- Part 1. What is a lithium-air battery?
- Part 2. How does a lithium-air battery work?
- Part 3. Advantages of lithium-air batteries
- Part 4. Challenges facing lithium-air batteries
- Part 5. Applications of lithium-air batteries
- Part 6. Comparison with other battery technologies
- Part 7. Prospects, advancements, and key players in lithium-air battery research
- Part 8. FAQs
Lithium-air batteries represent a significant advancement in energy storage technology, offering the potential for higher energy densities than traditional lithium-ion batteries. This guide will explore lithium-air batteries’ fundamentals, advantages and challenges, applications, and prospects.
Part 1. What is a lithium-air battery?
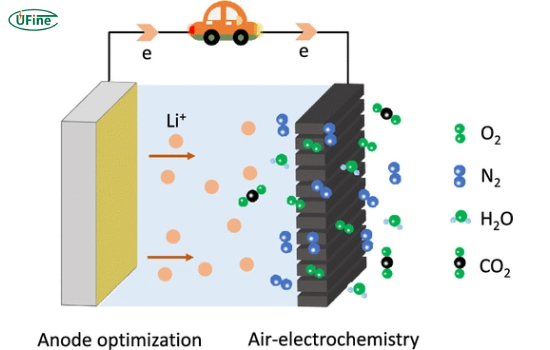
A lithium-air battery is a type of rechargeable battery that uses lithium as the anode and oxygen from the air as the cathode. This unique chemistry allows lithium-air batteries to achieve a theoretical energy density that is significantly higher than that of conventional lithium-ion batteries. The essential operation involves lithium ions moving from the anode to the cathode during discharge, reacting with oxygen to form lithium peroxide or lithium oxide.
Part 2. How does a lithium-air battery work?
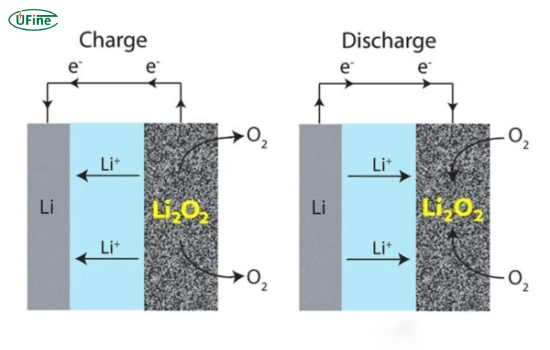
Lithium-air batteries operate through a series of electrochemical reactions. Here’s a simplified breakdown of the process:
- Discharge Cycle: When the battery discharges, lithium ions are released from the anode and travel through the electrolyte to the cathode. These ions react with oxygen at the cathode to form lithium oxide or peroxide.
- Charge Cycle: During charging, the battery decomposes lithium oxide into lithium ions and oxygen, allowing reuse.
A porous cathode facilitates this process by letting oxygen enter while keeping the electrolyte contained.
Part 3. Advantages of lithium-air batteries
Lithium-air batteries offer several advantages over traditional battery technologies:
- High Energy Density: Lithium-air batteries can reach up to 5,000 Wh/kg, far more than the 250 Wh/kg of lithium-ion batteries. This makes them perfect for lightweight and compact energy needs.
- Lightweight: These batteries are lighter because they use air for oxygen. This makes them great for electric vehicles and portable gadgets.
- Environmental Impact: Lithium-air batteries use common materials and may have a smaller environmental impact compared to other batteries.
Part 4. Challenges facing lithium-air batteries
Despite their advantages, lithium-air batteries face several significant challenges:
- Limited Cycle Life: Current lithium-air batteries suffer from a short cycle life, often due to the degradation of the cathode materials during repeated charge and discharge cycles.
- Electrolyte Issues: A significant challenge is to find a suitable electrolyte that can effectively conduct lithium ions while preventing side reactions with the air.
- Performance in Real-World Conditions: The performance of lithium-air batteries can be significantly affected by humidity and temperature, which complicates their practical application.
Part 5. Applications of lithium-air batteries
Lithium-air batteries have potential applications across various sectors, including:
- Electric Vehicles: The high energy density makes them an attractive option for electric vehicles, potentially extending their range significantly.
- Portable Electronics: Lighter batteries can improve the portability and usability of devices like smartphones and laptops.
- Grid Energy Storage: Lithium-air batteries could be used in energy storage systems, helping to balance supply and demand in renewable energy applications.
