Small battery charging is crucial for maintaining lithium-based power sources’ performance, safety, and longevity. Whether you’re charging a phone, a power bank, or a lithium battery for a solar system, following best practices can extend battery life and improve efficiency.
Due to their high energy density and long lifespan, lithium batteries are widely used in electronics, medical devices, drones, and even electric vehicles. However, improper charging can reduce efficiency, safety risks, and a shorter battery life.
This guide will cover everything you need to know about charging small lithium batteries, including safe charging methods, best practices, common mistakes to avoid, and how to extend battery life.
Part 1. What is small battery charging?
Small battery charging refers to replenishing energy in compact lithium-based batteries used in various consumer electronics and portable power sources. These batteries require precise charging techniques to prevent overheating, capacity loss, and safety hazards.
Why is proper charging necessary?
Lithium batteries have specific voltage and current requirements that must be met for safe and efficient charging. Overcharging, undercharging, or using the wrong charger can damage the battery and reduce lifespan.
Key benefits of proper lithium battery charging:
- Extends battery lifespan: Prevents premature degradation.
- Improves device performance: Ensures consistent energy output.
- Enhances safety: Reduces the risk of overheating or fire hazards.
Part 2. How do lithium batteries work?
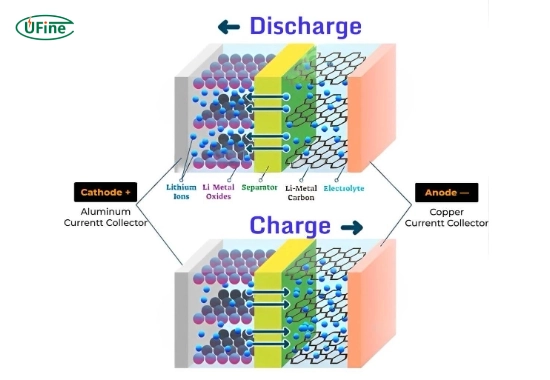
Lithium batteries store and release energy through the movement of lithium ions between two electrodes: the positive electrode (cathode) and the negative electrode (anode). This process occurs in a liquid or gel-like electrolyte that allows ion flow while preventing direct contact between the electrodes.
Charging process:
When a lithium battery charges, an external power source applies a voltage, forcing lithium ions to move from the cathode to the anode. These ions are stored in the anode material until the battery is discharged.
Discharging process:
When the battery is in use, the stored lithium ions return from the anode to the cathode, generating electrical energy that powers the connected device.
Key characteristics of lithium batteries:
- High energy density: More power in a smaller, lightweight design.
- Rechargeable: Can go through hundreds of charge cycles.
- Stable voltage output: Provides consistent performance.
- Low self-discharge rate: Can hold a charge longer when not in use.
With proper charging and care, lithium batteries can provide reliable and long-lasting performance for various applications, from portable electronics to renewable energy storage.
Part 3. How do you charge different types of small lithium batteries?
Lithium batteries require different charging methods based on size, capacity, and application.
1. Charging lithium-ion batteries (Li-ion)
Common in smartphones, laptops, and power tools, Li-ion batteries require constant current (CC) and constant voltage (CV) charging.
Best practices:
- Charge at room temperature (10°C – 30°C).
- Avoid deep discharges below 20%.
- Use chargers with voltage regulation to prevent overcharging.
2. Charging lithium-polymer batteries (LiPo)
Used in drones, RC cars, and wearable tech, LiPo batteries are sensitive to overcharging.
Best practices:
- Never charge above the recommended 4.2V per cell.
- Use a balanced charger to maintain even cell voltage.
- Store at 50% charge if not used for a long time.
3. Charging lithium iron phosphate batteries (LiFePO4)
Common in solar power systems and electric vehicles, LiFePO4 batteries have safer chemistry but require a special charger.
Best practices:
- Charge with a LiFePO4-compatible charger.
- Avoid charging in extreme cold (below 0°C).
- Do not mix with standard Li-ion chargers.
Part 4. What is the best way to charge a small lithium battery?
The best way to charge a small lithium battery is by using a dedicated lithium charger that follows the correct voltage and current settings.
