The world of batteries is constantly evolving. New technologies are emerging, promising better performance, safety, and cost-effectiveness. Among these, the lithium manganese iron phosphate (LMFP) battery is gaining attention as a potential contender to replace the popular lithium iron phosphate (LFP) and nickel manganese cobalt (NMC) batteries. This article explores the LMFP battery market outlook, examining its potential advantages and disadvantages and whether it will replace LFP and NMC batteries.
Part 1. What is an LMFP battery?
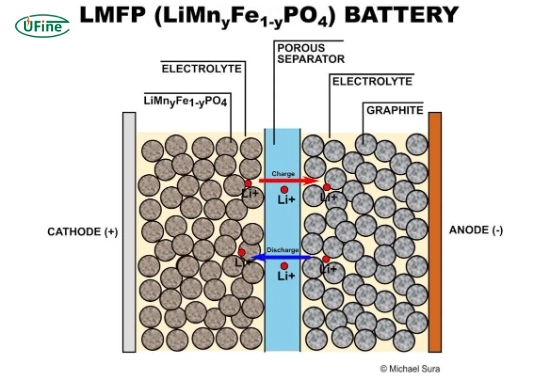
An LMFP battery is a lithium-ion battery that uses lithium manganese iron phosphate as its cathode material. It’s similar to LFP batteries but with an important addition: manganese.
How does manganese improve LFP batteries?
Adding manganese to the LFP structure enhances the battery’s voltage and energy density. This means LMFP batteries can store more energy and deliver higher power than LFP batteries.
Part 2. What are the advantages of LMFP batteries?
LMFP batteries offer several potential benefits:
- Higher energy density: Compared to LFP batteries, LMFP batteries have a higher energy density, meaning they can store more energy for a given size and weight.
- Improved power performance: The addition of manganese can improve the battery’s power output, making it suitable for applications requiring quick bursts of energy.
- Enhanced thermal stability: LMFP batteries exhibit good thermal stability, contributing to safer operation and a reduced risk of thermal runaway.
- Lower cost potential: LMFP batteries use abundant and inexpensive materials, which could lead to lower production costs compared to NMC batteries.
- Long lifespan: Like LFP batteries, LMFP batteries are expected to have a long cycle life, meaning they can be charged and discharged many times before degrading significantly.
Part 3. What are the disadvantages of LMFP batteries?
Despite the advantages, LMFP batteries also have some drawbacks:
- Lower energy density than NMC: While LMFP has a higher energy density than LFP, it’s still generally lower than NMC batteries.
- Potential for manganese dissolution: Manganese dissolution can occur during battery operation, leading to capacity fade and performance degradation over time.
- Relatively new technology: LMFP battery technology is still relatively new compared to LFP and NMC, so less long-term performance data is available.
Part 4. LMFP vs. LFP: What are the key differences?
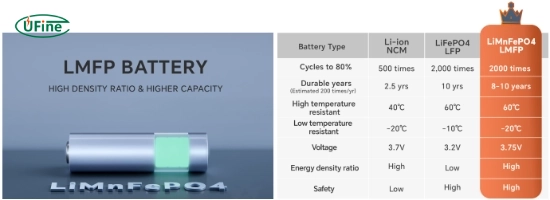
LMFP (Lithium Manganese Iron Phosphate) and LFP (Lithium Iron Phosphate) batteries share similarities. Still, the addition of manganese in LMFP leads to notable performance differences. The key advantage of LMFP over LFP is its higher energy density, which is about 15% to 20% greater due to a higher operating voltage (around 3.7V compared to LFP’s 3.2V). This results in potentially longer driving ranges for electric vehicles (EVs) using LMFP batteries. Additionally, the enhanced power performance makes LMFP suitable for applications requiring quick bursts of energy. However, LFP batteries are generally more cost-effective due to their established production and minimal use of rare earth elements like cobalt. While both offer excellent thermal stability and safety, LMFP aims to provide a performance upgrade over LFP without significantly increasing costs.
