Lithium batteries are a vital part of our daily lives. They power our smartphones, laptops, electric cars, and so much more. But like any technology, they’re not perfect. One of the most common concerns is battery leakage.
Is this something we need to worry about? What causes it, and how can we prevent it? Let’s dive deep into understanding lithium battery leaks and how to handle them safely.
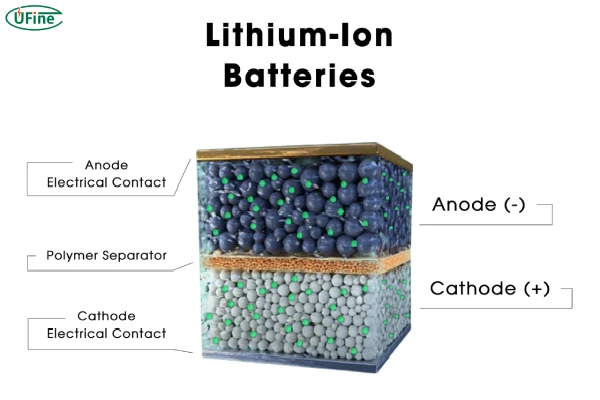
Part 1. The basic components of lithium batteries
To understand why lithium batteries might leak, let’s start with how they’re built. These little powerhouses are made up of four main components:
- Cathode and Anode: These are the positive and negative electrodes. They store lithium ions during the charging and discharging processes.
- Electrolyte: This liquid or gel allows lithium ions to move between the cathode and anode. It’s a crucial component, but it’s also the part most likely to leak.
- Separator: Think of this as a safety net. It keeps the cathode and anode from touching each other, preventing short circuits.
- Casing: This is the tough outer shell that holds everything together and protects the battery from damage.
When these parts work harmoniously, your battery performs well. But if one part fails—like the casing cracking or the electrolyte leaking—problems arise.
Part 2. What is battery leakage?
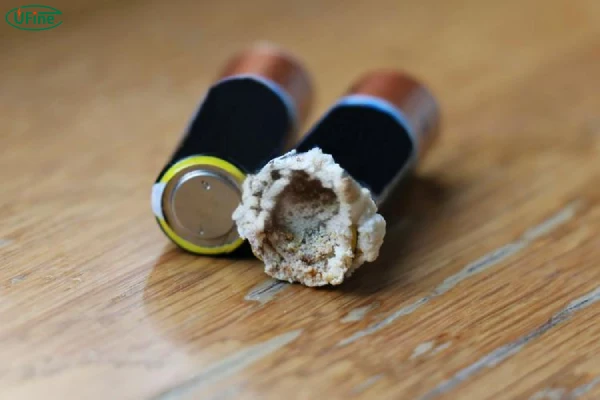
Battery leakage happens when the chemicals inside escape, usually through cracks or damage to the casing. What does it look like? Here’s what you might notice:
- A white, crusty residue around the battery terminals.
- A slimy or oily substance leaking from the casing.
- Swelling, cracks, or physical deformation of the battery.
Learn About the Cathode and Anode of the Battery
Leaking isn’t just a minor inconvenience. It can harm your devices, create safety hazards, and even put your health at risk.
Part 3. Signals of battery leakage
How can you tell if your battery is leaking? Here are some red flags to watch out for:
- Unusual Smells: Leaking batteries often release a chemical odor. If you notice a strange smell around your device, it could be a sign of trouble.
- Swelling or Bulging: A battery that’s swelling is under internal pressure. This is often a precursor to leakage or even explosion.
- Heat: Overheating is another signal. If your device gets unusually hot, turn it off and inspect the battery.
- Corrosion: If the terminals look discolored or corroded, the battery might be leaking.
Ignoring these signs can be dangerous. Always act quickly if you notice anything unusual.
Part 4. What is the leaked liquid? Is it dangerous?
The liquid leaking from a battery is typically the electrolyte. While it’s essential for the battery’s operation, it’s far from safe. Here’s why:
- It’s Toxic: Electrolytes contain chemicals like lithium salts, which can irritate your skin or eyes and harm your lungs if inhaled.
- It’s Corrosive: This liquid can damage your device’s components and corrode metal parts.
- It’s Flammable: Some electrolytes are highly flammable and can catch fire if exposed to heat or sparks.
So yes, it’s dangerous. If you suspect a battery is leaking, take it seriously.
Part 5. Will lithium battery leak?
Lithium batteries contain both liquid electrolytes and solid electrolytes. Theoretically, the probability of lithium batteries leaking is extremely small.