Step-by-step charging process:
- Check battery specifications: Ensure the charger matches the battery’s voltage and amperage.
- Use a quality charger: Cheap chargers may lack safety features.
- Monitor charging temperature: The ideal charging range is 10°C – 30°C.
- Unplug when fully charged: Prevents unnecessary stress on the battery.
Part 5. How to safely charge lithium batteries?
Safety is a top priority when charging small lithium batteries. Improper charging can lead to thermal runaway, which causes overheating and potential fire risks.
Best safety practices:
- Never use damaged batteries: Swollen or punctured batteries can be hazardous.
- Charge in a cool, ventilated area: Avoid charging near flammable materials.
- Do not leave batteries unattended: Reduce the risk of overheating.
- Avoid fast charging frequently: It generates excess heat, reducing battery lifespan.
Part 6. Common mistakes to avoid when charging small batteries
Many users unknowingly damage their lithium batteries by following bad charging habits.
Common mistakes:
- Overcharging: Leaving the battery plugged in too long.
- Using the wrong charger: Mismatched voltage can harm the battery.
- Charging in extreme temperatures: Too hot or cold can shorten battery life.
- Draining the battery completely: Avoid full discharges to extend lifespan.
Part 7. How long does it take to charge a small lithium battery?
Charging time depends on the battery capacity (mAh) and the charging speed of your adapter.
Estimated charging times:
- 1000mAh battery: About 1-2 hours with a 1A charger.
- 5000mAh battery: Around 5-6 hours with a 1A charger.
- Fast charging: It can reduce charging time by 50% but may shorten battery life.
Part 8. How can the lifespan of lithium batteries be extended?
With proper care, lithium batteries can last for years before losing significant capacity.
Best practices:
- Keep charge levels between 20% and 80% – Avoid full discharges.
- Store batteries properly: Keep them in a cool, dry place.
- Use slow charging when possible: Reduces battery stress.
- Avoid high-drain applications: Rapid discharge can shorten lifespan.
Part 9. Can you charge a lithium battery with a standard charger?
No, you should not charge a lithium battery with a standard charger unless it is designed explicitly for lithium-ion technology.
Why?
- Lithium batteries need precise voltage regulation.
- Overcharging can cause thermal runaway (risk of explosion).
- Incorrect charging can lead to permanent capacity loss.
Always use a dedicated lithium-ion charger for safety and efficiency.
Artikel Terkait: Small Battery: Definition, Types, and Applications
Part 10. FAQs about small battery charging
Can I leave my lithium battery plugged in overnight?
It is not recommended. Most modern devices have overcharge protection, but keeping the battery in for long can cause heat buildup and reduce lifespan.
What happens if I overcharge a lithium battery?
Overcharging can lead to battery swelling, overheating, or fire hazards. Always use a charger with auto shut-off to prevent this.
How do I know if my lithium battery is damaged?
Signs of a damaged battery include:
- Swelling or bulging
- Excessive heat while charging
- Shortened battery life
- Leaking fluid
Is fast charging bad for lithium batteries?
Yes, frequent fast charging generates excess heat, which can degrade the battery faster. Slow charging should be used when possible to extend battery life.
What is the ideal storage charge for lithium batteries?
If storing a lithium battery for a long time, keep it at around 40-60% charge in a cool and dry place to prevent degradation.
Related Tags:
More Articles

How to Choose the Best Floor Scrubber Battery for Commercial Cleaning?
Selecting the ideal floor scrubber battery ensures a long runtime, rapid charging, and minimal maintenance for efficient commercial cleaning operations.
Battery for Blower vs Battery for Leaf Vacuum: Which One Should You Choose?
Battery for blower vs leaf vacuum—learn the key differences in power, fit, and runtime to choose the right battery for your outdoor tool needs.
How to Choose the Right Battery for Blower?
Choosing the right blower battery? Consider voltage, capacity, chemistry & usage. This guide helps match the best battery for peak performance.
How to Choose the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries?
Choosing the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries? Discover key factors such as size, material, and safety for optimal protection and performance.
7 Critical Elements on a Lithium Battery Shipping Label
What must be on a lithium battery shipping label? Learn 7 key elements to ensure safety, legal compliance, and correct handling across all transport modes.