Here’s a comparison table summarizing the key differences:
| Feature | LMFP | LFP |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | 15-20% higher | Lower |
| Voltage | Around 3.7V | Around 3.2V |
| Power Performance | Better | Not as good |
| Cost | Potentially similar, but depends on the manufacturing scale | Generally lower, due to established production |
| Applications | Electric vehicles, energy storage systems | Electric vehicles, energy storage systems, power tools |
Part 5. LMFP vs. NMC: What are the key differences?
LMFP (Lithium Manganese Iron Phosphate) and NMC (Nickel Manganese Cobalt) batteries differ significantly in their composition and performance characteristics. NMC batteries are known for their high energy density, making them suitable for EVs requiring longer ranges. However, this comes at the cost of safety and using expensive and ethically concerning materials like cobalt. LMFP batteries, while having a lower energy density than NMC, offer enhanced thermal stability, reducing the risk of thermal runaway. The absence of cobalt and nickel in LMFP makes them cheaper and more environmentally friendly. LMFP balances safety and energy density, which is suitable for applications where both are important. At the same time, NMC is geared towards maximizing performance.
Here’s a comparison table highlighting the key differences:
| Feature | LMFP | NMC |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | Lower | Higher |
| Voltage | 3.7V | / |
| Cost | Potentially lower, due to cheaper materials | Higher, due to the use of cobalt and nickel |
| Thermal Stability | Better | Can be less stable, requiring more sophisticated thermal management systems |
| Applications | Electric vehicles, energy storage systems | Electric vehicles, power tools, consumer electronics |
Artikel Terkait: LFP vs. NMC Battery: What is the Difference?
Part 6. What applications are suitable for LMFP batteries?
LMFP batteries are well-suited for a variety of applications, including:
- Electric vehicles (EVs): LMFP batteries can balance energy density, power, and cost, making them attractive for EVs, especially in shorter-range or lower-cost models.
- Energy storage systems (ESS): LMFP batteries’ long cycle life and good thermal stability suit grid-scale and residential energy storage systems.
- Industrial equipment: LMFP batteries can power forklifts, construction equipment, and other industrial vehicles.
- E-bikes and scooters: LMFP’s improved energy density and power performance can enhance the range and performance of e-bikes and scooters.
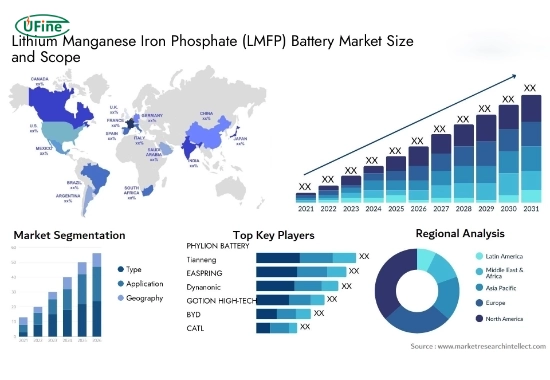
Part 7. What is the current LMFP battery market outlook?
The LMFP battery market is still in its early stages, but it’s expected to grow significantly in the coming years. Several factors are driving this growth:
- Increasing demand for EVs: The growing adoption is fueling demand for all lithium-ion batteries, including LMFP.
- Focus on lower-cost batteries: Automakers are looking for ways to reduce the cost of EVs, and LMFP batteries offer a potentially cheaper alternative to NMC batteries.
- Government support for battery manufacturing: Governments worldwide are investing in domestic battery production, which could boost the development and adoption of LMFP technology.
- Technological advancements: Ongoing research and development are improving the performance and lifespan of LMFP batteries.
Part 8. Will LMFP replace LFP and NMC batteries?
It’s unlikely that LMFP batteries will completely replace LFP and NMC batteries. Instead, they will likely find a niche in specific applications where their unique properties are most advantageous.
