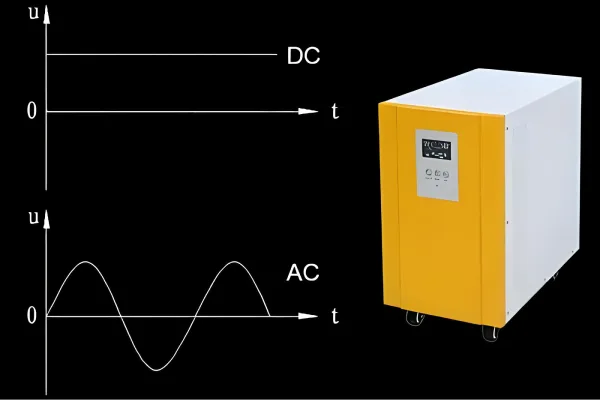
In the world of electricity, two fundamental types of current reign supreme: Direct Current (DC) and Alternating Current (AC). While both are essential for powering our modern world, they differ significantly in their characteristics and applications. DC to AC converters, also known as inverters, play a crucial role in bridging the gap between these two power types, enabling us to utilize DC power sources, such as batteries and solar panels, to power AC devices. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of DC and AC, exploring their advantages and disadvantages, and providing a detailed explanation of how DC to AC converters work, when you need them, and how to choose the right one for your specific needs.
Part 1. Understanding the basics: DC and AC
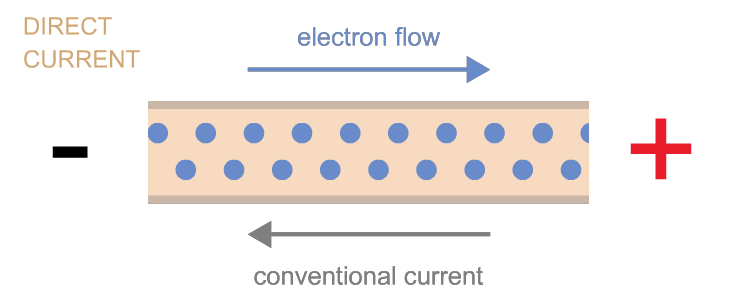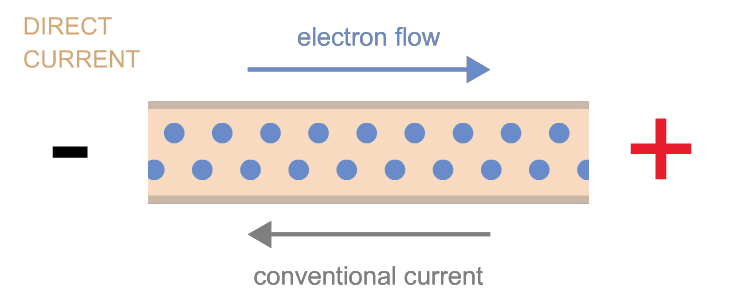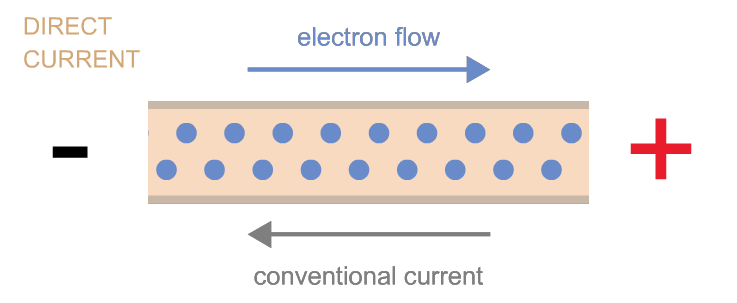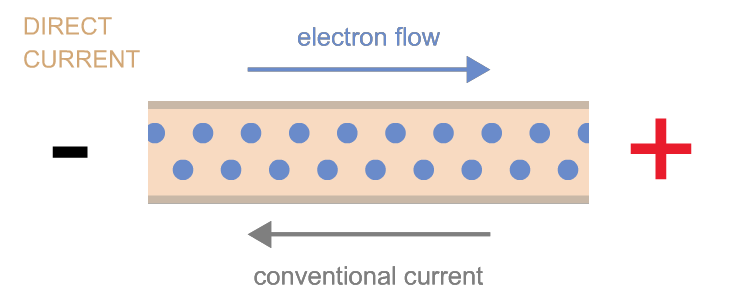
1. Direct Current (DC):
DC, as its name suggests, flows in a single direction. Imagine a river flowing steadily downstream; the water molecules move in a consistent direction, creating a continuous flow. DC power is commonly found in batteries, solar panels, and some electronic devices.
