Living off the grid represents a profound commitment to sustainability, independence, and self-sufficiency. At the heart of any off-grid system lies the battery, which ensures a reliable power supply when traditional utility grids are out of reach. This guide delves deep into off-grid batteries, offering insights, advice, and expert tips on choosing and maintaining the best battery for your needs.
Part 1. The unique importance of off-grid battery
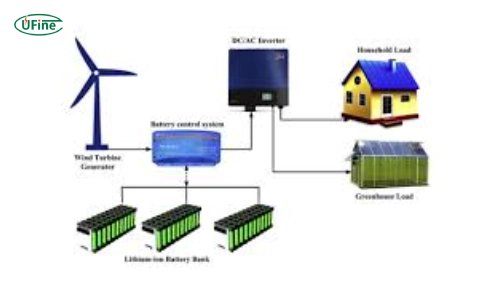
Off-grid batteries are not just any batteries but the backbone of an autonomous energy system. Unlike conventional batteries used in grid-tied systems, off-grid batteries must deliver consistent and dependable power with no fallback to a grid. This unique requirement makes their selection and management more critical.
Part 2. Understanding off-grid living
Living off the grid means generating, storing, and managing your electricity, often through renewable sources like solar panels or wind turbines. This self-reliant lifestyle demands a robust energy storage solution to ensure a steady power supply, regardless of weather conditions or time of day.
Part 3. Types of off-grid batteries
Choosing the correct type of battery for your off-grid system involves understanding the options available and their respective benefits and drawbacks. Here’s a deeper look into the main types of off-grid batteries:
1. Deep Cycle Lead-acid Batteries
Deep-cycle lead-acid batteries have been a reliable choice for decades. Designers create these batteries to provide a steady current over a long period, making them ideal for storing renewable energy. They come in two main varieties:
- Flooded Lead-acid (FLA): These require regular maintenance, including checking water levels and ensuring proper ventilation. They are cost-effective but need more care.
- Sealed Lead-acid (SLA): Also known as Valve-Regulated Lead-Acid (VRLA) batteries, these are maintenance-free and are safer because they don’t emit gases. However, they typically come at a higher cost.
2. Lithium-ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries are the modern choice for off-grid systems due to their high energy density, long lifespan, and minimal maintenance. Key points include:
- High Efficiency: Lithium-ion batteries have a higher efficiency rate, meaning more stored energy is usable.
- Long Lifespan: They can handle more charge/discharge cycles than lead-acid batteries, offering better long-term value.
- Lightweight: These lighter batteries make them easier to install and maintain.
3. Saltwater Batteries
Saltwater batteries are an emerging technology that promises safety and environmental benefits. They use a saltwater electrolyte, making them non-toxic and more recycling accessible. Although not as widespread, they offer:
- Safety: Non-flammable and non-toxic, minimizing risks.
- Eco-Friendly: Easier to dispose of and recycle compared to traditional batteries.
4. Nickel-Iron (NiFe) Batteries
Nickel-iron batteries are renowned for their incredible longevity and durability. Invented by Thomas Edison, these batteries can last several decades. However, they have some downsides:
- Long Lifespan: Can last up to 30 years with proper maintenance.
- Lower Efficiency: They are less efficient than lithium-ion batteries, resulting in higher energy losses.
- Bulkier: These batteries are larger and heavier, requiring more space.
Part 4. Critical considerations for choosing an off-grid battery
Selecting the correct off-grid battery requires careful consideration of several factors to ensure it meets your specific energy needs and conditions. Here’s what you need to focus on:
1. Assess Your Energy Needs
Start by understanding your energy consumption patterns. Calculate your daily and peak energy usage to determine your needed battery capacity. Consider the number of appliances, power ratings, and usage duration. This helps in:
- Sizing the Battery: Ensuring you have enough capacity to meet your energy demands.
- Avoiding Overinvestment: Preventing unnecessary costs by not oversizing your system.
2. Consider Climate and Environmental Conditions
The performance of batteries can vary based on environmental conditions. For instance, lithium-ion batteries perform well in a wide range of temperatures. In contrast, lead-acid batteries may require more controlled environments. Key points include:
- Temperature Tolerance: Ensure the battery can operate efficiently within the temperature range of your location.
- Humidity and Ventilation: Proper ventilation is crucial for some battery types to prevent overheating and gas buildup.
3. Budget and Cost Analysis
While initial costs are essential, consider the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and replacement. Though more expensive upfront, lithium-ion batteries often prove more cost-effective over their lifespan. Consider:
- Upfront Costs vs. Long-Term Savings: Higher initial investment might lead to more significant savings over time.
- Maintenance Costs: Some batteries require regular maintenance, impacting overall costs.
4. Evaluate Maintenance Requirements
Different batteries have varying maintenance needs. Lead-acid batteries may require regular checks and water refills, while lithium-ion batteries are generally maintenance-free. Consider:
- Maintenance Accessibility: Ensure you can perform necessary maintenance tasks or have access to professional services.
- Ease of Use: Opt for batteries that align with your willingness and ability to perform upkeep.
