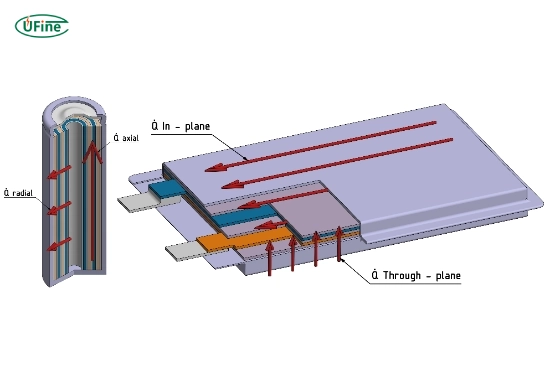
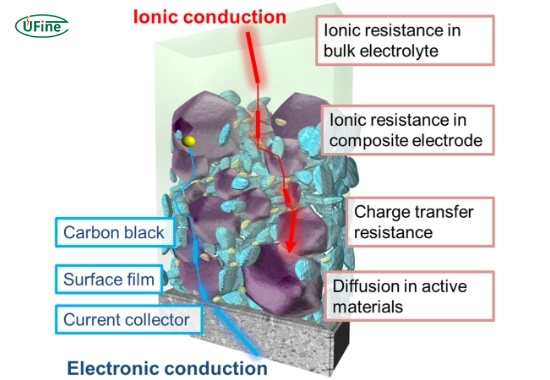
Most people think about voltage, capacity, or charging time when it comes to lithium batteries. But there’s something just as important that often gets overlooked: resistance and conductivity. These two terms might sound technical, but they play a massive role in how well your battery performs, lasts, and is safe.
In this article, we’ll explain resistance and conductivity simply and clearly. We’ll also explain how they affect your lithium battery and why you should care. Whether you’re powering an electric bike, solar system, or portable gadget, understanding these concepts can help you get the most out of your battery.
Let’s dive in.
Part 1. What do resistance and conductivity mean in simple terms?
Resistance is the amount of time a material tries to stop the flow of electric current. Think of it like water flowing through a pipe. A narrow pipe slows the water down, which is resistance.
Conductivity, on the other hand, is how easily electricity flows. If resistance is a narrow pipe, conductivity is wide and smooth. High conductivity means electricity flows fast and easily.
Lithium batteries should have low resistance and high conductivity. This will reduce energy waste and improve battery performance.
Part 2. Why do resistance and conductivity matter in lithium batteries?
This is a common question. The short answer is:
Resistance and conductivity directly affect a battery’s performance, efficiency, heat generation, and lifespan.
Here’s how:
- High resistance means more heat and energy loss.
- Low conductivity slows down charging and discharging.
- Low resistance + high conductivity = better battery performance.
When designing lithium batteries, manufacturers aim for materials and structures that allow electricity to flow smoothly. That’s the secret to longer-lasting, safer batteries.
Part 3. How do resistance and conductivity affect charging speed?
Have you ever wondered why some batteries charge faster than others?
It’s not just about the charger. Internal resistance plays a huge role inside the battery.
- Lower resistance = faster charging.
- High resistance slows the current, which means slower charging, more heat, and energy loss.
Conductivity also matters. If the battery’s internal components, like the electrolyte and electrodes, are highly conductive, electricity can move freely. This supports fast charging without overheating or damaging the battery.
So, if you want a quick charge, you need a battery with low internal resistance and high conductivity.
Part 4. What materials inside lithium batteries affect resistance and conductivity?
Let’s keep it simple. A lithium battery is made up of:
- Anode (usually graphite)
- Cathode (usually lithium metal oxides)
- Electrolyte (a liquid or gel that conducts lithium ions)
- Separator (keeps anode and cathode apart)
Each of these materials can either help or hurt conductivity:
- Graphite is a good conductor. That’s why it’s widely used in anodes.
- Lithium cobalt oxide or lithium iron phosphate used in cathodes also has good conductivity but varies.
- The electrolyte must allow lithium ions to move easily. If it doesn’t, resistance goes up.
Better materials = better conductivity = better battery.
Part 5. What is internal resistance, and why does it keep rising?
Internal resistance is the total resistance inside a battery. It includes all the small resistances from the anode, cathode, electrolyte, and other parts.
