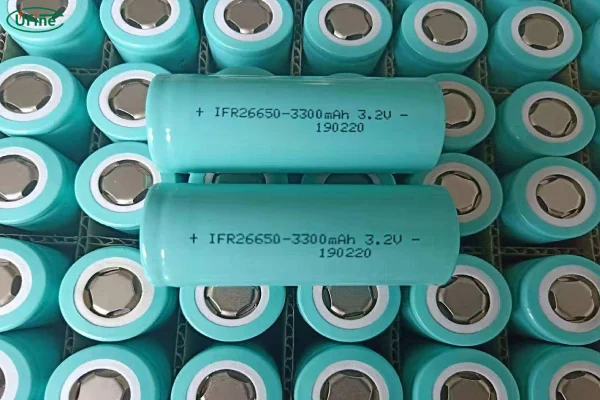
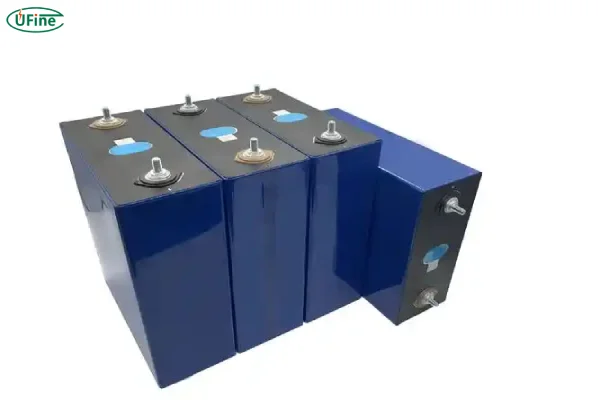
If you’re into electronics or renewable energy systems, you’ve likely heard of 3.2 volt lithium batteries. These batteries have become increasingly popular due to their high energy density, long lifespan, and versatility. But what exactly is a 3.2-volt lithium battery, and why should you care about them?
In this article, we’ll explore everything you need to know about 3.2 volt lithium batteries—from their chemistry and common models to their applications, advantages, and maintenance. Whether you’re planning to use them for off-grid solar storage, an electric vehicle, or DIY projects, you’ll get a comprehensive understanding of these batteries. Let’s dive in!
Part 1. What Is a 3.2 volt lithium battery?
A 3.2-volt lithium battery is a specific type of lithium-ion battery that operates at a nominal voltage of 3.2 volts. Unlike common 3.7-volt lithium batteries, these 3.2-volt batteries typically use lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) chemistry, which provides several distinct advantages, such as enhanced safety and longer cycles.
The 3.2V rating is important because it indicates the average voltage the battery provides during discharge. Lithium iron phosphate batteries are considered safer than other lithium batteries because they are less prone to overheating or catching fire. This makes them a favorite choice in applications requiring both power and safety.
Part 2. Chemistry
When we talk about the chemistry of a 3.2-volt lithium battery, we’re primarily referring to its composition and the electrochemical reaction that occurs within the battery. Most 3.2-volt lithium batteries use lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) as the cathode material.
LiFePO4 chemistry offers several benefits:
- Stable Voltage: LiFePO4 provides a stable discharge voltage (3.2 volts), making it a reliable power source.
- Enhanced Safety: LiFePO4 is known for its thermal stability and resistance to combustion compared to other lithium compounds, such as lithium cobalt oxide.
- Long Life Cycle: These batteries are known for their durability and can endure hundreds to thousands of charge-discharge cycles without significant degradation.
Simply put, the chemistry behind 3.2-volt lithium batteries makes them a safe, efficient, and long-lasting energy solution.
Part 3. Shapes
One of the key benefits of 3.2 volt lithium batteries is their flexibility in terms of shape. Unlike other batteries that may only come in a few standardized forms, 3.2-volt lithium batteries can be designed to fit various types of equipment and configurations.
Here are the common shapes you’ll find:
- Cylindrical 3.2 Volt Lithium Battery: These are the most common shape for 3.2-volt lithium batteries and are often used in applications like power tools, small devices, and portable electronics.
- Prismatic 3.2 Volt Lithium Battery : Prismatic batteries are more compact and are typically used in larger applications like electric vehicles (EVs) or solar energy storage systems. They have a flat, rectangular shape, which is great for efficient space usage.
- Pouch 3.2 Volt Lithium Battery : Flexible and lightweight, pouch-style batteries are used in various consumer electronics and can fit into compact spaces.
Part 4. Common models of 3.2 volt lithium battery
Now, let’s talk about the most common models of 3.2-volt lithium batteries you’ll encounter. The two main types you’ll find are cylindrical cells (18650, 26650) and prismatic cells.
- 18650 (Cylindrical Model): The 18650 cell is one of the most popular lithium battery sizes and is used in everything from laptops to electric bikes. It’s a versatile cell that’s widely available and offers great performance.
- 26650 (Cylindrical Model): A larger version of the 18650, the 26650 is used in higher-power applications like solar storage systems and high-powered tools.
- LiFePO4 Prismatic Cells: These cells are used in higher capacity applications like electric vehicles, large-scale energy storage, and renewable energy systems. They tend to have a higher capacity than cylindrical models.
