Integrating PV (photovoltaic) battery storage systems into residential and commercial setups is becoming increasingly important as the world shifts towards more sustainable energy solutions. These systems enhance energy efficiency and significantly reduce electricity costs and environmental impacts. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about PV battery storage, from its fundamentals to its future potential.
Part 1. What is PV battery storage?
PV battery storage systems are designed to store the electricity generated by solar panels for later use. This capability is crucial for maximizing the benefits of solar energy, especially when the sun isn’t shining. By storing excess energy, these systems ensure a continuous power supply, making solar energy a more reliable and practical option.
Part 2. The basics of photovoltaic systems
Before diving into the specifics of PV battery storage, let’s briefly cover the basics of photovoltaic systems. Photovoltaic (PV) systems convert sunlight directly into electricity using solar panels. These panels comprise many solar cells, typically made from silicon, which generate electric current when exposed to sunlight.
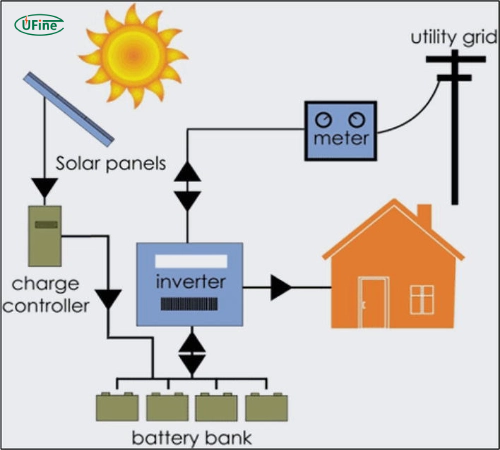
Part 3. How does PV battery storage work?
PV battery storage systems capture and store the excess electricity solar panels produce. Here’s a simplified breakdown of the process:
- Solar Panels Generate Electricity: During the day, solar panels convert sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity.
- Conversion to Alternating Current: An inverter converts DC electricity to alternating current (AC), which home appliances can use.
- Storing Excess Energy: Any surplus electricity is directed to the batteries for storage.
- Using Stored Energy: When solar panels aren’t producing enough electricity (e.g., at night or during cloudy days), the stored energy is released from the batteries to power the home.
Part 4. Types of PV batteries
There are several types of batteries used in PV storage systems, each with its advantages and disadvantages:
Lead-Acid Batteries
Lead-acid batteries are one of the oldest and most established types of rechargeable batteries. They are relatively inexpensive and widely available but have a shorter lifespan and lower energy density than newer technologies.
Lithium-ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries are currently the most popular choice for PV storage systems. They offer high energy density, longer lifespan, and better efficiency. However, they are more expensive than lead-acid batteries.
Flow Batteries
Flow batteries are a newer technology that stores energy in liquid electrolytes. They offer the advantage of scalability and long cycle life. Still, they are generally more expensive and less compact than lithium-ion batteries.
Part 5. Benefits of PV battery storage
PV battery storage systems offer numerous benefits that make them an attractive option for both homeowners and businesses:
1. Energy Independence
By storing excess solar energy, you can significantly reduce your dependence on the grid. This lowers your electricity bills and provides a reliable power source during outages.
2. Environmental Impact
Using stored solar energy reduces the need for electricity generated from fossil fuels, thus lowering your carbon footprint and contributing to a cleaner environment.
3. Cost Savings
Although the initial investment in PV battery storage can be high, the long-term savings on electricity bills can be substantial. Additionally, many regions offer incentives and rebates for installing solar energy systems.
4. Enhanced Grid Stability
On a larger scale, PV battery storage systems can help stabilize the grid by reducing peak demand and providing backup power during outages.
Part 6. Critical considerations for installing PV battery storage
When considering a PV battery storage system, several factors should be taken into account to ensure you make the best decision for your needs:
System Size and Capacity
Your PV battery storage system’s size and capacity should match your energy consumption patterns. This involves calculating your average daily energy usage and determining how much storage you need to cover periods when solar generation is low.
Battery Lifespan and Warranty
Different battery types come with varying lifespans and warranties. It’s essential to consider the battery’s expected lifespan and the warranty offered by the manufacturer to ensure long-term reliability and performance.
Installation and Maintenance Costs
While the cost of the battery itself is a significant factor, you should also consider the installation and ongoing maintenance costs. Professional installation is crucial for ensuring the system operates efficiently and safely.
Local Incentives and Regulations
Many regions offer incentives, rebates, and tax credits for installing PV battery storage systems. Researching and taking advantage of these opportunities is essential to reduce investment costs.
Part 7. PV battery storage case studies
Examining real-world examples of successful PV battery storage implementations can provide valuable insights and inspiration:
Residential Setup in California
A homeowner in California installed a PV battery storage system to reduce their electricity bills and ensure a reliable power supply during frequent outages. The system has met their energy needs and provided significant cost savings and environmental benefits.
Commercial Installation in Germany
A commercial building in Germany integrated a large-scale PV battery storage system to manage its energy consumption more efficiently. The system has helped the business reduce peak demand charges, lower electricity costs, and contribute to the country’s renewable energy goals.
Community Microgrid in Australia
An Australian community developed a microgrid with PV battery storage to enhance energy resilience and reduce reliance on the national grid. The project has improved local energy security and demonstrated the potential of community-based renewable energy solutions.
Part 8. FAQs
-
Is it worth getting a battery with PV panels?
Yes, a battery with PV panels allows you to store excess energy for use at night or during power outages, increasing your energy independence and savings. -
What are the three drawbacks to storing solar energy in batteries?
The main drawbacks are high initial and maintenance costs, a limited lifespan requiring replacements, and energy loss during charging and discharging. -
Are PV panels better than solar panels?
PV panels (photovoltaic) convert sunlight directly into electricity and are versatile. Solar thermal panels are more efficient for heating water but have limited applications. -
What is the best battery for PV panels?
Lithium-ion batteries are the best due to their high efficiency and long lifespan. However, lead-acid and flow batteries are also good options for specific needs.
Related Tags:
More Articles

How to Choose the Best Floor Scrubber Battery for Commercial Cleaning?
Selecting the ideal floor scrubber battery ensures a long runtime, rapid charging, and minimal maintenance for efficient commercial cleaning operations.
Battery for Blower vs Battery for Leaf Vacuum: Which One Should You Choose?
Battery for blower vs leaf vacuum—learn the key differences in power, fit, and runtime to choose the right battery for your outdoor tool needs.
How to Choose the Right Battery for Blower?
Choosing the right blower battery? Consider voltage, capacity, chemistry & usage. This guide helps match the best battery for peak performance.
How to Choose the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries?
Choosing the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries? Discover key factors such as size, material, and safety for optimal protection and performance.
7 Critical Elements on a Lithium Battery Shipping Label
What must be on a lithium battery shipping label? Learn 7 key elements to ensure safety, legal compliance, and correct handling across all transport modes.