Molten salt battery vs. lithium-ion battery: Which is the best energy storage solution for modern industries? As industries increasingly demand safer, more efficient, and cost-effective power sources, the debate between these two technologies is intensifying. Batteries power everything from smartphones and electric vehicles to grid storage systems. While lithium-ion batteries have long been the market leader due to their high energy density and proven performance, molten salt batteries are now drawing attention for their enhanced safety, lower cost, and better sustainability.
This article will compare molten salt batteries vs. lithium-ion batteries by examining performance, safety, efficiency, cost, and environmental impact. A detailed comparison table, answers to frequently asked questions, and tailored recommendations for various applications will help you determine which battery type best meets your needs.
Part 1. What is a molten salt battery?
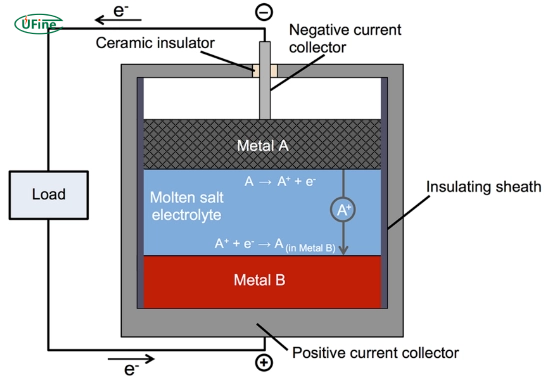
A molten salt battery is a type of rechargeable battery that uses molten salt as an electrolyte instead of the liquid or solid electrolytes found in lithium-ion batteries.
These batteries operate at high temperatures, typically above 200°C (392°F), which keeps the salt in a liquid state. This liquid electrolyte allows ions to move freely, generating electricity.
Molten salt batteries are known for:
- Long lifespan: Can last over 10,000 cycles
- High safety: No risk of fire or explosion
- Low cost: Use abundant and cheap materials
- Good performance in extreme temperatures
Key components of a molten salt battery:
- Anode: Usually made of sodium or magnesium
- Cathode: Often made of metal chlorides or sulfides
- Electrolyte: Molten salt, which allows ion movement
Molten salt batteries are mainly used for grid energy storage and industrial applications. They are not yet used in portable electronics or electric vehicles because of their high operating temperature.
Artikel Terkait: Liquid Metal Battery: Working Principles and Energy Potential
Part 2. What is a lithium-ion battery?
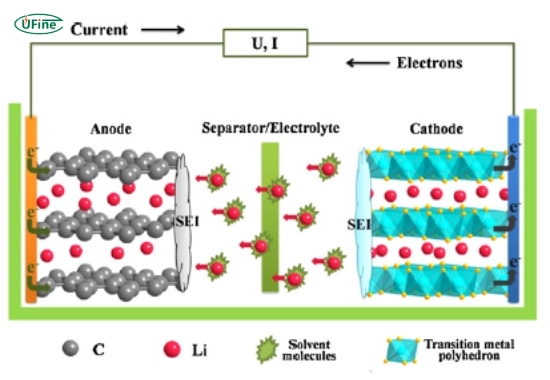
A lithium-ion (Li-ion) battery is a rechargeable battery that stores and releases energy using lithium ions. These batteries are widely used in smartphones, laptops, electric vehicles (EVs), and renewable energy storage.
Key components of a lithium-ion battery:
- Anode: Usually made of graphite
- Cathode: Made of materials like lithium cobalt oxide or lithium iron phosphate
- Electrolyte: A flammable liquid or gel that allows lithium-ion movement
Why are lithium-ion batteries popular?
- High energy density: Can store more energy in a small space
- Fast charging: Can reach 80% charge in under an hour
- Lightweight: Ideal for portable devices and EVs
However, lithium-ion batteries have some disadvantages:
- Fire risk: Can overheat and cause fires (thermal runaway)
- Limited lifespan: Typically lasts 500 to 3,000 cycles
- Expensive materials: Require lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which are costly and complex to mine
Part 3. Quick comparison: Molten salt battery vs. lithium-ion battery
Below is a concise summary of the key differences between molten salt and lithium-ion batteries. This comparison highlights the unique strengths of each technology to help you decide which energy storage solution best fits your needs.
| Feature | Lithium-Ion Battery | Molten Salt Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | 150–250 Wh/kg | 90–150 Wh/kg |
| Cycle Life | 500 – 3,000 cycles | 10,000+ cycles |
| Charging Speed | 30 min – 2 hours | Several hours |
| Fire Risk | High (thermal runaway) | Low (no fire risk) |
| Best Use Cases | EVs, electronics | Grid storage |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Environmental Impact | High (toxic materials) | Low (recyclable materials) |
Summary:
Lithium-ion batteries deliver higher energy density and faster charging, making them ideal for portable electronics and electric vehicles. However, they typically have a shorter cycle life, higher fire risk, and more significant environmental impact. In contrast, molten salt batteries offer a significantly longer cycle life, enhanced safety, lower cost, and better sustainability, positioning them as an attractive option for grid storage applications.