These models are all reliable options for various energy applications, offering long cycles and stable power output.
Part 5. Common capacity range of 3.2 volt lithium battery
The capacity of a battery is measured in ampere-hours (Ah) or milliampere-hours (mAh). The capacity of a 3.2-volt lithium battery varies depending on the battery’s size, type, and application.
- Small batteries: These typically have a capacity ranging from 500 mAh to 3,000 mAh and are found in devices like flashlights, small electronics, and remote controls.
- Medium-sized batteries: These range from 3 Ah to 10 Ah and are commonly used in power tools, electric bikes, and portable solar setups.
- Large batteries: High-capacity 3.2-volt lithium batteries, typically ranging from 10 Ah to 100 Ah, are used for energy storage systems, RV batteries, and electric vehicles.
The higher the capacity, the longer the battery will last on a single charge, but larger batteries are typically heavier and more expensive.
Part 6. Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages:
- Safety: LiFePO4 is the safest lithium battery chemistry, with a low risk of overheating or fire.
- Longevity: These batteries can last for 2,000+ cycles, much longer than traditional lead-acid batteries.
- Energy Efficiency: Lithium batteries offer higher energy density and efficiency compared to other battery chemistries.
- Low Maintenance: Unlike lead-acid batteries, lithium batteries require less maintenance and are more forgiving during charging and discharging.
Disadvantages:
- Cost: 3.2-volt lithium batteries tend to be more expensive upfront than other types, though their long-term benefits make them cost-effective over time.
- Temperature Sensitivity: Although they’re safer, they can still be sensitive to extreme temperatures. Proper care and installation are needed to maximize lifespan.
- Compatibility: Some older systems may not be compatible with lithium batteries, requiring you to upgrade or adjust your system.
Part 7. Charging and maintenance tips
Charging and maintaining your 3.2-volt lithium battery properly is key to ensuring it lasts for years. Here are a few essential tips:
- Use a Quality Charger: Always use a charger that’s specifically designed for 3.2V lithium batteries. Using the wrong charger can damage the battery and lead to performance issues.
- Avoid Overcharging: Overcharging can degrade the battery’s life. Most modern chargers are equipped with overcharge protection, but it’s still important to avoid leaving batteries on the charger too long.
- Store in a Cool Place: Heat is the enemy of lithium batteries. Always store your batteries in a cool, dry place to maximize their lifespan.
- Avoid Deep Discharge: Regularly discharging the battery all the way down to 0% can harm the battery. Try to keep it between 20% and 80% to maintain its health.
Part 8. Types of 3.2 volt lithium battery chargers
Charging your 3.2-volt lithium battery properly is critical. Here are the common types of chargers available:
- Standard LiFePO4 Battery Charger: These chargers are specifically designed to safely charge lithium iron phosphate batteries like the 3.2V models.
- Solar Chargers: If you’re using 3.2V lithium batteries in a solar power setup, a solar charger with a charge controller is a great option.
- Smart Chargers: Smart chargers automatically adjust the charging rate and provide overcharge protection, ensuring the battery is charged safely.
Part 9. Key parameters to consider when buying a 3.2 volt lithium battery
When purchasing a 3.2V lithium battery, it’s important to keep the following factors in mind:
- Capacity: Choose a capacity that meets your energy needs.
- Voltage: Make sure the battery’s voltage matches the requirements of your device or system.
- Cycle Life: A longer cycle life means the battery will last longer before losing capacity.
- Temperature Tolerance: Choose a battery that performs well in the temperature range where it will be used.
- Discharge Rate: The discharge rate determines how much power the battery can provide at once.
- Compatibility: Ensure the battery is compatible with your existing equipment.
- Price: Consider your budget, keeping in mind that the cheapest option may not always be the best long-term investment.
Part 10. Conclusion
3.2-volt lithium batteries, especially those using LiFePO4 chemistry, offer impressive advantages for a wide range of applications—from solar storage to electric vehicles and portable electronics. While they may come with a higher initial cost, their longevity, safety, and efficiency make them an excellent choice for those who need reliable and sustainable energy.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Paper Battery vs. Flexible Battery: What’s the Difference and Which Is Better?
Paper vs. flexible batteries: learn the key differences, benefits, and which power source fits best for wearables, sensors, and smart tech.
What to Know Before Buying a Tiny LiPo Battery for Your Project
Tiny LiPo batteries are powerful and compact. Learn how to choose the right one for your project with specs, safety, and charging tips.
Bloated LiPo Battery: Will It Explode?
Will a bloated LiPo battery explode? Discover the causes, risks, safety steps, and expert tips to avoid disaster and protect your gear. Must-read safety guide!
12V 100Ah Lithium Ion Battery Price: Full Guide
Learn about 12V 100Ah lithium-ion battery price, from cost ranges to best brands, hidden fees, and how to get the best deal. A must-read for smart buyers!
Resistance and Conductivity: What It Means for Your Lithium Batteries
Resistance and conductivity impact lithium battery performance, lifespan, and safety—learn how they work and why they matter.