5. Longevity and Warranty
Invest in batteries with a proven track record of longevity and robust warranties. This ensures reliability and peace of mind. Key aspects include:
- Cycle Life: The number of charge/discharge cycles a battery can handle before its capacity significantly degrades.
- Manufacturer Warranty: A good warranty can protect your investment and reduce long-term costs.
Part 5. Off-grid battery installation and safety tips
Proper installation and maintenance of your off-grid battery system are crucial for optimal performance and longevity. Here’s how to ensure your setup is safe and efficient:
1. Ensure Proper Ventilation
Batteries, especially lead-acid types, can emit gases during charging and discharging. Proper ventilation is essential to prevent the buildup of potentially harmful gases and to maintain temperature control. Tips include:
- Ventilated Enclosures: Enclosures allow airflow while protecting batteries from external elements.
- Temperature Control: Install where temperature can be monitored and controlled.
2. Secure Mounting and Placement
Batteries should be securely mounted to prevent movement and damage. Proper placement also ensures safety and ease of access. Consider:
- Stable Surfaces: Place batteries on stable, non-conductive surfaces to avoid short circuits.
- Accessibility: Ensure easy access for maintenance and inspections.
3. Regular Inspections and Maintenance
Conduct regular inspections to check for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage. Early detection can prevent more significant issues down the line. Key practices include:
- Visual Checks: Look for corrosion, leaks, or swelling.
- Connection Checks: Ensure all connections are tight and free of corrosion.
- Cleaning: Keep terminals clean and free of debris.
4. Use Appropriate Safety Gear
Always use appropriate safety gear to protect yourself from potential hazards when handling batteries. This includes:
- Gloves and Goggles: Protect against acid spills and other chemical hazards.
- Proper Tools: Use insulated tools to prevent accidental short circuits.
5. Implement Battery Management Systems (BMS)
A battery management system (BMS) helps monitor and manage battery performance. It ensures optimal operation by:
- Monitoring Health: Tracks battery health and alerts you to potential issues.
- Optimizing Performance: Balances the charging and discharging cycles to extend battery life.
Part 6. Real-world applications of off-grid batteries
1. Remote Homes and Cabins
Off-grid batteries provide a reliable power source for remote homes and cabins, enabling a comfortable lifestyle far from the grid. They ensure:
- Consistent Power Supply: Even in isolated locations with no access to the utility grid.
- Sustainable Living: Utilizing renewable energy sources to power all household needs.
2. Emergency Backup Systems
Off-grid batteries are crucial backup systems in areas prone to natural disasters or frequent power outages, ensuring continuous power supply. Benefits include:
- Power Continuity: Keeps essential systems running during grid failures.
- Peace of Mind: Knowing you have a dependable power source during emergencies.
3. Mobile and Recreational Vehicles
For RVs, boats, and other mobile applications, off-grid batteries offer the flexibility to travel and explore without compromising on power needs. Advantages include:
- Mobility: Power your adventures without relying on external power sources.
- Convenience: Modern battery systems are lightweight and efficient, perfect for mobile setups.
Part 7. FAQs
-
What is the best battery for off-grid?
The best battery for off-grid use depends on your needs. Lithium-ion batteries are famous for their long life and efficiency. They charge quickly and last longer than other types. Lead-acid batteries are cheaper but need more maintenance. They are reliable and widely used. -
How much battery do I need to live off the grid?
First, determine your daily energy use in kilowatt-hours (kWh) to calculate the battery capacity you need. Multiply this by the number of days you want to store energy. For example, if you use 10 kWh daily and want three days of storage, you need 30 kWh of battery capacity. Always add a buffer for cloudy days or extra usage. -
How long do off-grid batteries last?
The lifespan of off-grid batteries varies. Lithium-ion batteries can last 10-15 years with proper care. Lead-acid batteries typically last 5-7 years. The lifespan depends on usage, maintenance, and environmental factors. Regular maintenance and correct usage can extend battery life. -
What voltage is best for off-grid?
The best voltage for off-grid systems is usually 24V or 48V. These voltages are efficient for most homes. Higher voltage systems, like 48V, reduce energy loss and are better for larger systems. Choose a voltage that matches your energy needs and the size of your system. Always consult with an expert to ensure compatibility with your equipment.
Related Tags:
More Articles

How to Choose the Best Floor Scrubber Battery for Commercial Cleaning?
Selecting the ideal floor scrubber battery ensures a long runtime, rapid charging, and minimal maintenance for efficient commercial cleaning operations.
Battery for Blower vs Battery for Leaf Vacuum: Which One Should You Choose?
Battery for blower vs leaf vacuum—learn the key differences in power, fit, and runtime to choose the right battery for your outdoor tool needs.
How to Choose the Right Battery for Blower?
Choosing the right blower battery? Consider voltage, capacity, chemistry & usage. This guide helps match the best battery for peak performance.
How to Choose the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries?
Choosing the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries? Discover key factors such as size, material, and safety for optimal protection and performance.
7 Critical Elements on a Lithium Battery Shipping Label
What must be on a lithium battery shipping label? Learn 7 key elements to ensure safety, legal compliance, and correct handling across all transport modes.