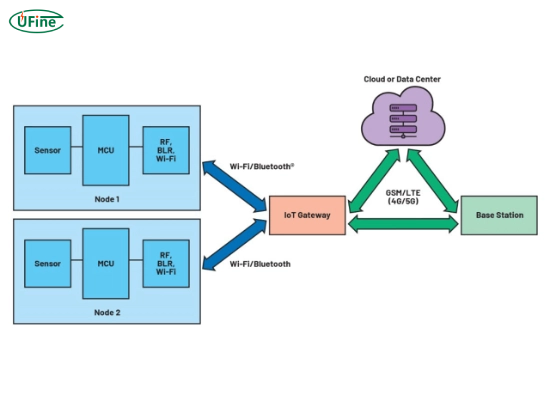
The Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing how we interact with the world around us. IoT devices, from smart homes to industrial automation, are becoming integral to our daily lives. One of the most critical components of these devices is the battery. This guide will delve into everything you need to know about choosing and using the correct battery for IoT devices to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Part 1. What is a battery for IoT devices?
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the network of interconnected devices that communicate and exchange data with each other over the Internet. These devices range from simple sensors and household appliances to complex industrial systems designed to make our lives more efficient and connected.
A battery for IoT devices is a crucial component that powers these interconnected gadgets, enabling them to function autonomously in various environments. IoT devices, or the Internet of Things, range from simple sensors to complex systems requiring reliable, long-lasting power sources. Batteries for IoT devices must be efficient, durable, and capable of supporting the specific power needs of these devices.
Part 2. Why are batteries necessary for IoT devices?
Batteries are the lifeblood of IoT devices, especially those deployed in remote or hard-to-reach locations. The importance of batteries in IoT devices can be summarized as follows:
- Autonomy: Batteries enable IoT devices to operate independently without a constant power supply.
- Reliability: A reliable battery ensures the continuous operation of IoT devices, which is critical for applications like healthcare monitoring and industrial automation.
- Longevity: Long-lasting batteries reduce the need for frequent replacements, saving time and maintenance costs.
Part 3. Types of batteries used in IoT devices
Choosing the correct type of battery for IoT devices depends on various factors such as power requirements, size, and environmental conditions. Here are some common types of batteries used in IoT devices:
- Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries are among the most popular types used in IoT devices. They offer high energy density, long cycle life, and low self-discharge rates, making them ideal for long-term power applications.
- Lithium polymer (LiPo) batteries are similar to Li-ion but come in lightweight packaging. This makes them suitable for compact, portable IoT devices with premium space.
- Alkaline batteries are a common choice for low-power IoT devices. They are readily available and inexpensive but have a shorter lifespan than lithium-based batteries.
- Nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries offer a good balance between cost and performance. They are environmentally friendly and have a higher energy density than alkaline batteries.
Part 4. Factors to consider when choosing a battery for IoT devices
Selecting the correct battery for your IoT device involves considering several factors:
- Energy Density: Higher energy density means the battery can store more energy in a given volume, which is crucial for compact IoT devices.
- Voltage Requirements: Ensure the battery voltage matches the device’s requirements to avoid damage and ensure optimal performance.
- Operating Temperature: Choose batteries that can operate efficiently within the temperature range of the deployment environment.
- Life Cycle: Consider the number of charge-discharge cycles the battery can endure before its capacity significantly degrades.
- Size and Weight: The battery’s physical dimensions and weight should match the device’s design constraints.
Part 5. How can battery life in IoT devices be optimized?
Optimizing battery life in IoT devices is essential for maximizing operational efficiency and longevity. Here are some strategies to achieve this:
- Power Management: Implement power-saving modes such as sleep or hibernate to reduce energy consumption during inactivity.
- Efficient Communication Protocols: Use low-power communication protocols like Zigbee, Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), or LoRaWAN.
- Hardware Optimization: Choose energy-efficient components and optimize the circuit design to minimize power loss.
- Software Optimization: Optimize the firmware and software running on the device to reduce unnecessary processing and power usage.
Part 6. Common challenges with batteries in IoT devices
Despite their importance, batteries in IoT devices face several challenges:
- Limited Lifespan: Batteries degrade over time, reducing their capacity and efficiency.
- Environmental Factors: Extreme temperatures, humidity, and other environmental factors can affect battery performance.
- Size Constraints: Balancing battery size with the device’s compact design can be challenging.
- Cost: High-quality batteries can be expensive, impacting the overall cost of the IoT device.
Part 7. Case studies: Successful battery implementations in IoT devices
Smart Home Automation
In smart home automation, IoT devices like sensors, cameras, and smart locks rely on batteries for uninterrupted operation. Lithium-ion batteries are commonly used due to their high energy density and reliability.
Industrial IoT
Industrial IoT devices, such as remote monitoring systems and predictive maintenance sensors, often use rugged batteries like lithium-thionyl chloride, which can operate in harsh environments and have a long shelf life.
Healthcare Monitoring
Wearable health monitors and medical sensors require lightweight and long-lasting batteries. Lithium polymer batteries are preferred for their flexibility and high energy density, ensuring continuous monitoring without frequent recharges.
Part 8. FAQs
-
What type of battery is best for IoT devices?
The best type of battery for IoT devices depends on the specific application, power requirements, and environmental conditions. Lithium-ion and lithium polymer batteries are popular due to their high energy density and long lifespan. -
How long do batteries in IoT devices typically last?
Battery lifespan in IoT devices can vary widely depending on usage patterns, power consumption, and environmental factors. On average, lithium-ion batteries can last between 2 to 5 years. -
Can IoT devices use renewable energy sources?
Yes, IoT devices can use renewable energy sources such as solar power. Energy harvesting technologies are increasingly being integrated into IoT devices to reduce reliance on traditional batteries. -
What are the signs of a failing battery in an IoT device?
Signs of a failing battery in an IoT device include reduced operating time, frequent need for recharging, overheating, and physical swelling of the battery. -
What factors affect the performance of IoT batteries?
Factors affecting the performance of IoT batteries include energy density, voltage requirements, operating temperature, life cycle, size, and environmental conditions.
Related Tags:
More Articles

How to Choose the Best Floor Scrubber Battery for Commercial Cleaning?
Selecting the ideal floor scrubber battery ensures a long runtime, rapid charging, and minimal maintenance for efficient commercial cleaning operations.
Battery for Blower vs Battery for Leaf Vacuum: Which One Should You Choose?
Battery for blower vs leaf vacuum—learn the key differences in power, fit, and runtime to choose the right battery for your outdoor tool needs.
How to Choose the Right Battery for Blower?
Choosing the right blower battery? Consider voltage, capacity, chemistry & usage. This guide helps match the best battery for peak performance.
How to Choose the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries?
Choosing the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries? Discover key factors such as size, material, and safety for optimal protection and performance.
7 Critical Elements on a Lithium Battery Shipping Label
What must be on a lithium battery shipping label? Learn 7 key elements to ensure safety, legal compliance, and correct handling across all transport modes.