- Part 1. 5 Types of lithium battery charging methods: CC, CV, CC-CV, CP, CP-CV
- Part 2. 7 Types of lithium battery discharging methods: CC, CV, CC-CV, CP, CP-CC-CV, CR, CR-CV
- Part 3. The most common charging method of lithium batteries
- Part 4. How to choose the charging and discharging method of lithium batteries?
- Part 5. FAQs
Part 1. 5 Types of lithium battery charging methods: CC, CV, CC-CV, CP, CP-CV
In addition to the CC-CV charging method required by the standard, lithium batteries can also be charged by CC, CV, CP, CP-CV, etc.
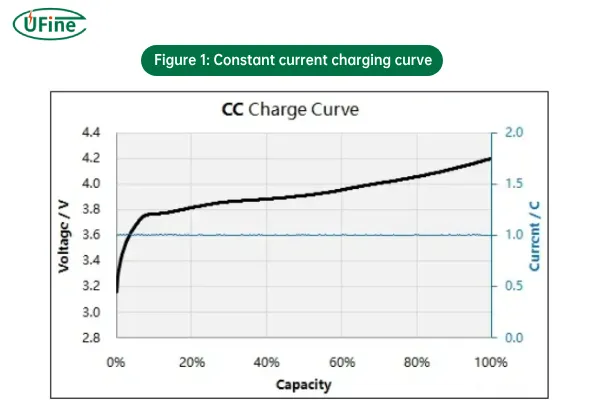
1. Constant Current (CC) Charging
Constant Current (CC) charging refers to the phase of the charging process where the current is kept constant while the battery voltage gradually increases. This method is typically used in the initial phase of charging a lithium-ion battery.
- How it works: The charger applies a fixed current to the battery, and as the battery charges, its voltage rises. The charging process continues at this constant current until the battery reaches its maximum voltage (usually 4.2V for lithium-ion batteries).
- Why it’s used: CC charging is effective for the bulk charging stage because it provides a steady flow of current, ensuring the battery gains charge efficiently.
- Risks: If used for too long or if the battery reaches maximum voltage without switching to CV, it can cause overcharging, overheating, or battery damage.
Figure 1: Constant current charging curve
How to Read Lithium Battery Discharge Curve and Charging Curve?
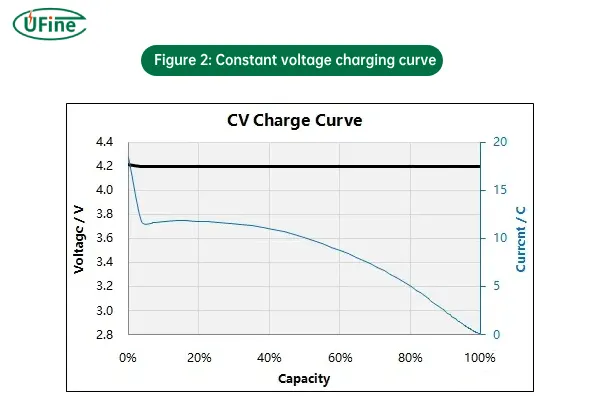
2. Constant Voltage (CV) Charging
Constant Voltage (CV) charging happens once the battery reaches its maximum voltage, typically after the CC stage. In this mode, the charging system switches to maintaining a constant voltage while the current gradually decreases.
- How it works: Once the battery reaches its full voltage (typically 4.2V for lithium-ion batteries), the charger switches to maintaining that voltage. As the battery nears full capacity, the current begins to decrease, preventing the battery from being overcharged.
- Why it’s used: CV charging is necessary to prevent overcharging and ensure the battery isn’t damaged. Lithium-ion batteries cannot be charged indefinitely at constant current, and the voltage must be held steady to prevent overheating or degradation.
- Risks: Without CV charging, the battery could be exposed to excess current at full charge, risking damage.