Lithium batteries leak only in certain situations. The main reasons for lithium battery leakage include poor manufacturing quality, improper use, overcharging, mixing of different models of batteries, etc. Lithium battery leakage may cause the battery to fail to work, external deformation, volume expansion, and even cracks. In severe cases, it may cause short circuits and release toxic gases.
In contrast, LiFePO4 Battery is a non-leaking battery. LiFePO4 Battery uses an organic solvent containing lithium salt as the electrolyte. The electrolyte is completely adsorbed on the diaphragm, and there is no flowing liquid, so there is no leakage. This design not only avoids the problem of leakage, but also has the characteristics of large capacity, small size, light weight, high current discharge, and excellent low-temperature performance, which is particularly suitable for high-end and precision digital products.
In contrast, common battery types such as nickel-metal hydride batteries and nickel-cadmium batteries use liquid electrolytes to transfer charge, so if these batteries are damaged or aged, they may leak. The electrolyte of lithium batteries is solid, so even if there is a problem with the battery, the electrolyte inside will not flow out.
Part 6. How to deal with leaking battery?
Handling a leaking battery requires caution. Here’s a step-by-step guide to stay safe:
- Protect Yourself: Wear gloves and avoid direct contact with the leaking liquid. If it gets on your skin, wash thoroughly with soap and water.
- Ventilate the Area: Leaking batteries can release harmful fumes. Open windows or work in a well-ventilated space.
- Handle Carefully: Remove the battery from the device, if possible. Use tools to avoid direct handling.
- Dispose Safely: Don’t toss leaking batteries in the trash! Take them to a recycling center or a hazardous waste disposal site.
- Clean Up Spills: Neutralize any leaked liquid with baking soda or vinegar, depending on the type of electrolyte, and wipe up with disposable materials.
Part 7. Why does battery leak?
Several factors can cause battery to leak. Here’s a closer look:
- Overcharging: Charging a battery beyond its capacity generates heat, which can damage internal components and cause leaks.
- Physical Damage: Dropping or puncturing a battery can crack the casing and let the chemicals out.
- Aging: Batteries don’t last forever. Over time, the materials inside degrade, increasing the risk of leakage.
- Poor Manufacturing: Defective materials or improper assembly during production can lead to leaks.
- Extreme Conditions: High temperatures, excessive moisture, or freezing conditions can compromise the battery’s structure.
Understanding these causes can help you take preventative measures.
Part 8. How to prevent battery from leaking?
Prevention is always better than dealing with a leak. Follow these tips to keep your batteries in good shape:
- Use the Right Charger: Always use a charger recommended by the device manufacturer.
- Avoid Overcharging: Unplug your device once it’s fully charged to prevent overheating.
- Store Properly: Keep batteries in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight or moisture.
- Inspect Regularly: Check batteries for signs of damage or wear before using them.
- Handle with Care: Avoid dropping or puncturing batteries, as physical damage can lead to leaks.
- Replace Old Batteries: Don’t push an aging battery to its limits. Replace it before problems arise.
These habits can significantly extend your battery’s life and reduce the risk of leaks.
Part 9. Can leaking batteries still be used?
This is a hard no. Using a leaking battery is incredibly risky. Here’s why:
- It can damage your device. The leaking electrolyte is corrosive and may ruin internal components.
- It poses safety hazards. Leaking batteries can overheat, catch fire, or even explode.
- It’s a health risk. Handling leaking batteries exposes you to toxic chemicals.
If you find a leaking battery, don’t try to fix or reuse it. Dispose of it properly and replace it with a new one.
Part 10. Conclusion
Lithium batteries are reliable and efficient, but they’re not invincible. Understanding the causes and risks of battery leakage can help you prevent it and deal with it safely when it happens.
Take care of your batteries, and they’ll take care of your devices!
Related Tags:
More Articles

How to Choose the Best Floor Scrubber Battery for Commercial Cleaning?
Selecting the ideal floor scrubber battery ensures a long runtime, rapid charging, and minimal maintenance for efficient commercial cleaning operations.
Battery for Blower vs Battery for Leaf Vacuum: Which One Should You Choose?
Battery for blower vs leaf vacuum—learn the key differences in power, fit, and runtime to choose the right battery for your outdoor tool needs.
How to Choose the Right Battery for Blower?
Choosing the right blower battery? Consider voltage, capacity, chemistry & usage. This guide helps match the best battery for peak performance.
How to Choose the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries?
Choosing the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries? Discover key factors such as size, material, and safety for optimal protection and performance.
7 Critical Elements on a Lithium Battery Shipping Label
What must be on a lithium battery shipping label? Learn 7 key elements to ensure safety, legal compliance, and correct handling across all transport modes.