Lithium-ion (Li-ion) cells are at the heart of many devices we use daily, powering everything from smartphones to laptops and even electric cars. Understanding how to charge these batteries correctly is essential for ensuring their longevity and, more importantly, your safety. This comprehensive guide delve into the principles of charging Li-ion cells, the parameters to keep an eye on, and step-by-step instructions for safe charging. Additionally, we’ll provide useful tips and answer frequently asked questions to help you get the most out of your Li-ion batteries.
Part 1. Li-ion cells charging
1. Li-ion cel charging Principle
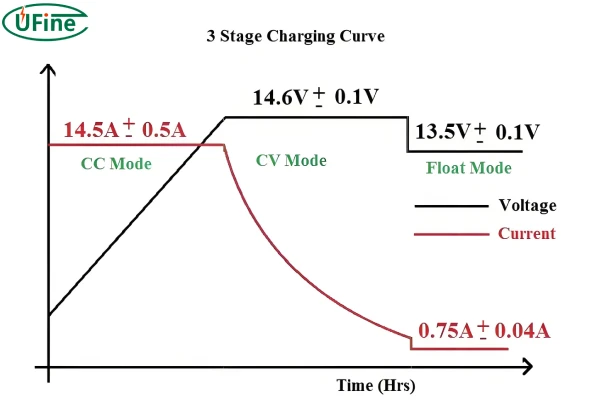
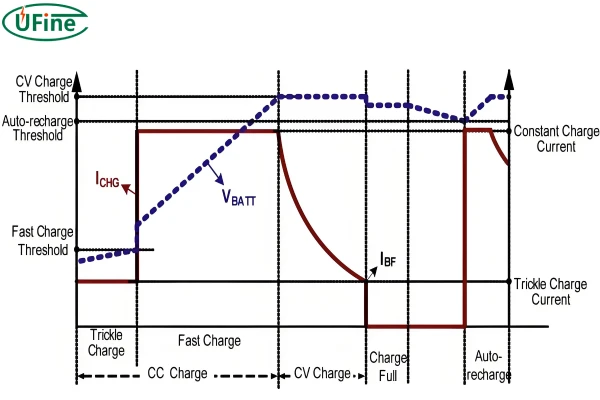
The process of charging a Li-ion cell involves two main stages: constant current (CC) and constant voltage (CV). Initially, during the constant current phase, the battery is charged at a steady current. This phase continues until the battery voltage reaches a preset threshold, typically 4.2 volts per cell. Once this voltage is achieved, the charger switches to the constant voltage phase, where it maintains this voltage while the current gradually decreases as the battery reaches full capacity. This method ensures the battery is charged efficiently and safely.
2. Li-ion cell charging Voltage
The charging voltage is a critical parameter for Li-ion cells. For most Li-ion batteries, the standard charging voltage is around 4.2 volts per cell. It’s crucial not to exceed this voltage, as overcharging can lead to severe consequences, including battery overheating, swelling, and in extreme cases, explosions. Therefore, always use a charger that regulates voltage accurately to avoid these risks.
3. Li-ion cell charging Current
The charging current is usually specified in terms of the battery’s capacity, referred to as “C-rate.” A common recommendation is to charge at a rate between 0.5C to 1C. For example, if you have a 2000mAh battery, a 1C charging rate would be 2000mA (2A). Charging at higher currents may reduce the battery’s lifespan and increase the risk of overheating. Always adhere to the manufacturer’s recommended charging current to ensure safety and longevity.
4. Li-ion cell important parameters
When charging Li-ion cells, it’s essential to monitor several key parameters:
- Voltage: Ensure that the charging voltage does not exceed 4.2 volts per cell.
- Current: Maintain the charging current within the recommended range (0.5C to 1C).
- Temperature: Avoid charging in extreme temperatures. Ideal charging conditions are typically between 10°C and 30°C (50°F to 86°F).
By keeping these parameters in check, you can ensure a safe and efficient charging process for your Li-ion batteries.
Part 2. Li-ion cells discharge
1. Li-ion cell discharge principle
Discharging a Li-ion cell involves the flow of ions from the anode to the cathode through the electrolyte, releasing stored energy to power your device. This process reverses during charging, where ions move back to the anode.
2. Li-ion cell discharge voltage
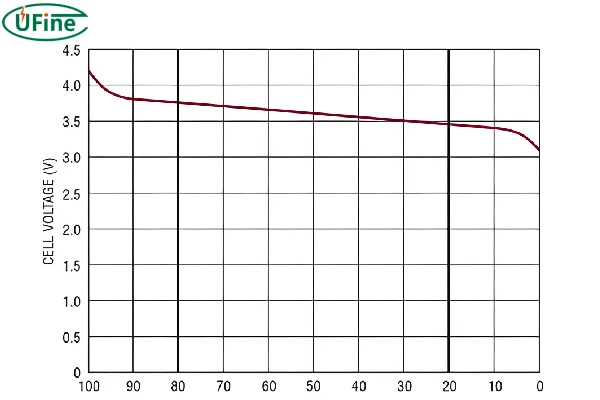
The discharge voltage for Li-ion cells typically ranges from 4.2 volts (fully charged) down to about 3.0 volts (discharged). Operating the battery within this voltage range is crucial to prevent damage and ensure optimal performance. Discharging a battery below 3.0 volts can cause irreversible damage and significantly reduce its lifespan.
3. Li-ion cell discharge current
The discharge current depends on the device’s power requirements. High discharge rates can generate excessive heat and stress the battery, potentially leading to thermal runaway. It’s essential to ensure that the discharge current remains within the battery’s safe operating limits to avoid these issues.
