Part 1. What is a group 24 battery?
Before diving into the specifics of a Group 24 battery, it’s important to understand what group size refers to in general. The term group size is a standard established by the Battery Council International (BCI). It refers to the physical dimensions of the battery—its length, width, and height—so that it fits properly in different battery compartments.
However, group size doesn’t only dictate physical dimensions. It can also give an idea about the capacity, power output, and even the intended applications of the battery. This is particularly important for batteries used in vehicles, boats, or off-grid systems where space and power needs are crucial factors.
A Group 24 battery is a medium-sized battery commonly used in a wide variety of applications, from marine use to backup power systems. The “Group 24” label is based on the standardized size set by BCI. These batteries typically offer a balance between capacity and size, which makes them highly versatile.
Part 2. Types of group 24 battery
There are several types of Group 24 batteries available on the market, each offering unique benefits and characteristics:
- Flooded Lead-Acid: The most common and affordable option. It requires regular maintenance and is prone to leakage and corrosion over time. Suitable for cost-conscious consumers who don’t mind periodic upkeep.
- AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat): A step up from flooded lead-acid, AGM batteries are maintenance-free and offer better performance with faster charging and lower self-discharge rates. However, they tend to be more expensive.
- Gel: Similar to AGM, Gel batteries provide reliable power and are ideal for deep cycle applications. They perform well in extreme temperatures but are typically more costly.
- Lithium-Ion (LiFePO4): The premium option, offering longer lifespan, lighter weight, and higher efficiency. Lithium-ion Group 24 batteries are perfect for users who prioritize performance, durability, and ease of use, but they come with a higher price tag.
Part 3. Risks of the wrong battery size
Choosing a battery size that is too small or too large can cause several issues:
- Too Small: A battery that is too small may not provide enough power, potentially leading to poor performance, short run times, or failure to start your vehicle.
- Too Large: A battery that is too large may not fit properly in the designated battery compartment, potentially causing mechanical issues. It may also result in overcharging if the alternator is not designed for a larger capacity.
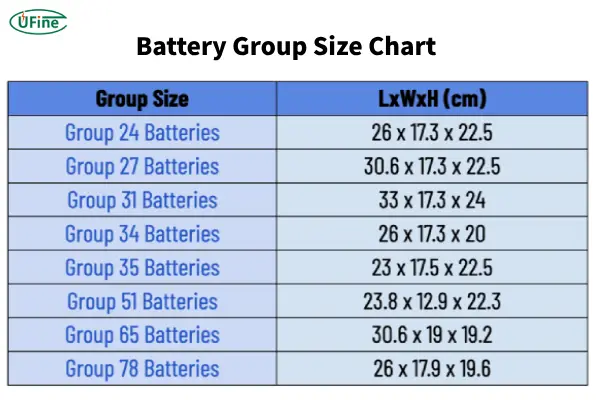
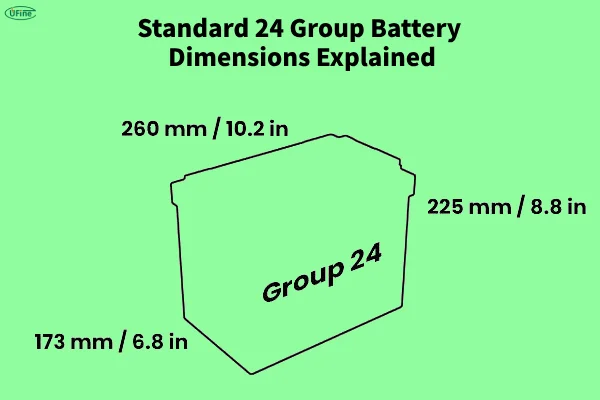
Part 4. What are the standard dimensions of group 24 battery?
The standard dimensions of a Group 24 battery are typically:
- Length: 10.25 inches (260 mm)
- Width: 6.8125 inches (173 mm)
- Height: 8.875 inches (225 mm)
These standardized dimensions ensure that a Group 24 battery will fit into the appropriate battery compartments in various vehicles or devices, whether it’s for a boat, an RV, or an industrial backup system.
It’s always crucial to double-check your battery compartment to ensure the dimensions fit your specific application, as some battery compartments may vary slightly depending on the manufacturer.
Part 5. Do Group 24 battery dimensions vary by brand?
While Group 24 batteries are standardized to a certain extent, slight variations can occur between brands. Generally, the core dimensions of Group 24 batteries — length: 10.25 inches, width: 6.81 inches, and height: 8.88 inches — are consistent across manufacturers. However, brands may have slight variations due to casing design, terminal placement, or internal components. It’s important to check the manufacturer’s specifications for exact measurements.
Can they be used universally?
Yes, the Group 24 size is standardized enough that most batteries of this type can be used interchangeably, but it’s always a good idea to verify the specific requirements for your application, especially with regard to terminal type and battery type (e.g., flooded, AGM, or gel).
Part 6. Do battery types affect Group 24 dimensions?
No, the dimensions of Group 24 batteries can vary depending on the battery chemistry. For instance:
-
Flooded Lead-Acid (FLA): This is the most common and standard form of Group 24 batteries, and its dimensions are generally consistent with the Group 24 size.
-
Absorbent Glass Mat (AGM): AGM batteries typically have similar dimensions to standard flooded batteries but may be a bit taller due to the construction, as they use an absorbed electrolyte system.
