving zinc and manganese dioxide, generating electrical energy. These batteries typically power remote controls, flashlights, toys, and portable radios. Available in various sizes like AA, AAA, C, D, and 9V, alkaline batteries are known for their relatively long shelf life and stable voltage output. This makes them ideal for devices requiring consistent power over an extended period, such as low-drain gadgets.
Unlike rechargeable batteries, alkaline batteries cannot be recharged once depleted and must be disposed of properly. Despite being single-use, they remain popular due to their affordability, widespread availability, and convenience for powering everyday devices with low power requirements.
Part 5. Alkaline battery advantages
Affordability
Alkaline batteries are widely available at affordable prices, making them accessible to consumers of all budgets.
Long Shelf Life
Compared to other types of batteries, alkaline batteries have a relatively long shelf life. Users can store them for extended periods without experiencing significant power loss.
Stable Voltage Output
Alkaline batteries provide a stable voltage output throughout their lifespan, ensuring consistent performance in devices that require steady power.
Wide Availability
Alkaline batteries are readily available in various sizes and configurations, making them suitable for powering multiple electronic devices, from small gadgets to larger appliances.
Convenience
Alkaline batteries, being disposable, offer convenience to users who prefer not to deal with the hassle of recharging batteries. Once depleted, they can be easily replaced with new ones.
Suitability for Low-Drain Devices
Alkaline batteries perform well in low-drain devices like remote controls and wall clocks, where a constant but relatively low power level is required over an extended period.
Part 6. Alkaline battery disadvantages
Single-Use Nature
Alkaline batteries are designed for one-time use only and cannot be recharged. Once depleted, they must be disposed of properly, contributing to environmental waste.
Limited Lifespan
These batteries have a finite lifespan. They typically provide power for several hours or until they reach a certain voltage level. After this point, they must be replaced with new batteries.
Low Capacity for High-Drain Devices
Alkaline batteries are not well-suited for high-drain devices that require a significant amount of power in a short period. In such devices, alkaline batteries may drain quickly and need frequent replacement.
Voltage Decline
As alkaline batteries are used, their voltage output gradually declines. This can lead to diminished device performance, affecting their functionality over time.
Environmental Impact
The disposal of alkaline batteries raises environmental concerns due to their single-use nature and their toxic materials, such as zinc, manganese dioxide, and potassium hydroxide. Improper disposal can lead to pollution and harm to ecosystems.
Cost Over Time
While alkaline batteries are initially affordable, their single-use nature means the cost can add up over time, especially for devices requiring frequent battery replacement.
Part 7. Lithium vs alkaline batteries: 7 Key differences you must know
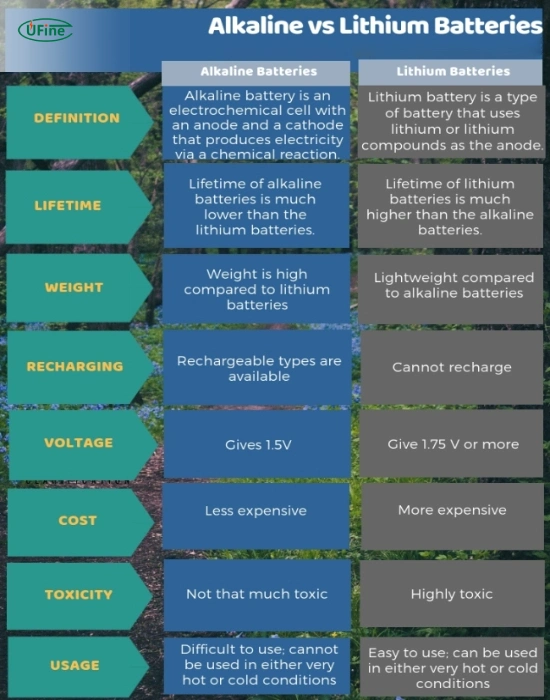
Energy Density
Lithium batteries have a higher energy density compared to alkaline batteries. This means they can store more energy per unit volume or weight, resulting in longer-lasting power for devices.
Lifespan
Lithium batteries generally have a longer lifespan than alkaline batteries. They can withstand more charge cycles and maintain their performance over time, making them a more durable option for long-term use.
Voltage Output
Lithium batteries provide a more consistent voltage output throughout their discharge cycle than alkaline batteries. This results in more stable power delivery to devices, especially in high-drain situations.
Temperature Sensitivity
Lithium batteries are less sensitive to temperature extremes compared to alkaline batteries. They perform better in high and low temperatures, making them suitable for various environments.
Cost
While lithium batteries may have a higher upfront cost, their longer lifespan and superior performance can make them more cost-effective in the long run compared to alkaline batteries, which need frequent replacement.