Advantages of DC:
- Stable and Consistent: DC power is inherently stable and consistent, with a constant voltage and current flow. This makes it ideal for powering sensitive electronic devices that require a steady supply of power.
- Easy to Store: DC power is easily stored in batteries, allowing for convenient energy storage and portability.
- Safer: DC power is generally considered safer than AC power, as it does not fluctuate and is less likely to cause electrical shocks.
Disadvantages of DC:
- Limited Transmission Distance: DC power is not as efficient for long-distance transmission as AC power. The voltage drop over long distances can significantly reduce power delivery.
- Limited Device Compatibility: Many common devices, such as appliances, are designed to operate on AC power. Therefore, DC power requires conversion to AC power to be used with these devices.
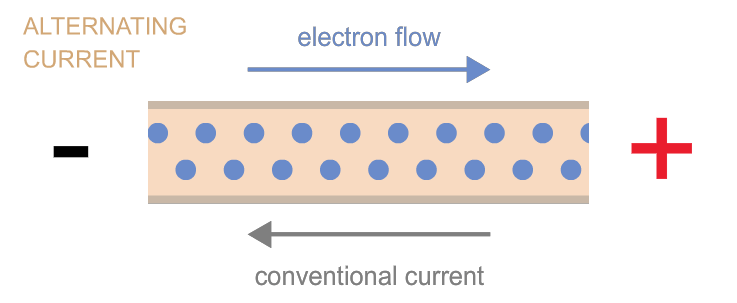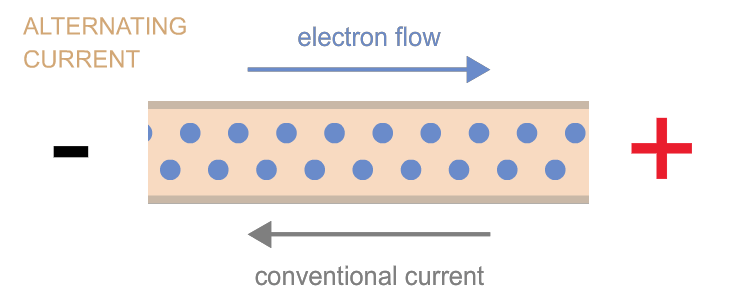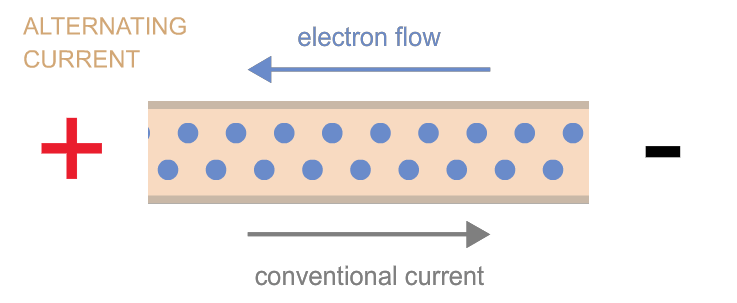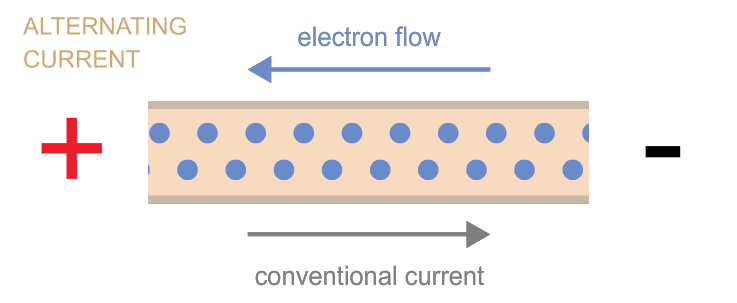
2. Alternating Current (AC):
AC, unlike DC, changes direction periodically. Think of a seesaw moving back and forth; the motion alternates between two directions. AC power is what comes out of your wall outlets and is commonly used to power appliances, electronics, and lighting systems.
Advantages of AC:
- Efficient Long-Distance Transmission: AC power can be transmitted over long distances with minimal energy loss. This is achieved through the use of transformers, which can step up the voltage for efficient transmission and then step it down again for safe use in homes and businesses.
- Wide Device Compatibility: Most modern devices are designed to operate on AC power, making it the dominant power type in homes and industries.
Disadvantages of AC:
- Less Stable: AC power is less stable than DC power, as the voltage and current fluctuate constantly. This can pose challenges for sensitive electronic devices that require a steady power supply.