4. Li-ion cell important parameters
When discharging Li-ion cells, pay attention to:
- Voltage: Avoid letting the battery voltage drop below 3.0 volts.
- Current: Ensure the discharge current is within safe limits to prevent overheating.
- Temperature: Proper ventilation is necessary to dissipate heat generated during discharge.
By monitoring these parameters, you can extend the life of your Li-ion batteries and maintain their performance.
Part 3. How to charge li-ion cells?
Regarding how to charge a lithium cell, the following are the scenario steps.
- Check the Charger: Ensure that your charger is compatible with the Li-ion cells you are using. The charger should be capable of regulating both voltage and current accurately.
- Connect Properly: Attach the battery to the charger, ensuring the correct polarity. Incorrect connections can damage the battery and the charger.
- Set Parameters: Configure the charger to the appropriate settings. Set the voltage to 4.2 volts per cell and the current to a rate between 0.5C and 1C.
- Start Charging: Turn on the charger to begin the charging process. Initially, the charger will operate in constant current mode, supplying a steady current to the battery.
- Monitor the Process: Keep an eye on the charging process. Check the voltage to ensure it doesn’t exceed 4.2 volts per cell. Observe the current to see if it gradually decreases as the battery approaches full charge. Also, the temperature of the battery must be monitored. If it becomes excessively hot, stop charging immediately.
- End Charging: Once the battery is fully charged, the charger will typically switch off or indicate that the battery is fully charged, often by changing the LED color or turning off the light. Disconnect the battery from the charger promptly to avoid overcharging.
By following these steps, you can charge your Li-ion cells safely and effectively, ensuring their longevity and optimal performance.
Part 4. Tips for safe charging of li-ion cells
To ensure the safe charging of Li-ion cells, consider the following tips:
- Use Quality Chargers: Always use chargers recommended by the battery or device manufacturer. Poor-quality chargers may not regulate voltage and current properly, posing safety risks.
- Avoid Overcharging: Do not leave batteries charging unattended for extended periods. Overcharging can lead to overheating, swelling, and potential hazards. Modern chargers often have an automatic shut-off feature to prevent this.
- Monitor Temperature: Charge batteries in a cool, well-ventilated area. Avoid charging in direct sunlight or near heat sources. High temperatures can cause the battery to overheat and potentially fail.
- Inspect Batteries: Before charging, inspect the batteries for any signs of damage, such as cracks, swelling, or leakage. Damaged batteries should not be charged as they pose a significant safety risk.
- Follow Guidelines: Adhere strictly to the manufacturer’s instructions and specifications for charging. This includes recommended voltage, current, and temperature ranges.
By implementing these tips, you can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and ensure that your Li-ion batteries charge safely.
By following this guide, you can ensure that your Li-ion cells are charged safely and effectively, enhancing their performance and longevity while minimizing the risk of accidents. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast or just someone looking to take better care of your devices, understanding the proper way to charge Li-ion batteries is a valuable skill.
Part 5. FAQs
-
Can I use any charger for my Li-ion battery?
No, you should use a charger specifically designed for Li-ion batteries. Using an incompatible charger can result in improper voltage and current regulation, leading to potential safety hazards, including overheating and battery damage. -
How long does it take to charge a Li-ion battery?
The charging time for a Li-ion battery typically ranges from 1 to 4 hours, depending on the battery’s capacity and the charging current. For example, a 2000mAh battery charging at 1C (2000mA) would take about an hour to charge fully. However, charging at a lower current (e.g., 0.5C) would take longer. -
Is it safe to leave Li-ion batteries charging overnight?
It is generally not recommended to leave Li-ion batteries charging overnight or unattended. While many modern chargers have built-in safety features to prevent overcharging, there is still a risk of overheating or other issues. It’s best to monitor the charging process and disconnect the charger once the battery is fully charged. -
What happens if I overcharge a Li-ion battery?
Overcharging a Li-ion battery can lead to several issues, including overheating, swelling, and, in extreme cases, fire or explosion. Overcharging stresses the battery’s internal components, reducing its lifespan and potentially causing it to fail catastrophically. Always use a charger with overcharge protection to mitigate this risk. -
How can I tell if my Li-ion battery is fully charged?
Most chargers will indicate when a Li-ion battery is fully charged. This is often signaled by a change in the LED light color (e.g., from red to green) or the light turning off. Additionally, in the constant voltage phase, when the current drops to a very low level (typically around 0.05C), the battery is considered fully charged.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Aluminum Air Battery Design: Materials, Assembly & Efficiency Tips
An aluminum air battery uses aluminum and air to generate power. Learn its materials, assembly steps, and tips to boost energy output and efficiency.
7 Advantages of a Heated Lithium Battery in Cold Climates
Looking to power batteries in freezing temps? Heated lithium batteries excel in cold climates. Here are 7 key benefits and how they work.
How to Choose the Best Floor Scrubber Battery for Commercial Cleaning?
Selecting the ideal floor scrubber battery ensures a long runtime, rapid charging, and minimal maintenance for efficient commercial cleaning operations.
Battery for Blower vs Battery for Leaf Vacuum: Which One Should You Choose?
Battery for blower vs leaf vacuum—learn the key differences in power, fit, and runtime to choose the right battery for your outdoor tool needs.
How to Choose the Right Battery for Blower?
Choosing the right blower battery? Consider voltage, capacity, chemistry & usage. This guide helps match the best battery for peak performance.