When it comes to energy storage, lithium-ion batteries have been the top choice for decades. However, potassium ion batteries are emerging as a new option. These batteries are being researched as a cheaper, safer, and more sustainable alternative. But how do they compare to lithium-ion batteries? Let’s explore the differences and determine which is better for your needs.
Part 1. What is a potassium ion battery?
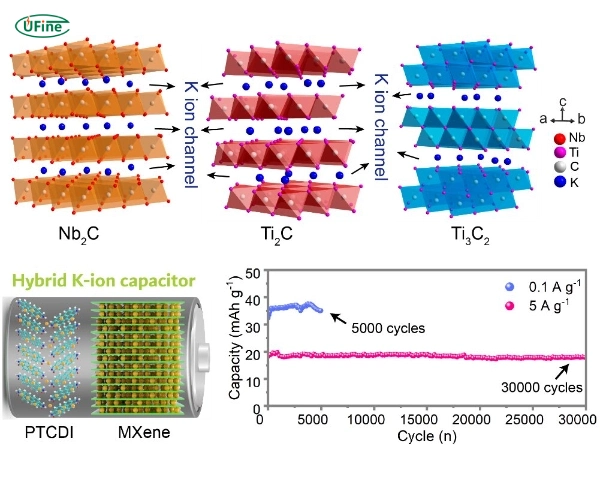
A potassium ion battery (KIB) is a rechargeable battery that stores and releases energy using potassium ions. Potassium ions move between the anode and cathode through an electrolyte, creating electricity.
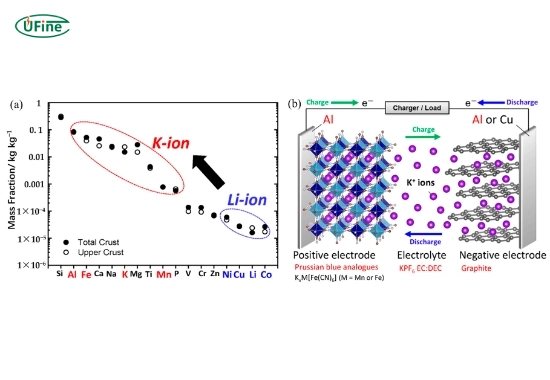
Potassium ion batteries are unique because they use potassium, a cheap, abundant, and widely available material. Scientists are developing these batteries to address rising costs and environmental concerns for lithium-based technologies.
Part 2. How do potassium ion batteries work?
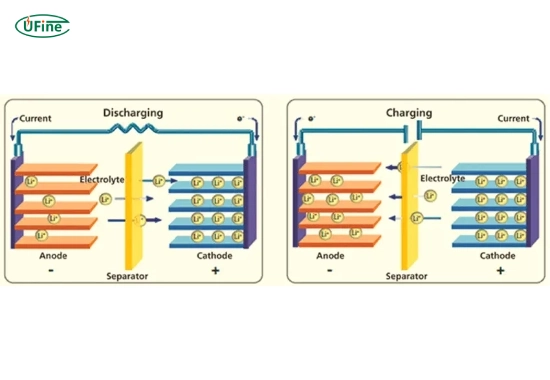
Potassium ion batteries work similarly to lithium-ion batteries. Potassium ions move between the cathode and anode through an electrolyte. During charging, the ions flow to the anode. During discharging, they return to the cathode, releasing energy.
Potassium ions are more significant than lithium ions, which makes them harder to move. This can reduce the battery’s energy density. However, advancements in materials are improving their performance.
Part 3. What is a lithium-ion battery?
A lithium-ion battery (LIB) stores energy by moving lithium ions between the cathode and anode during charging and discharging. These batteries are known for their high energy density, meaning they can store much energy in a small space.
Lithium-ion batteries are widely used in electronics, electric cars, and renewable energy systems. However, they have some challenges, such as high costs, limited lithium supply, and safety risks like overheating.
Part 4. How do lithium-ion batteries work?
Lithium-ion batteries also move ions between the cathode and anode. Lithium is a very light and small element, which allows these batteries to store a high amount of energy in a compact size.
Despite their high efficiency, lithium-ion batteries can overheat, which poses safety risks. Additionally, their reliance on rare and expensive materials, like cobalt, makes them less sustainable.
Part 5. Key differences between potassium ion batteries and lithium-ion batteries
Potassium ion batteries and lithium-ion batteries have some significant differences. Here is an easy-to-read breakdown of their key distinctions:
- Materials and cost: Potassium is one of the most abundant elements on Earth, making potassium ion batteries potentially cheaper to produce. Lithium, on the other hand, is a limited resource. Due to high demand, the cost of lithium has increased significantly in recent years.
- Energy density: Lithium-ion batteries have a higher energy density, meaning they can store more energy in a smaller size. This makes them ideal for portable devices like smartphones and laptops. Potassium ion batteries, however, have a lower energy density, which means they are better suited for large-scale applications like grid energy storage.