- Potential Safety Hazards: AC power, due to its fluctuating nature, can be more dangerous than DC power. The alternating current can cause electrical shocks and potentially start fires if not handled properly.
Part 2. What is the DC to AC converter?
The fundamental differences between DC and AC power necessitate the use of DC to AC converters, also known as inverters, to bridge the gap between these two power types. DC to AC converters are essential for powering AC devices from DC sources, such as batteries and solar panels. They convert the direct current flow of DC power into the alternating current flow of AC power, making it compatible with AC devices.
Part 3. How does a DC to AC converter convert DC into AC?
DC to AC converters utilize a combination of electronic circuits to transform DC power into AC power. The process typically involves three main steps:
-
Rectification: The DC power is first fed into a rectifier circuit, which converts the direct current into a pulsating DC signal. This involves converting the unidirectional DC flow into a pulsating waveform that alternates between positive and negative values.
-
Filtering: The pulsating DC signal is then passed through a filter circuit, which smooths out the pulsations and creates a more stable DC signal. This filtering process reduces the ripple effect and produces a smoother waveform closer to a pure DC signal.
-
Inversion: The filtered DC signal is then fed into an inverter circuit, which converts the DC signal into an AC signal. This involves using electronic switches to rapidly switch the polarity of the DC signal, creating an alternating current waveform.
Part 4. Types of DC to AC Converters
DC to AC converters come in various types, each with its own characteristics and applications. Some common types include:
- Modified Sine Wave Inverters: These inverters produce a modified sine wave output, which is less pure than a true sine wave. They are typically more affordable but may not be suitable for all devices, especially sensitive electronics.
- Pure Sine Wave Inverters: These inverters produce a pure sine wave output, which is identical to the AC power from your wall outlets. They are ideal for powering sensitive electronics and appliances that require a clean power source.
Part 5. What is the DC to AC converter used For?
DC to AC converters have a wide range of applications in various sectors, including:
- Off-Grid Power Systems: DC to AC converters are essential for powering homes and businesses that are not connected to the electrical grid. They allow users to utilize solar panels or batteries as their primary power source and convert the DC power into usable AC power.
- Backup Power Systems: DC to AC converters can provide backup power in case of power outages. They can be connected to batteries, which can power essential appliances and electronics during power interruptions.
- Electric Vehicles: DC to AC converters are used in electric vehicles to convert the DC power from the battery into AC power to drive the electric motors.
- Renewable Energy Systems: DC to AC converters are crucial for integrating renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, into the electrical grid. They convert the DC power generated by these sources into AC power, making it compatible with the grid.
Part 6. How to choose a DC to AC inverter?
Selecting the right DC to AC converter depends on your specific needs and the devices you plan to power. Here are some key factors to consider:
- Power Output: Choose a converter with sufficient power output to handle the combined wattage of all the devices you plan to power.
- Waveform: For sensitive electronics and appliances, opt for a pure sine wave inverter, as it provides a cleaner power source. Modified sine wave inverters may suffice for less sensitive devices.
- Efficiency: Consider the efficiency of the converter, as it determines how much energy is lost during the conversion process. Higher efficiency means less energy waste and lower operating costs.
- Features: Look for features such as remote monitoring, battery charging capabilities, and safety features that enhance the functionality and safety of the converter.
Part 7. Final words
DC to AC converters are essential components in the modern world, bridging the gap between DC and AC power and enabling us to utilize DC power sources to power AC devices. By understanding the differences between DC and AC, how DC to AC converters work, and the factors to consider when choosing the right one, you can make informed decisions about your power needs and harness the power of DC to AC conversion. Whether you’re powering a home off-grid, providing backup power during outages, or integrating renewable energy sources, DC to AC converters play a crucial role in ensuring a reliable and sustainable power supply.
Related Tags:
More Articles

How to Choose the Best Floor Scrubber Battery for Commercial Cleaning?
Selecting the ideal floor scrubber battery ensures a long runtime, rapid charging, and minimal maintenance for efficient commercial cleaning operations.
Battery for Blower vs Battery for Leaf Vacuum: Which One Should You Choose?
Battery for blower vs leaf vacuum—learn the key differences in power, fit, and runtime to choose the right battery for your outdoor tool needs.
How to Choose the Right Battery for Blower?
Choosing the right blower battery? Consider voltage, capacity, chemistry & usage. This guide helps match the best battery for peak performance.
How to Choose the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries?
Choosing the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries? Discover key factors such as size, material, and safety for optimal protection and performance.
7 Critical Elements on a Lithium Battery Shipping Label
What must be on a lithium battery shipping label? Learn 7 key elements to ensure safety, legal compliance, and correct handling across all transport modes.