Figure 2: Constant voltage charging curve
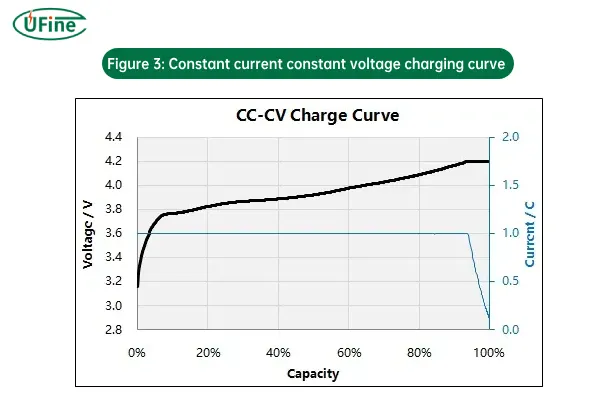
3. CC-CV (Constant Current – Constant Voltage) Charging
CC-CV is a combination of the two methods above and is the standard charging process for most lithium-ion batteries. It uses both constant current and constant voltage phases in sequence.
- How it works:
- CC phase: The charger applies a constant current to the battery, causing the voltage to rise.
- CV phase: Once the battery reaches its full voltage (4.2V), the charger switches to constant voltage mode and reduces the current.
- Why it’s used: This method is used to ensure both fast charging and safe termination. The CC phase efficiently charges the battery to a certain voltage, while the CV phase prevents overcharging and keeps the battery from being damaged.
- Risks: The risk is minimal when CC-CV is followed correctly, but failure to transition properly between the CC and CV phases could result in battery damage, especially if the current doesn’t decrease in the CV phase.
Figure 3: Constant current constant voltage charging curve
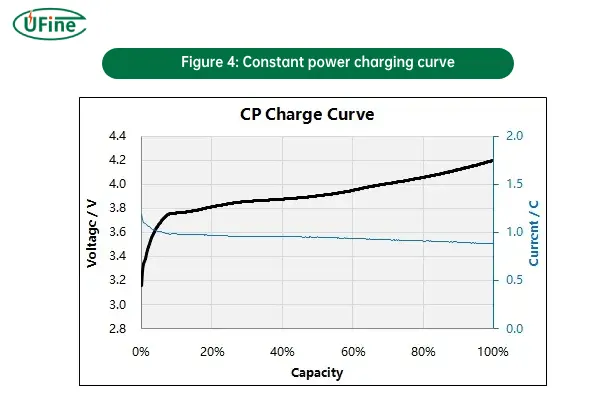
4. Constant Power (CP) Charging
Constant Power (CP) charging involves delivering a fixed amount of power to the battery, where both current and voltage adjust to maintain the target power output.
- How it works: The charger dynamically adjusts both current and voltage to ensure that a constant power level (measured in watts) is delivered to the battery throughout the charging process. This method can be particularly useful when the battery’s voltage and current need to be optimized together for power-based applications.
- Why it’s used: CP charging is less common but can be used in applications requiring steady power delivery, like certain types of energy storage systems or high-power devices.
- Risks: One challenge of CP charging is ensuring that both the current and voltage stay within safe limits for the battery. Excessive current or voltage could damage the battery if not controlled carefully.
Figure 4: Constant power charging curve
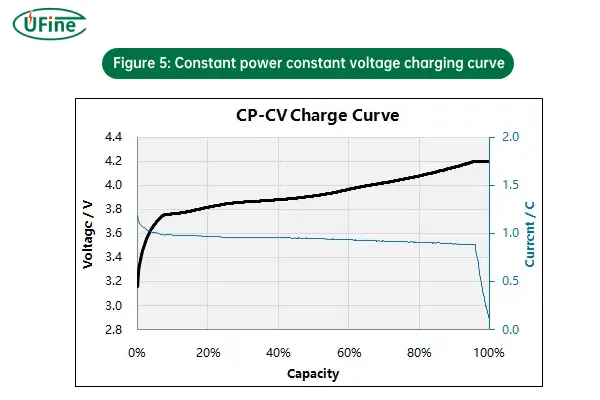
5. CP-CV (Constant Power – Constant Voltage) Charging
CP-CV is a hybrid charging method that begins with constant power (CP) charging and then switches to constant voltage (CV) charging as the battery approaches full charge.
- How it works:
- CP phase: Initially, the charger applies constant power, adjusting both current and voltage to maintain the desired power output.
- CV phase: As the battery reaches its voltage limit, the charger switches to constant voltage mode and reduces the current to prevent overcharging.
- Why it’s used: CP-CV charging is useful for applications where maintaining a fixed power input is critical, such as in some industrial or renewable energy systems. The shift to CV ensures that the battery isn’t overcharged.
- Risks: As with CP charging, there’s a risk of exceeding safe current or voltage limits if the transition between power-based charging and voltage-based charging isn’t well managed.
