- Part 1. What is a lithium-sulfur (Li-S) battery?
- Part 2. How do lithium-sulfur batteries Work?
- Part 3. Advantages of lithium-sulfur batteries
- Part 4. Challenges and limitations of lithium-sulfur batteries
- Part 5. How do lithium-sulfur batteries differ from lithium-ion batteries?
- Part 6. Advancements in lithium-sulfur battery technology
- Part 7. Prospects and applications
- Part 8. FAQs
Lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries are emerging as a revolutionary alternative to traditional energy storage technologies. With their high energy density and environmentally friendly materials, they promise to transform various industries, including electric vehicles and renewable energy storage. This guide will delve into the fundamental aspects of Li-S batteries, their advantages, challenges, and how they compare to lithium-ion batteries.
Part 1. What is a lithium-sulfur (Li-S) battery?
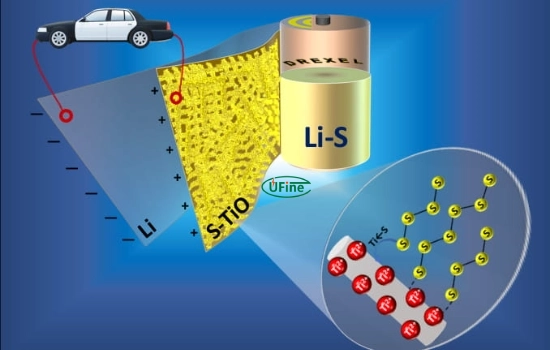
A lithium-sulfur (Li-S) battery is a rechargeable battery that utilizes lithium ions and sulfur in its electrochemical processes. The battery consists of a lithium metal anode, a sulfur-based cathode, and an electrolyte that facilitates the movement of lithium ions between the two electrodes. Li-S batteries are known for their potential to achieve significantly higher energy densities than conventional lithium-ion batteries, making them an attractive option for various applications.
Part 2. How do lithium-sulfur batteries Work?
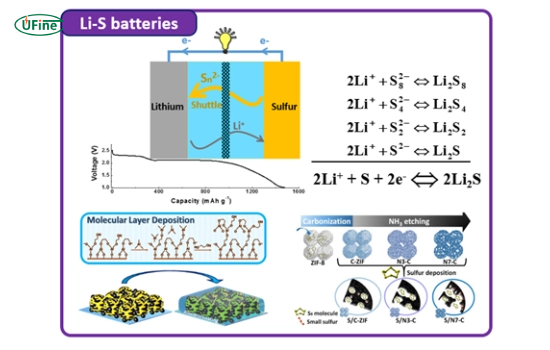
Li-S batteries operate on the principle of a reversible electrochemical reaction between lithium and sulfur. During discharge, lithium ions (Li+) migrate from the anode to the cathode, where they react with sulfur to form lithium polysulfides (Li2Sx, 4 ≤ x ≤ 8). During discharge, polysulfides reduce further to form lithium sulfide (Li2S), the final product. During charging, the reverse occurs as Li2S oxidizes to sulfur. This unique chemistry allows Li-S batteries to achieve high theoretical energy densities of up to 2,600 Wh/kg, significantly higher than lithium-ion batteries.
Part 3. Advantages of lithium-sulfur batteries
- High energy density: Li-S batteries have the potential to achieve energy densities up to five times higher than conventional lithium-ion batteries, making them ideal for applications where weight and volume are critical factors.
- Low cost: Sulfur is an abundant and inexpensive material, which helps to reduce the overall cost of Li-S batteries compared to lithium-ion batteries.
- Environmental friendliness: Sulfur is a non-toxic and environmentally friendly material, making Li-S batteries a more sustainable option than batteries that use heavy metals or other hazardous materials.
Part 4. Challenges and limitations of lithium-sulfur batteries
Despite their numerous advantages, Li-S batteries face challenges that developers must resolve before achieving widespread commercialization.
- Polysulfide shuttling: During cycling, the formation of soluble lithium polysulfides can lead to the “polysulfide shuttle,” where these species migrate between the anode and cathode, causing capacity loss and reduced efficiency.
- Volumetric changes: The significant changes associated with the formation and dissolution of sulfur and lithium sulfides during cycling can lead to mechanical degradation of the electrode materials and reduced cycle life.
