- Part 1. What are silver zinc batteries?
- Part 2. What are zinc-air batteries?
- Part 3. Silver zinc battery vs. zinc air battery: performance comparison
- Part 4. Advantages of silver zinc and zinc air batteries
- Part 5. Disadvantages of silver zinc and zinc air batteries
- Part 6. Applications of silver zinc and zinc air batteries
- Part 7. FAQs
Silver-zinc and zinc-air batteries are two technologies often discussed regarding energy storage solutions. Both have unique characteristics, applications, and advantages that make them suitable for different uses. This article will explore the differences between these two battery types, their chemistry, performance, applications, and much more.
Part 1. What are silver zinc batteries?
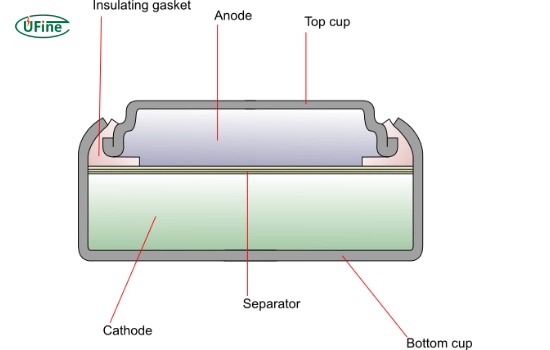
Silver zinc batteries are rechargeable and utilize silver oxide and zinc as the primary materials. They are known for their high energy density, excellent performance, and reliability.
Key Features of Silver Zinc Batteries
- High Energy Density: Silver zinc batteries can deliver high energy relative to their weight and size, making them ideal for applications where space and weight are critical.
- Rechargeable: Silver-zinc batteries can recharge multiple times, enhancing their longevity and reducing waste, unlike other battery types.
- Low Self-Discharge Rate: These batteries have a low rate, meaning they can retain their charge for extended periods when unused.
Chemistry of Silver Zinc Batteries
The electrochemical reaction in silver-zinc batteries occurs between silver oxide (AgO) and zinc (Zn). Zinc oxidizes and releases electrons during discharge, while silver ions reduce to silver metal. You can represent the overall reaction as:
Ag2O + Zn -> 2Ag + ZnO
This reaction allows for efficient energy conversion and storage.
Part 2. What are zinc-air batteries?
Zinc air batteries are another type of battery that uses zinc as the anode and oxygen from the air as the cathode. They are known for their high energy density and are commonly used in applications such as hearing aids and other portable electronic devices.
Key Features of Zinc-Air Batteries
- High Energy Density: Zinc air batteries also boast a high energy density, making them suitable for compact devices.
- Cost-Effective: They are generally less expensive to produce than other battery technologies, primarily due to abundant materials.
- Environmentally Friendly: Zinc-air batteries are considered more environmentally friendly as they utilize air as a reactant and do not contain toxic heavy metals.
Chemistry of Zinc-Air Batteries
The electrochemical reaction in zinc-air batteries involves the oxidation of zinc and the reduction of oxygen. The overall reaction can be summarized as follows:
Zn + 1/2 O2 + H2O -> Zn(OH)2
This reaction allows for efficient energy production, especially in devices that require sustained power.
Part 3. Silver zinc battery vs. zinc air battery: performance comparison
When comparing silver-zinc batteries and zinc-air batteries, several performance metrics come into play, including energy density, cycle life, discharge rates, cost, environmental impact, safety, and charging speed. Below is a detailed comparison highlighting these aspects.
| Feature | Silver Zinc Batteries | Zinc Air Batteries |
| Energy Density | High (100-150 Wh/kg) | Very High (200+ Wh/kg) |
| Cycle Life | Moderate to High (150-300 cycles) | Limited (non-rechargeable) |
| Discharge Rate | High | Moderate |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Environmental Impact | Moderate | Low |
| Safety | Generally safe with low thermal runaway risk | Safe but humidity sensitive |
| Charging Speed | Slower charging | Not applicable (non-rechargeable) |
Energy Density
Silver zinc batteries typically have an energy density ranging from 100 to 150 watt-hours per kilogram (Wh/kg). In contrast, zinc-air batteries generally offer a higher energy density, often exceeding 200 Wh/kg, making them ideal for applications requiring long-lasting power in a compact form.
Cycle Life
Silver zinc batteries can endure approximately 150 to 300 recharge cycles before a significant capacity loss occurs, whereas zinc-air batteries have a limited lifespan as they are not rechargeable. Performance diminishes once the air activates the battery.
