Looking to understand what a pouch cell is? You’re in the right place. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know about pouch cells, from their structure and advantages to their applications and safety.
Let’s dive in!
Part 1. What is a pouch cell?
A pouch cell is a type of rechargeable battery. It gets its name from its packaging, which looks like a flat, flexible pouch. Unlike cylindrical and prismatic batteries, pouch cells are lightweight and can be shaped to fit various devices. This flexibility makes them a popular choice for modern technology, especially where space and weight are critical factors.
Pouch cells are widely used in everything from consumer electronics to electric vehicles. Their unique design allows efficient energy storage while maintaining a compact and lightweight form. This makes them ideal for various applications where traditional battery shapes might not fit or would add unnecessary weight.
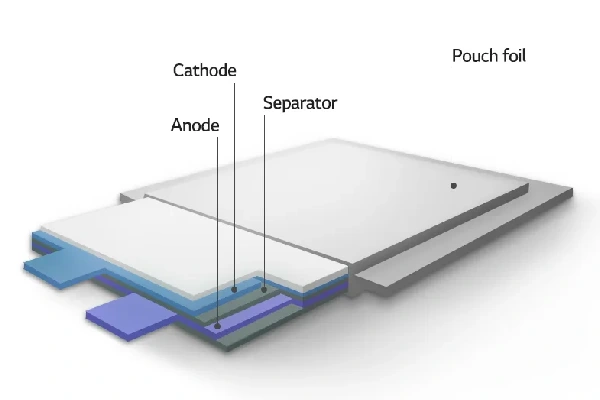
Part 2. Pouch cell structure composition
Pouch cells have a unique structure. Here’s a breakdown of their main components:
- Anode: The anode is usually made of graphite. It is the negative electrode during discharge, where lithium ions are stored.
- Cathode: The cathode is often composed of lithium metal oxides, such as lithium cobalt oxide (LCO), lithium iron phosphate (LFP), or lithium nickel manganese cobalt oxide (NMC). It acts as the positive electrode during discharge.
- Separator: A thin, porous membrane that separates the anode and cathode. This prevents short circuits while allowing ions to pass through.
- Electrolyte: A liquid or gel that facilitates the movement of lithium ions between the anode and cathode. Common electrolytes include lithium salts dissolved in organic solvents.
- Pouch: The outer casing is laminated aluminum foil. This flexible packaging holds all the internal components together and provides some degree of protection.
The pouch cell design allows for a high degree of flexibility in terms of shape and size. This is a significant advantage over rigid battery formats, which can be more challenging to integrate into compact or uniquely shaped devices.
Part 3. Pouch cell advantages and disadvantages
Advantages
- Lightweight: Pouch cells are lighter than cylindrical and prismatic batteries, making them ideal for portable devices and applications where weight is critical.
- Flexible Shape: The flexible packaging allows pouch cells to be molded to fit specific spaces within a device, maximizing space efficiency.
- High Energy Density: Pouch cells can store more energy in a smaller volume compared to other battery types, providing longer battery life for devices.
- Safety: Pouch cells have a lower risk of leaking than cylindrical batteries, thanks to their sealed design.
Disadvantages
- Durability: The flexible pouch can be more prone to physical damage compared to the rigid casings of cylindrical and prismatic batteries.
- Cost: Pouch cells are generally more expensive to manufacture, making them costlier for end users.
- Thermal Management: Managing heat in pouch cells can be more challenging due to their flexible packaging, which does not dissipate heat as effectively as metal casings.
Part 4. Cylindrical battery vs. pouch cell vs. prismatic battery
Cylindrical batteries are known for their robustness and ease of manufacturing, making them a cost-effective option. However, they are limited by their shape and weight. Prismatic batteries offer a compromise with a more flexible shape than cylindrical batteries and better structural integrity than pouch cells. Pouch cells, on the other hand, excel in applications where weight and space are at a premium despite their higher cost and potential thermal management challenges.
| Feature | Cylindrical Battery | Pouch Cell | Prismatic Battery |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shape | Cylindrical | Flat and flexible | Rectangular |
| Energy Density | Moderate | High | Moderate |
| Cost | Lower | Higher | Moderate |
| Thermal Management | Easier | Harder | Moderate |
| Durability | High | Moderate | High |
| Weight | Heavier | Lightest | Heavier |
Part 5. Pouch cell price
Pouch cell prices can vary depending on the capacity, quality, and manufacturer.
On average, they range from $5 to $15 per cell. Higher-capacity cells, which store more energy and provide longer battery life, are more expensive. Prices can also fluctuate based on market demand, advancements in technology, and the cost of raw materials.
For instance, a high-capacity pouch cell in electric vehicles might cost significantly more than a smaller cell in consumer electronics. As technology advances and production scales up, we can expect prices to gradually decrease, making pouch cells even more accessible for various applications.
Part 6. Where is the pouch cell used?
Pouch cells are versatile and find applications in numerous fields:
- Consumer Electronics: They power smartphones, tablets, laptops, and wearable devices due to their lightweight and compact form.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): Pouch cells are used in EVs for their high energy density and ability to be shaped to fit the vehicle’s design.
- Medical Devices: Portable medical devices, such as defibrillators and infusion pumps, often use pouch cells for their reliability and lightweight characteristics.
- Drones: Pouch cells’ lightweight and high energy density makes them ideal for drones, providing longer flight times.
- Energy Storage Systems: Used in renewable energy storage solutions, pouch cells help store energy from solar panels and wind turbines.
Part 7. How long is the life of the pouch cell?
The lifespan of a pouch cell can vary based on usage patterns, charging habits, and the quality of the cell. Typically, pouch cells last between 500 to 1000 charge cycles. If you charge your device daily, a pouch cell could last 1.5 to 3 years. Proper care, such as avoiding extreme temperatures and not overcharging, can help extend the lifespan of pouch cells.
Part 8. Is the pouch cell safe?
Pouch cells are generally safe when used correctly. They incorporate several safety features to prevent overcharging, overheating, and short-circuiting. The flexible pouch design also reduces the risk of electrolyte leakage. However, they must be handled carefully to avoid punctures or damage to the pouch, which could lead to safety hazards.
Manufacturers also implement rigorous testing and safety standards to ensure the reliability of pouch cells. Pouch cells provide a safe and efficient power source for various applications when used within their specified guidelines.
With this enriched guide, you now understand pouch cells comprehensively. Whether you’re considering them for a specific project or just curious about their capabilities, this information equips you with the knowledge to make informed decisions.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Paper Battery vs. Flexible Battery: What’s the Difference and Which Is Better?
Paper vs. flexible batteries: learn the key differences, benefits, and which power source fits best for wearables, sensors, and smart tech.
What to Know Before Buying a Tiny LiPo Battery for Your Project
Tiny LiPo batteries are powerful and compact. Learn how to choose the right one for your project with specs, safety, and charging tips.
Bloated LiPo Battery: Will It Explode?
Will a bloated LiPo battery explode? Discover the causes, risks, safety steps, and expert tips to avoid disaster and protect your gear. Must-read safety guide!
12V 100Ah Lithium Ion Battery Price: Full Guide
Learn about 12V 100Ah lithium-ion battery price, from cost ranges to best brands, hidden fees, and how to get the best deal. A must-read for smart buyers!
Resistance and Conductivity: What It Means for Your Lithium Batteries
Resistance and conductivity impact lithium battery performance, lifespan, and safety—learn how they work and why they matter.