- Anode protection: The use of metallic lithium anodes in Li-S batteries can lead to the formation of lithium dendrites, which can cause short circuits and safety issues. Protecting the anode from these issues is a critical challenge.
Part 5. How do lithium-sulfur batteries differ from lithium-ion batteries?
Lithium-sulfur batteries differ from lithium-ion batteries in several key aspects:
- Chemistry: Li-S batteries utilize sulfur as the cathode material, whereas lithium-ion batteries typically use metal oxides or phosphates.
- Energy Density: Li-S batteries have the potential to achieve much higher theoretical energy densities (up to 2,600 Wh/kg) compared to lithium-ion batteries, which typically range from 150 to 250 Wh/kg.
- Cost: The use of abundant and inexpensive sulfur makes Li-S batteries potentially cheaper to produce than lithium-ion batteries that rely on more expensive materials like cobalt and nickel.
- Environmental Impact: Li-S batteries are more environmentally friendly due to the non-toxic nature of sulfur, while lithium-ion batteries often contain heavy metals that can pose environmental hazards.
Lithium-Sulfur Vs. Lithium-Ion Batteries
Part 6. Advancements in lithium-sulfur battery technology
Researchers worldwide are working to address Li-S batteries’ challenges and improve their performance further. Some of the latest advancements include:
- Nanostructured sulfur cathodes: Developing nanostructured sulfur cathodes with high surface area and porous structures can help mitigate the polysulfide shuttling effect and improve active material utilization.
- Electrolyte additives: Electrolyte additives, such as lithium nitrate (LiNO3) and polysulfide compounds, can help stabilize the lithium metal anode and improve the cycling performance of Li-S batteries.
- Separators with polysulfide trapping: Advanced separators with polysulfide trapping mechanisms, such as those based on metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) or conductive polymers, can help to prevent the migration of polysulfides and improve the efficiency of Li-S batteries.
Part 7. Prospects and applications
As Li-S battery technology continues to advance, it is expected to find applications in a wide range of areas, including:
- Electric vehicles: The high energy density of Li-S batteries makes them a promising candidate for use in electric cars, potentially increasing driving range and reducing charging times.
- Portable electronics: Li-S batteries could power various portable electronic devices, such as smartphones, laptops, and wearables, offering longer runtimes and reduced weight.
- Renewable energy storage: Li-S batteries can store energy from renewable sources like solar and wind. This helps balance the grid and boost clean energy adoption.
Part 8. FAQs
-
What are the main components of a lithium-sulfur battery?
The main components of a Li-S battery are a lithium metal anode, a sulfur-based cathode, and an electrolyte solution that facilitates the transfer of lithium ions between the two electrodes. -
What is the polysulfide shuttling effect, and how does it affect the performance of lithium-sulfur batteries?
Polysulfide shuttling refers to the migration of soluble lithium polysulfides between the cathode and anode during cycling. This can lead to capacity loss, reduced efficiency, and accelerated battery degradation. -
How can the volumetric changes associated with lithium-sulfur batteries be addressed?
Researchers are exploring various strategies to mitigate the effects of volumetric changes in Li-S batteries, such as using nanostructured electrode materials, flexible binders, and advanced cell designs. -
What is the current state of commercialization for lithium-sulfur batteries?
Researchers and manufacturers must overcome several technical and economic hurdles before widely commercializing Li-S batteries despite their great promise in the laboratory. However, with ongoing research and development efforts, Li-S batteries are expected to become commercially viable in the coming years.
Related Tags:
More Articles

How Long Do Rechargeable AA Batteries Last?
How long do rechargeable AA batteries last? Compare NiMH and lithium AA lifespan, recharge cycles, key factors, and performance vs alkaline batteries.
12V STD vs 12V AGM: Meaning, Differences, and Which Is Better
Understand what STD and AGM batteries mean, their key differences, and which 12V battery fits your needs best in 2026.
Battery Reconditioning Explained: A Comprehensive Guide
Learn what battery reconditioning is, how it works, how long it takes, and when reconditioning chargers are used for lead-acid and lithium-ion batteries.
Recommended 10 Best Batteries For Smoke Detectors
Compare the best batteries for smoke detectors in 2026. See which 9V lithium and alkaline batteries last longest and perform best in smoke alarms.
Triple A Battery Voltage: Everything You Need to Know
How many volts is a AAA battery? See a clear AAA battery voltage chart, compare alkaline, lithium and NiMH cells, and learn how voltage affects device use.