Figure 5: Constant power constant voltage charging curve
Part 2. 7 Types of lithium battery discharging methods: CC, CV, CC-CV, CP, CP-CC-CV, CR, CR-CV
In addition to the CC discharge method required by the standard, lithium batteries can also be discharged by CV, CC-CV, CP, CP-CC-CV, CR, CR-CV, etc.
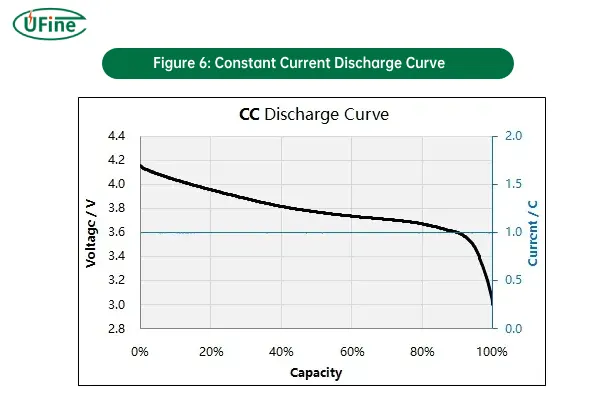
1. Constant Current (CC) Discharging
Constant Current (CC) discharging involves discharging the battery at a fixed current, regardless of the voltage drop as the battery discharges.
- How it works: During CC discharging, the battery’s current output remains constant. As the battery discharges, the voltage gradually decreases. This method is typically used in applications where a consistent current is required from the battery, and the device is designed to handle the drop in voltage.
- Why it’s used: CC discharging is useful in systems where stable current is critical, such as power supplies, testing devices, or energy storage systems that need consistent performance.
- Risks: If the battery discharges too deeply, it may lead to over-discharge, which can damage the battery and reduce its lifespan.
Figure 6: Constant Current Discharge Curve
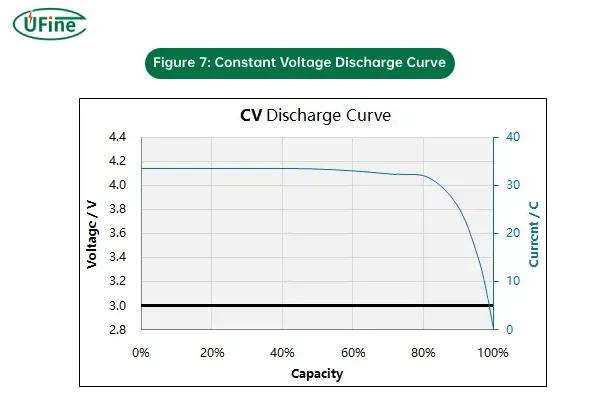
2. Constant Voltage (CV) Discharging
Constant Voltage (CV) discharging is a method where the battery voltage is held constant while the current decreases as the battery discharges.
- How it works: In this method, the voltage remains steady while the current gradually drops. This approach is typically used when maintaining a stable voltage output is more important than the rate at which the battery discharges.
- Why it’s used: CV discharging is used in applications where the device or circuit requires a consistent voltage for a period of time, regardless of the battery’s state of charge.
- Risks: If not carefully managed, holding the voltage constant could lead to the battery being excessively drained, which may damage the cells or reduce capacity over time.
Figure 7: Constant Voltage Discharge Curve
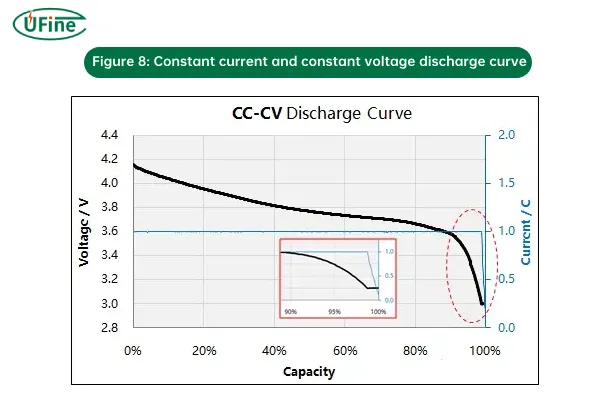
3. CC-CV (Constant Current – Constant Voltage) Discharging
CC-CV discharging combines constant current and constant voltage phases. Initially, the battery discharges at a constant current until the voltage reaches a pre-defined threshold, after which the voltage is held constant, and the current decreases.