- Safety: Potassium ion batteries are safer because they are less prone to overheating and thermal runaway. Lithium-ion batteries can overheat, which can lead to fires or explosions.
- Environmental impact: Potassium ion batteries are more sustainable because they use widely available materials and are easier to recycle. Lithium-ion batteries rely on mining rare metals like cobalt, which has environmental and ethical concerns.
- Lifespan and performance: Lithium-ion batteries are proven to have a long lifespan and stable performance. Potassium ion batteries are still developing, so their lifespan is not yet fully understood.
Here is a simple table to summarize the differences:
| Feature | Potassium Ion Battery | Lithium-Ion Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Material availability | Potassium is abundant and low-cost. | Lithium is limited and expensive. |
| Energy density | Lower energy density, suitable for large systems. | High energy density, ideal for small devices. |
| Safety | Less risk of overheating or fire. | It can overheat, leading to safety concerns. |
| Cost | Cheaper materials make it cost-effective. | It is expensive due to rare materials. |
| Environmental impact | More sustainable, easy to recycle. | Environmental concerns due to mining. |
| Technology maturity | Still under development. | Proven and widely used. |
Part 6. Advantages of potassium ion batteries
- Low cost: The materials used in potassium ion batteries, like potassium, are cheap and widely available, which could make them much more affordable than lithium-ion batteries.
- Abundant materials: Potassium is one of the most common elements, so there’s no fear of shortages.
- Safety: Potassium ion batteries are less prone to overheating, making them safer for large-scale applications.
- Eco-friendly: Since potassium is easy to mine and recycle, these batteries have a lower environmental impact.
Part 7. Advantages of lithium-ion batteries
- High energy density: Lithium-ion batteries can store more energy in a smaller space, making them ideal for portable electronics.
- Proven performance: These batteries have been used for decades and are reliable for many applications.
- Long lifespan: Lithium-ion batteries can last thousands of charge cycles with minimal degradation.
- Wide availability: They are commercially available and used in many industries.
Part 8. Applications of potassium ion batteries
Potassium ion batteries are still in development, but they have potential for several applications:
- Grid energy storage: Their lower cost makes them ideal for large-scale energy storage, such as solar or wind power storage.
- Renewable energy systems: They can help provide backup power for renewable energy sources.
- Low-energy devices: These batteries could be used in devices that don’t require high energy density.
Part 9. Applications of lithium-ion batteries
Lithium-ion batteries dominate the market and are used in many applications:
- Consumer electronics: Smartphones, laptops, and tablets rely on lithium-ion batteries for portability and long battery life.
- Electric vehicles (EVs): EVs like Tesla cars use lithium-ion technology for high energy density and extended driving ranges.
- Renewable energy: Lithium-ion batteries are widely used to store energy from solar panels and wind turbines.
- Medical devices: Portable medical devices, like pacemakers and defibrillators, depend on lithium-ion batteries.
Part 10. Which battery is better for your application?
The right battery depends on your needs:
- Choose potassium ion batteries if you need a low-cost, eco-friendly solution for large-scale energy storage. These batteries are ideal for grid storage and renewable energy systems.
- Choose lithium-ion batteries if you need a compact, high-energy solution for portable devices, electric vehicles, or medical equipment.
Part 11. FAQs
-
What is the most significant advantage of a potassium ion battery?
The most significant advantage is its low cost and abundant materials, making it a sustainable and affordable alternative to lithium-ion batteries. -
Are potassium-ion batteries safer than lithium-ion batteries?
Potassium ion batteries are safer because they are less likely to overheat or catch fire. -
Why are lithium-ion batteries more commonly used?
Lithium-ion batteries are popular because they have high energy density, a long lifespan, and are a proven technology with established supply chains. -
Can potassium ion batteries replace lithium-ion batteries?
Potassium ion batteries have the potential to replace lithium-ion batteries in some applications, especially where cost and sustainability are more important than energy density. However, the technology is still under development. -
Which battery is better for renewable energy storage?
Potassium ion batteries could be better for renewable energy storage in the future due to their lower cost and environmental benefits. However, lithium-ion batteries are currently the standard for this application.
Related Tags:
More Articles

How to Choose the Best Floor Scrubber Battery for Commercial Cleaning?
Selecting the ideal floor scrubber battery ensures a long runtime, rapid charging, and minimal maintenance for efficient commercial cleaning operations.
Battery for Blower vs Battery for Leaf Vacuum: Which One Should You Choose?
Battery for blower vs leaf vacuum—learn the key differences in power, fit, and runtime to choose the right battery for your outdoor tool needs.
How to Choose the Right Battery for Blower?
Choosing the right blower battery? Consider voltage, capacity, chemistry & usage. This guide helps match the best battery for peak performance.
How to Choose the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries?
Choosing the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries? Discover key factors such as size, material, and safety for optimal protection and performance.
7 Critical Elements on a Lithium Battery Shipping Label
What must be on a lithium battery shipping label? Learn 7 key elements to ensure safety, legal compliance, and correct handling across all transport modes.