Part 4. Performance comparison: How long do molten salt vs. Lithium-ion batteries last?
Energy density
- Lithium-ion batteries: 150–250 Wh/kg (higher energy density, better for EVs and electronics)
- Molten salt batteries: 90–150 Wh/kg (lower energy density, better for grid storage)
Cycle life (number of charge/discharge cycles before capacity drops)
- Lithium-ion batteries: 500 – 3,000 cycles (varies by type and usage)
- Molten salt batteries: 10,000+ cycles (very long-lasting)
Charging speed
- Lithium-ion batteries: Fast charging (30 min – 2 hours)
- Molten salt batteries: Slower charging (several hours)
Best use cases
- Lithium-ion batteries: Best for portable electronics, EVs, and home battery systems
- Molten salt batteries: Best for large-scale energy storage and industrial applications
Part 5. Safety comparison: Are molten salt batteries safer than lithium-ion batteries?
Fire and explosion risk
- Lithium-ion batteries: Can overheat and cause thermal runaway, leading to fire or explosion
- Molten salt batteries: No risk of fire due to non-flammable electrolyte
Stability in extreme temperatures
- Lithium-ion batteries: Perform poorly in extreme cold or heat
- Molten salt batteries: Work well in extreme temperatures
Toxicity and environmental safety
- Lithium-ion batteries: Contain toxic materials like cobalt and nickel
- Molten salt batteries: Made from non-toxic, abundant materials
Part 6. Efficiency & applications: Real-world uses of molten salt vs. Lithium-ion batteries
Grid energy storage
- Molten salt batteries are ideal for renewable energy storage (solar, wind)
- Lithium-ion batteries are used in home solar systems but degrade faster
Electric vehicles (EVs)
- Lithium-ion batteries are better for EVs due to higher energy density and fast charging.
- Molten salt batteries are unsuitable for EVs because of their large size and high-temperature requirements.
Portable electronics
- Lithium-ion batteries power smartphones, laptops, and cameras
- Molten salt batteries are not used in portable electronics
Part 7. Cost analysis: Which is cheaper – molten salt or lithium-ion batteries?
Production costs
- Lithium-ion batteries: Expensive due to lithium, cobalt, and nickel
- Molten salt batteries: Cheaper because they use abundant materials
Long-term cost efficiency
- Lithium-ion batteries: Need frequent replacements, increasing long-term cost
- Molten salt batteries: Last longer, reducing the overall cost
Part 8. Environmental impact: Sustainability of molten salt vs. Lithium-ion battery technologies
Raw material extraction
- Lithium-ion batteries require lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which cause environmental damage.
- Molten salt batteries use earth-abundant materials, reducing mining impact
Recyclability
- Lithium-ion batteries are difficult to recycle due to complex chemistry
- Molten salt batteries are easier to recycle and have lower environmental impact
Part 9. FAQs about molten salt battery vs. lithium-ion battery
Are molten salt batteries better than lithium-ion batteries?
It depends. Molten salt batteries are safer and last longer, but lithium-ion batteries have higher energy density and faster charging.
Can molten salt batteries replace lithium-ion batteries?
Not entirely. Molten salt batteries are great for grid storage, but lithium-ion batteries are better for EVs and portable electronics.
Why are lithium-ion batteries more common?
They are lightweight, energy-dense, and fast charging, making them ideal for smartphones, laptops, and EVs.
Are molten salt batteries environmentally friendly?
Yes, they use non-toxic materials and are easier to recycle than lithium-ion batteries.
What is the biggest downside of molten salt batteries?
Their high operating temperature makes them unsuitable for portable devices and EVs.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Understanding 9 Volt Battery Capacity: What Do mAh and Voltage Mean?
9V battery capacity affects performance and lifespan. This guide covers mAh, voltage, and key factors to help you choose the best battery.
The Ultimate Guide to Lithium Ion Battery Generators
Lithium-ion battery generators offer lightweight, efficient, quiet power for camping, emergencies, and daily use. Learn how they work and their benefits.
How to Test Battery Capacity for True Ampere-Hours (mAh)?
Learn how to test battery mAh capacity accurately, avoid common mistakes, and understand why real-world results differ from claims. Expert guide inside.
Charging Batteries in Parallel: Safety & Efficiency Guide
Learn if charging batteries in parallel is safe. Discover the right way to do it. Get tips for safe parallel charging to avoid damage!
The Ultimate Guide to a Molten Salt Battery
Molten salt batteries use liquid salts as electrolytes, offering high efficiency, long lifespan, and low cost. Explore their working, benefits, and uses.