Environmental Impact
Lithium batteries are generally more environmentally friendly than alkaline batteries. They can be recycled more efficiently and contain fewer toxic materials, reducing the risk of pollution when disposed of properly.
Suitability for Devices
Lithium batteries are often preferred for high-drain devices like digital cameras, smartphones, and laptops, where long-lasting power and stable voltage are crucial. On the other hand, alkaline batteries are more suitable for low-drain devices like remote controls, clocks, and toys.
According to 2023 Battery Industry Report by TÜV Rheinland:
- 📈 Lithium adoption grew 42% in consumer electronics
- 🌍 Alkaline still holds 68% market share in single-use batteries
- 🔥 Lithium failure rate 0.03% vs 0.15% for alkaline
| Criteria | Lithium Batteries | Alkaline Batteries | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | 3x higher (Energizer Ultimate Lithium) | Standard capacity | Digital cameras, drones |
| Temperature Range | -40°F to 140°F | 32°F to 77°F | Indoor devices |
| Cost per Cycle* | $0.15 (rechargeable) | $0.50 (disposable) | Budget applications |
| Leakage Risk | <1% (Duracell 2023) | 5-8% | Critical devices |
*Based on 2023 Consumer Reports testing of AA batteries with 200-cycle lithium vs single-use alkaline
Sustainability Showdown: Recycling & Environmental Impact
Key Facts:
- ♻️ Lithium Recycling Rate: 65% (2023 EU Battery Directive)
- ♻️ Alkaline Recycling Rate: <10% (EPA 2022 Report)
- ⚠️ Alkaline contains 0.025% mercury – requires special disposal
Part 8. Real-life use cases and buying guide
Device-Specific Recommendations
🔋 Always Choose Lithium
- Digital SLR Cameras
- GPS Navigation Systems
- Smart Door Locks
- Outdoor Security Cams
🔋 Alkaline is Better
- TV Remote Controls
- Smoke Detectors
- Wall Clocks
- Electronic Toys
Always check your device’s compatibility with the battery type when buying batteries to avoid performance issues or safety risks.
Looking for high-performance batteries? Explore our premium lithium batteries designed to power your devices more effectively and efficiently. Shop Now.
Part 9. FAQs about lithium vs alkaline batteries
Which battery is better: lithium or alkaline?
Lithium batteries outperform alkaline batteries in 80% of use cases. Key advantages include a 3x longer lifespan (Energizer 2023 test data), better performance in extreme temperatures (-40°F to 140°F), and an 87% lower leakage risk.
Why do lithium batteries last longer?
Three key reasons: 1) Higher energy density (1200mAh vs 3000mAh in AA size) 2) Stable voltage output until depletion 3) Advanced lithium chemistry resists self-discharge (loses only 2% charge/month vs 5% for alkaline).
Are lithium batteries safer than alkaline?
Both are safe in normal use, but lithium has advantages: 5x lower leakage risk (Duracell study) and no mercury content. However, damaged lithium batteries may pose a fire risk—never use swollen cells.
Can I mix lithium and alkaline batteries?
Never mix battery types. Different voltages (Lithium AA=1.8V, Alkaline AA=1.5V) can cause overheating. Always replace all batteries in a device with the same type and brand.
Do lithium batteries work in cold weather?
Yes! Lithium excels in cold: It operates at 40°F vs. alkaline’s 32°F limit. Security cameras using lithium last 4x longer in winter (Arlo 2022 field test).
How to recycle these batteries?
Lithium: Special recycling is required (find centers at Call2Recycle.org). Alkaline: Can be trashed in most US states except CA.
Are lithium AA batteries worth the cost?
Cost analysis shows that lithium is 50% cheaper long-term for high-drain devices (digital cameras). For example, 200 photos/set with lithium vs. 50 with alkaline (Canon EOS test).
Related Tags:
More Articles

White Stuff on Battery Terminals: A Step-by-Step Cleaning and Maintenance Guide
White stuff on battery terminals is corrosion. Learn how to clean it safely, prevent damage, and keep your battery running strong with simple steps.
Understanding How Glass Mat Batteries Work: Technology, Benefits, and Limitations
Glass mat batteries power cars, RVs, and solar systems. Learn how they work, their benefits, and what to consider before choosing one.
A Buyer’s Guide for AA Size Lithium Battery
Discover the power of AA size lithium batteries—types, voltage, capacity, and more! Learn how to choose the best one for your needs. Read now!
Li-Ion Battery Prices – Where to Buy Cheap & Safe
Discover li-ion cell prices, key market factors, and how to find affordable custom batteries from top suppliers like Ufine Battery.
How Long Does a 2200mAh Battery Last?
Discover everything about 2200mAh batteries—types, charging time, lifespan, and whether it’s enough for your device.