How it works:
- CC phase: The battery discharges at a fixed current, and its voltage gradually drops.
- CV phase: Once the voltage limit is reached, the current starts to decrease, and the voltage is maintained at a steady value.
- Why it’s used: CC-CV discharging is commonly used in systems that require a stable output voltage or where the device can handle both constant current and constant voltage stages. It helps prevent deep discharge and maintains performance during the discharge cycle.
- Risks: If the transition from CC to CV is not done properly, there could be issues with over-discharge or inefficiency.
Figure 8: Constant current and constant voltage discharge curve
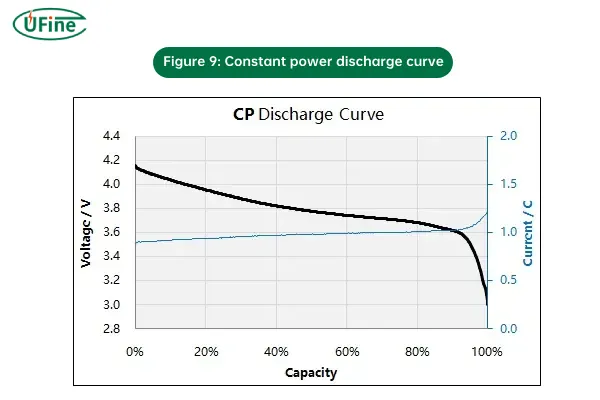
4. Constant Power (CP) Discharging
Constant Power (CP) discharging is a method where the power output (measured in watts) is kept constant while the current and voltage adjust dynamically to meet the power demand.
- How it works: During CP discharging, the battery maintains a constant power level, meaning that the current and voltage are adjusted as needed to keep the power output steady. This method is typically used in applications where a constant power consumption is critical, such as in certain energy storage systems or power electronics.
- Why it’s used: CP discharging is ideal for scenarios where power output is the primary concern, and the system needs to maintain consistent energy delivery, despite variations in battery voltage.
- Risks: Since the current and voltage can fluctuate, it may lead to less efficient discharge or cause issues with voltage limits, potentially resulting in over-discharge or excessive battery strain.
Figure 9: Constant power discharge curve
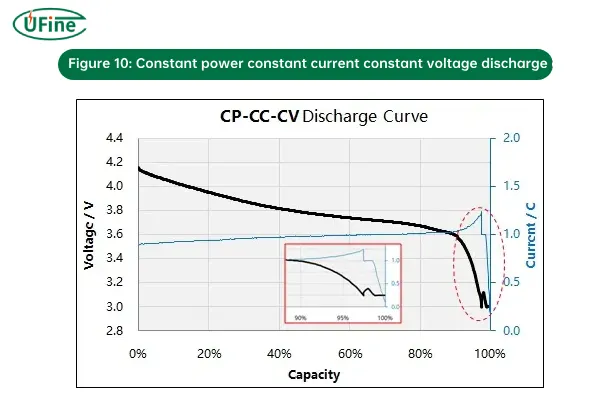
5. CP-CC-CV (Constant Power – Constant Current – Constant Voltage) Discharging
CP-CC-CV discharging is a more advanced and hybrid approach that integrates constant power, constant current, and constant voltage phases during the discharge cycle.
- How it works:
- CP phase: The battery discharges at a fixed power output, with the current and voltage dynamically adjusting.
- CC phase: As the battery voltage drops, the current is maintained constant for a period.
- CV phase: Once the voltage limit is reached, the voltage is held constant, and the current decreases.
- Why it’s used: This method is particularly useful in systems where power needs to be delivered at a stable rate throughout the discharge process, while ensuring the battery voltage and current stay within safe limits as it approaches depletion.
- Risks: The complexity of managing three phases can make this method more difficult to implement, and improper transitions between phases can lead to over-discharge or inefficiency.