Part 6. Comparison with other battery technologies
When comparing lithium-air batteries to other prevalent technologies like lithium-ion and lead-acid batteries, several vital differences emerge that highlight their unique strengths and weaknesses.
Lithium-Ion Batteries:
People widely use lithium-ion batteries in consumer electronics and electric vehicles, with energy densities ranging from 150 to 250 Wh/kg. They excel in:
- Cycle Life: Typically lasts between 500 to 1,500 cycles, making them durable for long-term use.
- Efficiency: High charge and discharge efficiencies (over 90%), minimizing energy loss.
- Established Infrastructure: Cost-effective and readily available due to a well-developed supply chain.
Lead-Acid Batteries:
People commonly use lead-acid batteries in automotive and backup power applications, and they have lower energy densities of 30 to 50 Wh/kg. Their advantages include:
- Cost-Effectiveness: Generally cheaper to manufacture, making them budget-friendly.
- Robustness: Can withstand deep discharges and are less sensitive to temperature variations.
- Recyclability: High recycling rates contribute to environmental sustainability.
Lithium-Air Batteries:
Lithium-air batteries offer a theoretical energy density of up to 5,000 Wh/kg, making them promising for lightweight and high-capacity applications. However, they currently face challenges:
- Limited Cycle Life: Typically only 100 to 200 cycles, which limits their practical use.
- Environmental Sensitivity: Performance can be affected by humidity and temperature.
- Material Development: Ongoing research is needed to enhance stability and efficiency.
The following table summarizes the key differences between these battery technologies:
| Feature | Lithium Air | Lithium-Ion | Lead-Acid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | Up to 5,000 Wh/kg | 150-250 Wh/kg | 30-50 Wh/kg |
| Cycle Life | Limited (100-200 cycles) | 500-1,500 cycles | 500-1,000 cycles |
| Weight | Lightweight | Moderate | Heavy |
| Environmental Impact | Low (potentially) | Moderate | High |
Part 7. Prospects, advancements, and key players in lithium-air battery research
The future of lithium-air batteries is promising. Ongoing research is working to solve current challenges. New materials for cathodes and electrolytes are key to better performance and longer life.
Recent progress has improved stability and efficiency. Researchers are testing different cathode materials, including new catalysts to boost reactions. They are also working on better electrolytes to reduce degradation and enhance conductivity.
Several companies and research institutions are in charge of developing lithium-air batteries. Notable players include:
- IBM: Known for its research in battery technology, IBM has been exploring lithium-air batteries for their potential in energy storage.
- A123 Systems: This company is developing advanced battery technologies, including lithium-air systems.
- University Research Labs: Various universities are researching lithium-air batteries, focusing on materials science and electrochemistry.
Part 8. FAQs
-
What is the main advantage of lithium-air batteries?
The primary advantage of lithium-air batteries is their high energy density, which allows for longer-lasting power in a lighter package than traditional batteries. -
Why are lithium-air batteries not widely used yet?
They face challenges such as limited cycle life and performance issues in real-world conditions, which researchers are currently addressing. -
Can lithium-air batteries be recharged?
Yes, designers make lithium-air batteries rechargeable so users can use them multiple times. -
What materials are used in lithium-air batteries?
Lithium-air batteries use lithium for the anode and oxygen from the air for the cathode, along with specialized electrolytes. -
What industries could benefit from lithium-air batteries?
Advances in lithium-air battery technology could greatly benefit industries such as automotive (electric vehicles), consumer electronics, and renewable energy storage.
Related Tags:
More Articles

What are Watts and Watt Hours in Battery?
Understand watt vs watt-hour in batteries, how to calculate battery watt hours, and what Wh means for car batteries, devices, and energy storage.
A Complete Guide to the Best Batteries for Flashlights
Compare the best batteries for flashlights, including AA, AAA, 18650, 21700, CR123A. See which battery offers the best brightness, runtime, and reliability.
How Long Do Rechargeable AA Batteries Last?
How long do rechargeable AA batteries last? Compare NiMH and lithium AA lifespan, recharge cycles, key factors, and performance vs alkaline batteries.
How Much Current Can a 9V Battery Really Supply?
Discover how many amps a 9V battery can supply, its actual current output, discharge rate, and capacity for alkaline, lithium, and rechargeable 9V batteries.
12V STD vs 12V AGM: Meaning, Differences, and Which Is Better
Understand what STD and AGM batteries mean, their key differences, and which 12V battery fits your needs best in 2026.