LFP batteries are expected to remain popular in applications where cost is a primary concern, and energy density is less critical, such as in some entry-level EVs and energy storage systems.
NMC batteries will likely continue to be used in high-performance EVs and other applications where high energy density is essential.
LMFP batteries will likely be used in applications that require a balance of energy density, power, cost, and safety.
Part 9. What are the key players in the LMFP battery market?
The LMFP battery market includes several key players across different regions, each contributing to the development and production of these batteries.
Chinese Battery Manufacturers:
- Ufine Battery: Ufine Battery is a Chinese battery manufacturer that is actively involved in the LMFP battery market.
- LISHEN: LISHEN invests heavily in LMFP battery technology and expands its production capacity.
- CATL & BYD: These companies, while also major players in LFP and NMC batteries, are exploring LMFP technology to broaden their product offerings.
International Battery Companies:
- Some major international battery manufacturers, including LG Energy Solution, Samsung SDI, SK On, and Panasonic, are also researching and developing LMFP batteries.
Regional Market Share: The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China, is expected to dominate the LMFP battery market due to the increasing demand for EVs and energy storage systems. Europe and North America also show significant growth, driven by government initiatives promoting electric vehicle adoption.
Automakers: Some automakers invest in LMFP battery development to reduce EV costs. This investment signals confidence in the potential of LMFP batteries as a cost-effective alternative to NMC batteries.
Part 10. What are the future trends in LMFP battery technology?
Several trends are shaping the future of LMFP battery technology:
- Improving energy density: Researchers are working to further increase the energy density of LMFP batteries by optimizing the material composition and cell design.
- Enhancing cycle life: Efforts are focused on improving the long-term stability and cycle life of LMFP batteries by addressing issues such as manganese dissolution.
- Reducing costs: Manufacturers are working to lower the production costs of LMFP batteries through economies of scale and improved manufacturing processes.
- Developing advanced cell designs: New cell designs, such as cell-to-pack (CTP) and cell-to-body (CTB) technologies, are being developed to improve energy density and reduce the weight of LMFP battery packs.
Part 11. FAQs
-
What is the main advantage of LMFP over LFP?
LMFP batteries have a higher energy density and better power performance than LFP batteries. This means they can store more energy and deliver more power for a given size and weight. -
Are LMFP batteries safer than NMC batteries?
Yes, LMFP batteries generally offer better thermal stability than NMC batteries, reducing the risk of thermal runaway. -
Will LMFP batteries make EVs more affordable?
Potentially, yes. LMFP batteries use cheaper materials than NMC batteries, which could lead to lower production costs and more affordable EVs. -
How long do LMFP batteries last?
LMFP batteries are expected to have a long cycle life, similar to LFP batteries, meaning they can be charged and discharged many times before degrading significantly. -
Are there any environmental concerns with LMFP batteries?
LMFP batteries are generally considered more environmentally friendly than NMC batteries because they do not contain nickel or cobalt, which are associated with environmental and ethical concerns.
Related Tags:
More Articles
10000mAh Battery Explained: How Long It Lasts, How It Works
A full guide on 10000mAh li-ion batteries, voltage, usage time, and tips. Discover how a 10000mAh battery works, how long it lasts, and how to choose.
10440 Battery Guide: Size, Voltage, Capacity, Uses & More
Understand 10440 batteries better—size, voltage, safety, and how they compare to AAA. Find the best fit for your high-performance devices.
White Stuff on Battery Terminals: A Step-by-Step Cleaning and Maintenance Guide
White stuff on battery terminals is corrosion. Learn how to clean it safely, prevent damage, and keep your battery running strong with simple steps.
Understanding How Glass Mat Batteries Work: Technology, Benefits, and Limitations
Glass mat batteries power cars, RVs, and solar systems. Learn how they work, their benefits, and what to consider before choosing one.
A Buyer’s Guide for AA Size Lithium Battery
Discover the power of AA size lithium batteries—types, voltage, capacity, and more! Learn how to choose the best one for your needs. Read now!