-
Gel Batteries: Gel batteries can also fit within the Group 24 dimensions but may be slightly bulkier in certain cases due to their construction.
Part 7. What size of battery can replace a Group 24 battery?
If you’re looking to replace a Group 24 battery, there are other Group size batteries that may fit, depending on the specific requirements. The most common options are:
- Group 27: Slightly larger, typically offering higher capacity, and can replace a Group 24 battery if there’s extra space.
- Group 22NF: A smaller alternative, with slightly reduced capacity but may still work in applications with less power demand.
Before selecting an alternative, ensure that the battery fits the compartment and meets the required voltage and capacity for your needs.
Part 8. Where to check Group 24 battery dimensions?
To check the dimensions of a Group 24 battery, you can:
- Consult the product’s datasheet or manufacturer website: This will provide the most accurate and detailed information about the battery’s physical size and specifications.
- Look at the battery label: Most batteries will have their physical dimensions printed directly on the label, often in inches or millimeters.
- Contact the manufacturer or retailer: If in doubt, always reach out to the supplier or battery manufacturer for detailed specifications to ensure you’re choosing the right one.
Part 9. Key factors beyond size to consider
When purchasing a Group 24 battery, aside from its size, you should consider the following key parameters:
- Voltage: Most Group 24 batteries are 12V, but it’s crucial to double-check compatibility with your vehicle or equipment.
- Capacity (Ah or mAh): The amp-hour rating determines how much charge the battery can store and how long it will last during use.
- Cold Cranking Amps (CCA): This rating indicates the battery’s ability to start an engine in cold temperatures.
- Reserve Capacity (RC): This is the number of minutes a battery can supply power to a vehicle’s electrical system without the engine running.
- Terminal Type: Ensure the terminal configuration (such as top-post, side-post, or dual-terminal) matches your vehicle’s requirements.
- Battery Chemistry: Choose the right chemistry based on your needs (flooded, AGM, or gel) for better performance and reliability.
Part 10. How to determine the right battery size?
To determine the correct battery size for your vehicle or equipment, you should:
- Check the owner’s manual: This will often list the recommended battery size, voltage, and chemistry.
- Look for the battery group size on the existing battery: If you’re replacing an old battery, you can check the markings on the current battery for its size and specifications.
- Consider your power needs: Larger batteries may be necessary for high-power applications, such as RVs, boats, or large vehicles.
If you’re uncertain, visit a professional retailer or technician to get advice on the right size based on your specific needs.
Part 11. Is group 24 lithium battery the best battery?
Out of all the types of Group 24 batteries, lithium-ion batteries, particularly those using LiFePO4 technology, stand out as the best option for modern power needs. While they are more expensive upfront, the long-term benefits far outweigh the cost.
- Longer Lifespan: Lithium-ion batteries can last up to 10 times longer than flooded lead-acid batteries, with some models offering up to 5,000 charge cycles.
- Lighter Weight: Lithium batteries are 50-60% lighter than their lead-acid counterparts, making them easier to install and transport.
- Fast Charging: These batteries charge much faster than lead-acid ones, reducing downtime in off-grid or marine settings.
- Maintenance-Free: Lithium-ion batteries require no ongoing maintenance, unlike flooded lead-acid batteries that need regular water refills and corrosion checks.
Part 12. How long does a group 24 battery last?
The lifespan of a Group 24 battery depends largely on the type of battery chemistry:
- Flooded Lead-Acid: Typically lasts 2-5 years with regular maintenance.
- AGM and Gel: These batteries tend to last 3-7 years, offering better durability than flooded batteries.
- Lithium-Ion (LiFePO4): The longest-lasting option, with lifespans ranging from 10-15 years or more, depending on usage patterns and maintenance.
Part 13. Is group 24 deep cycle battery worth it?
A Group 24 deep cycle battery is specifically designed for sustained, consistent power delivery, making it ideal for applications like marine trolling motors, RVs, and off-grid solar systems. Unlike starting batteries, which provide short bursts of high power, deep cycle batteries can be discharged more deeply and frequently, offering longer-lasting energy.
Here’s why a Group 24 deep cycle battery might be worth the investment:
- Durability: Deep cycle batteries are built to withstand frequent deep discharges, making them highly durable for long-term use.
- Efficiency: They deliver a steady amount of energy over extended periods, perfect for applications that require continuous power.
- Versatility: Whether you’re using it for your boat, RV, or home solar setup, deep cycle Group 24 batteries are flexible enough to handle various tasks.
Related Tags:
More Articles

How to Choose the Best Floor Scrubber Battery for Commercial Cleaning?
Selecting the ideal floor scrubber battery ensures a long runtime, rapid charging, and minimal maintenance for efficient commercial cleaning operations.
Battery for Blower vs Battery for Leaf Vacuum: Which One Should You Choose?
Battery for blower vs leaf vacuum—learn the key differences in power, fit, and runtime to choose the right battery for your outdoor tool needs.
How to Choose the Right Battery for Blower?
Choosing the right blower battery? Consider voltage, capacity, chemistry & usage. This guide helps match the best battery for peak performance.
How to Choose the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries?
Choosing the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries? Discover key factors such as size, material, and safety for optimal protection and performance.
7 Critical Elements on a Lithium Battery Shipping Label
What must be on a lithium battery shipping label? Learn 7 key elements to ensure safety, legal compliance, and correct handling across all transport modes.