Figure 10: Constant power constant current constant voltage discharge curve
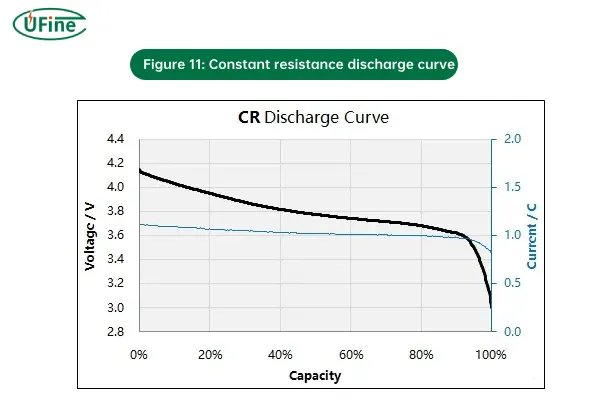
6. Constant Resistance (CR) Discharging
Constant Resistance (CR) discharging involves discharging the battery through a fixed resistance. The current varies depending on the battery voltage, but the load resistance remains constant throughout the discharge.
- How it works: The battery is connected to a resistor with a fixed resistance value. As the battery discharges, the voltage decreases, causing the current to drop according to Ohm’s law (I = V/R). The resistance is kept constant, but the current will decrease as the voltage decreases.
- Why it’s used: CR discharging is often used for testing the battery’s behavior under different load conditions. It helps simulate real-world usage scenarios where devices operate at a fixed resistance, like some sensors or small electronic gadgets.
- Risks: The primary concern with CR discharging is that the battery can discharge too quickly if the load is too low, leading to potential over-discharge. Additionally, managing constant resistance for certain applications might not be efficient enough for optimal battery performance.
Figure 11: Constant resistance discharge curve
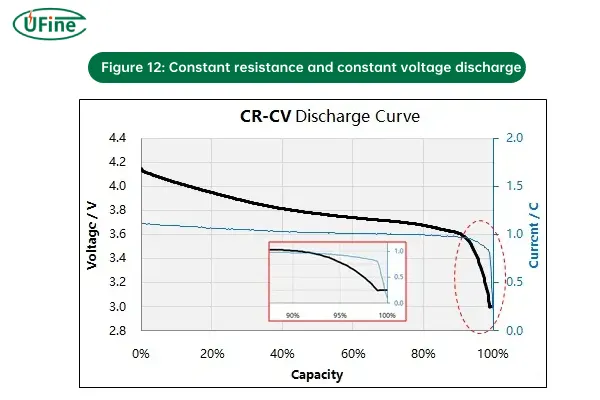
7. CR-CV (Constant Resistance – Constant Voltage) Discharging
CR-CV discharging combines constant resistance with a constant voltage phase. Initially, the battery discharges through a fixed resistance, but once the voltage reaches a certain point, the voltage is held constant, and the current decreases.
- How it works:
- CR phase: The battery discharges through a constant resistance, and as the voltage decreases, the current also drops.
- CV phase: Once the voltage reaches a pre-defined threshold, the charging system switches to constant voltage mode, where the voltage is kept steady, and the current decreases.
- Why it’s used: This method is used when both the load conditions (constant resistance) and battery protection (constant voltage) need to be managed together. It is especially useful in battery testing and some low-power applications.
- Risks: Similar to other discharging methods, improper transition from CR to CV phases could lead to over-discharge, especially if the resistance is too low or the battery is not designed to handle it.
Figure 12: Constant resistance and constant voltage discharge curve
Part 3. The most common charging method of lithium batteries
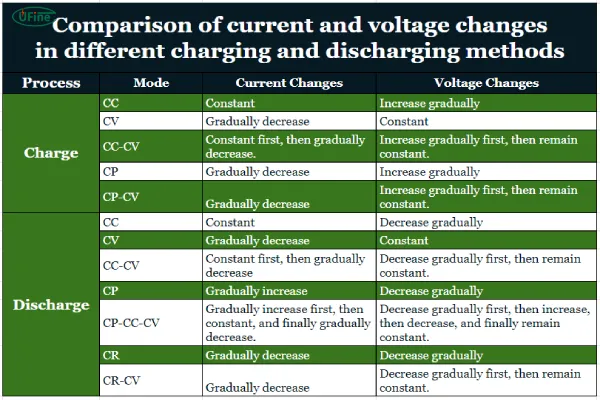
In summary, the charging and discharging methods of lithium batteries are diverse, but in the final analysis, they are single-step or combined processes based on CC (constant current), CV (constant voltage), CP (constant power) or CR (constant resistance). The current and voltage changes of these charging and discharging methods are shown in the table below.