Discharge Rate
Silver zinc batteries can provide a higher discharge rate, making them ideal for applications requiring quick bursts of energy, such as aerospace and military applications.
Cost
Due to their silver content, silver-zinc batteries are more expensive to produce, leading to higher initial costs. In contrast, zinc-air batteries are generally more cost-effective, as they utilize abundant materials and are less costly to manufacture.
Environmental Impact
Silver zinc batteries are more environmentally friendly due to their use of less toxic materials and easier recycling processes. Zinc air batteries are also considered eco-friendly, but their disposable nature can lead to waste if not properly recycled.
Safety
Silver zinc batteries are generally safe, with a lower risk of thermal runaway than other battery types. Zinc air batteries are also safe but can pose dangers if exposed to high temperatures or humidity, affecting their performance.
Charging Speed
Silver zinc batteries typically have slower charging rates, resulting in longer charging times. In contrast, zinc-air batteries are non-rechargeable, making charging speed irrelevant.
Part 4. Advantages of silver zinc and zinc air batteries
Advantages of Silver Zinc Batteries
- High Efficiency: Silver zinc batteries have a high energy conversion efficiency, which is crucial for applications requiring reliable power.
- Temperature Stability: They perform well in extreme temperatures, making them suitable for harsh environments.
- Low Maintenance: These batteries require minimal maintenance compared to other rechargeable batteries.
Advantages of Zinc-Air Batteries
- Cost-Effectiveness: Using inexpensive materials makes zinc-air batteries cost-effective for many applications.
- Lightweight: Their lightweight nature makes them ideal for portable devices.
- Sustainability: Zinc-air batteries are less environmentally harmful, increasing their popularity.
Part 5. Disadvantages of silver zinc and zinc air batteries
Disadvantages of Silver Zinc Batteries
- Cost: Silver makes these batteries more expensive than other options.
- Limited Availability: Silver zinc batteries may not be as widely available as other battery types.
Disadvantages of Zinc-Air Batteries
- Limited Cycle Life: Zinc air batteries typically have a shorter lifespan than silver-zinc batteries.
- Humidity Sensitivity: They can be affected by humidity levels, which may impact their performance.
Part 6. Applications of silver zinc and zinc air batteries
Applications of Silver Zinc Batteries
- Aerospace: Used in satellites and spacecraft due to their high energy density and reliability.
- Military: Employed in military equipment where weight and performance are critical.
- Medical Devices: People use these in specific medical devices that need reliable and compact power sources.
Applications of Zinc-Air Batteries
- Hearing Aids: Widely used in hearing aids due to their compact size and high energy density.
- Consumer Electronics: Found in various portable electronic devices, including cameras and remote controls.
- Electric Vehicles: There is emerging interest in using zinc-air batteries for electric vehicles due to their potential for high energy density.
Part 7. FAQs
-
What is the main difference between silver zinc and zinc air batteries?
Silver zinc batteries use silver oxide and zinc, while zinc air batteries use zinc and oxygen from the air as reactants. -
Which battery has a higher energy density?
Zinc-air batteries generally have a higher energy density than silver-zinc batteries. -
Are silver-zinc batteries rechargeable?
Yes, you can recharge silver-zinc batteries and cycle them multiple times. -
What are the typical applications for zinc-air batteries?
People commonly use zinc-air batteries in hearing aids and portable electronic devices. -
Which battery type is more environmentally friendly?
People consider zinc-air batteries more environmentally friendly because they use air and non-toxic materials.
Related Tags:
More Articles

고방전 배터리는 높은 전류와 발열로 배터리수명이 줄어듭니다. 구조적 한계, 사용 패턴, 충전 습관 등 실제 수명 단축 요인을 체계적으로 분석했습니다.
Capacitor vs Battery: What is the Difference?
Capacitor vs battery explained in detail. Learn the difference between capacitor and battery in energy storage, charging speed, lifespan, and real applications.
18650 Battery vs AA: Which Is Better for Your Device?
Compare 18650 vs AA batteries in capacity, voltage, rechargeability, and applications. Learn which battery type fits high-drain or everyday devices.
What is the Difference Between Battery Cell, Battery Control Module, and Battery Pack?
Compare battery cells, modules, and packs. Learn functions, design differences, control modules, and selection tips for EV, ESS, and industrial use.
How to Prevent LiPo Battery Explosion?
Can LiPo batteries explode or catch fire? Learn key causes of LiPo battery fires and proven charging, storage, and handling tips to reduce explosion risk.