Over time, as the battery ages:
- Materials degrade.
- Electrodes become dirty or blocked.
- The electrolyte may break down.
All these things increase resistance.
And when resistance goes up:
- The battery heats up more.
- Power output drops.
- Charging takes longer.
- The battery wears out faster.
So, keeping resistance low is key to a long battery life.
Part 6. How do you measure resistance and conductivity in a lithium battery?
There are two main ways:
- Using a multimeter: You can measure the DC internal resistance by checking voltage drop under load.
- Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS): A lab test that provides a detailed view of resistance across frequencies.
For conductivity, you usually test it in the materials phase (before complete battery assembly), such as:
- Ionic conductivity of electrolytes
- Electrical conductivity of electrode materials
Battery engineers use these numbers to design better batteries.
Part 7. What are the signs of high resistance in your battery?
Here are some real-world signs:
- The battery gets hot during use or charging
- You notice slower charging
- The battery drains faster than it used to
- Power output is weaker, especially under load
- The voltage drops suddenly when using the battery
If you notice these issues, the battery’s internal resistance may rise. It might be time to replace it or check for damage.
Part 8. How does temperature affect resistance and conductivity?
Temperature has a significant impact.
- Cold temperatures increase resistance. That’s why your phone may shut down in freezing weather.
- High temperatures lower resistance—but too much heat can damage the battery.
The best performance usually happens around 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F).
That’s why battery management systems (BMS) are so important. They help control the temperature and resistance to protect the battery.
Artikel Terkait: Internal Resistance of Lithium Ion Batteries: What You Need to Know
Part 9. Can you improve the conductivity of a lithium battery?
Yes, and engineers do it all the time! Some methods include:
- Coating electrodes with conductive materials (like carbon)
- Using nanomaterials for better contact and flow
- Designing 3D structures that reduce resistance paths
- Improving electrolyte formulas for better ionic movement
These innovations are already in modern lithium batteries, making them lighter, faster, and longer-lasting.
Part 10. What does this mean for everyday battery users?
If you’re a regular user, here’s why resistance and conductivity matter to you:
- Choose quality batteries: Cheap batteries often have poor conductivity and higher resistance.
- Avoid extreme temperatures: Both heat and cold can harm conductivity.
- Charge correctly: Use the correct charger and avoid overcharging or deep discharges.
- Watch for signs of ageing: Heat, slow charge, and fast drain are red flags.
Understanding these terms helps you make smarter decisions about buying, using, and caring for lithium batteries.
Part 11. FAQs about resistance and conductivity
What is the difference between resistance and conductivity?
Resistance is how much a material blocks electric current, while conductivity is how easily it lets electricity flow. They are opposites: high resistance means low conductivity, and vice versa.
Why is low resistance significant in lithium batteries?
Low resistance reduces energy loss, heat, and charging time. It also extends the battery’s lifespan and improves performance.
Can high resistance damage a lithium battery?
Yes. High resistance causes overheating, reduces efficiency, and increases the risk of failure or fire.
How do I know if my battery’s conductivity is good?
You can check battery specs or performance. A battery that charges quickly stays cool and holds a charge well likely has good conductivity.
Does battery resistance increase with age?
Yes. As the battery ages, materials degrade, increasing resistance and reducing efficiency. This is a regular part of battery life.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Paper Battery vs. Flexible Battery: What’s the Difference and Which Is Better?
Paper vs. flexible batteries: learn the key differences, benefits, and which power source fits best for wearables, sensors, and smart tech.
What to Know Before Buying a Tiny LiPo Battery for Your Project
Tiny LiPo batteries are powerful and compact. Learn how to choose the right one for your project with specs, safety, and charging tips.
Bloated LiPo Battery: Will It Explode?
Will a bloated LiPo battery explode? Discover the causes, risks, safety steps, and expert tips to avoid disaster and protect your gear. Must-read safety guide!
12V 100Ah Lithium Ion Battery Price: Full Guide
Learn about 12V 100Ah lithium-ion battery price, from cost ranges to best brands, hidden fees, and how to get the best deal. A must-read for smart buyers!
What Is a Semi Solid State Battery and Why Should You Care?
Semi-solid-state batteries combine safety and high energy density, making them ideal for EVs, electronics, and future energy storage.