Comparison of current and voltage changes in different charging and discharging methods table
At present, the mainstream charging method of lithium batteries is still mainly CC-CV.
This is because lithium batteries have polarization phenomenon (that is, the instant voltage is not a steady-state voltage). In the CC stage, the current is large and the charging speed is fast. After the voltage rises to the upper limit voltage, it maintains a constant potential. The electrons in the external circuit react with Li+ at the negative electrode.
As the negative electrode inserts lithium, the active sites decrease, the number of electrons participating in the reaction decreases, and the current gradually decreases. When the current is reduced to 0 (ideal situation), the polarization is completely eliminated and the lithium battery is fully charged.
However, during the discharge process, lithium batteries usually use CC mode, which may be to make it easier to calculate capacity or estimate SOC. In actual working conditions, constant power discharge is mostly used.
Part 4. How to choose the charging and discharging method of lithium batteries?
The selection of lithium battery charging and discharging methods should take into account the convenience of data processing, charging/discharging efficiency, and the risk of internal damage to lithium batteries. It is necessary to give full play to the performance of lithium batteries and to conduct fast and accurate detection.
At present, lithium batteries are mainly tested in CC-CV charging mode and CC discharge mode, but in actual terminal use conditions, CP mode is the main mode.
Part 5. FAQs
-
What is the difference between CC and CV charging methods?
The main difference between CC and CV charging methods lies in how the current and voltage are managed: In CC mode, the charging current is kept constant, and the voltage rises. In CV mode, once the voltage limit is reached, the current is reduced, and the voltage stays constant. The two methods work together in the CC-CV charging process, which ensures efficient and safe charging of lithium batteries. -
How does CC-CV charging protect the lithium-ion battery from overcharging?
The CC-CV charging process protects lithium-ion batteries from overcharging by first applying a constant current until the battery reaches its maximum voltage (typically 4.2V). Once this voltage limit is reached, the charger switches to constant voltage mode, reducing the charging current. This prevents the battery from receiving excessive current, which could otherwise cause overheating, battery swelling, or even thermal runaway. -
What happens if you use constant current charging for too long?
If constant current charging is used for too long without switching to constant voltage, the battery could be overcharged, which can damage the battery cells. This can result in overheating, capacity loss, and even dangerous conditions like battery swelling or thermal runaway. That’s why the transition to constant voltage (CV) is essential in ensuring the battery is safely charged and protected from damage. -
When should you use CP or CP-CV charging methods for lithium batteries?
CP and CP-CV charging methods are typically used in specific applications where power rather than current or voltage needs to be carefully regulated. For example, CP charging might be used in high-power applications like electric vehicles or renewable energy storage systems where a consistent power output is necessary to optimize battery efficiency. CP-CV charging would then take over once the battery approaches full charge to ensure voltage does not exceed the battery’s safe limit. -
Can a lithium battery be damaged by using the wrong charging method?
Yes, using the wrong charging method can damage a lithium battery. For instance, using constant current (CC) without transitioning to constant voltage (CV) can overcharge the battery, potentially causing overheating or thermal runaway. Similarly, using constant power (CP) charging without proper regulation can lead to excessive current or voltage being applied, which may degrade the battery’s lifespan or cause it to fail prematurely. Always follow the manufacturer’s recommended charging method for optimal performance and safety.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Battery Load Test: A Comprehensive Guide
Step-by-step battery load test guide for car, solar & industrial use. Learn how to load test a battery, interpret voltage charts, and avoid common mistakes.
The Comprehensive Guide to Battery Balancing and Battery Balancer
Discover how battery balancers improve lithium battery performance, lifespan, and safety. Learn types, functions, and tips to choose the right balancer.
What Is the Best Voltage for a Chainsaw Battery?
Compare 12V-80V chainsaw batteries for light pruning, medium firewood, and professional cutting. See best battery chainsaw with runtime charts and safety tips.
Lithium VS. Alkaline Batteries: A Comprehensive Comparison
Lithium batteries last 3–7× longer than alkaline and perform better in cold weather. Compare lifespan, cost, safety, and best uses to choose the right battery.
Comparing Lithium-Sulfur and Lithium-Ion Batteries: Which is Right for You?
Compare lithium-sulfur (Li-S) and lithium-ion batteries on energy, lifespan, cost, safety, and applications. Best choice for drones, EVs, and electronics.