Selecting the right battery port is crucial when dealing with electronic devices, vehicles, or any system that requires power. A battery port is the key point of connection where a battery links to the device it powers. These ports come in various types, each designed to handle specific applications. Knowing their differences can help you make an informed decision and ensure your equipment’s efficiency, safety, and longevity.
In this article, we’ll explore the different types of battery ports, their unique features, and how to choose the one that fits your needs.
Part 1. What is a battery port?
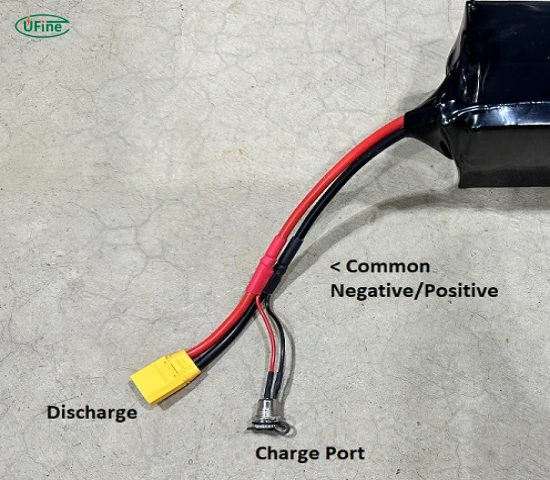
A battery port is the interface between the battery and the powered device. It allows electricity to flow from the battery to the device, ensuring proper functioning. Battery ports come in different shapes and sizes, each designed for specific electrical needs, power capacities, and environmental conditions.
The Importance of Battery Ports
- Power delivery: Smooth and reliable energy transfer from the battery to the device.
- Safety: Protecting against short circuits, overloading, or overheating.
- Durability: Withstanding frequent use, wear, and external conditions.
Choosing the right type of battery port can significantly impact the performance and lifespan of your equipment.
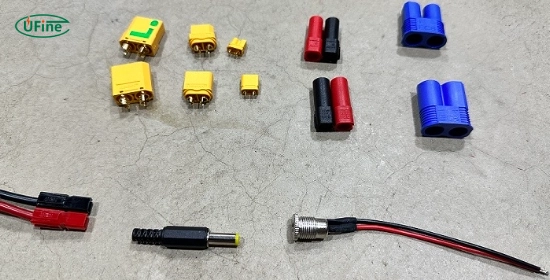
Part 2. Common types of battery ports
1. Anderson Powerpole Connectors
Anderson Powerpole connectors are widely used in high-power applications. These connectors provide a secure, low-resistance connection and can handle higher current levels than more miniature connectors. They’re commonly used in amateur radio, robotics, and electric vehicles.
Advantages: High current capacity, durable, and secure.
Disadvantages: Larger sizes may not suit compact devices.
2. DC Barrel Connectors
DC barrel connectors are small, cylindrical battery ports in consumer electronics like routers, cameras, and LED lighting systems. They are designed for low—to medium-power applications and are often used for devices that require continuous power.
Advantages: Compact and easy to use.
Disadvantages: Limited to lower current applications.
3. XT60 Connectors
XT60 connectors are primarily used in the RC (remote control) and drone industries. They are built to handle currents up to 60A, making them ideal for powering high-demand equipment like drones and remote-controlled vehicles.
Advantages: Secure connection, high current rating, and easy to connect/disconnect.
Disadvantages: They are more significant than other connectors, making them less ideal for compact devices.
4. USB Battery Ports
With the rise of personal electronics, USB battery ports have become the go-to for charging smartphones, tablets, and laptops. USB ports come in various forms, including USB-A, USB-C, and micro-USB. The latest USB-C port is known for its faster charging capabilities and universal compatibility.
Advantages: Widely available, easy to use, and fast charging with USB-C.
Disadvantages: Not suitable for high-power applications.
5. SAE Connectors
SAE connectors are a popular choice in the automotive and recreational vehicle industries. These battery ports connect batteries in vehicles, motorcycles, and RVs. They are simple, reliable, and cost-effective for low—to medium-current applications.
Advantages: Easy to use, affordable, and accessible.
Disadvantages: Limited to moderate current handling.
Part 3. How to choose the right battery port for your application?
Choosing the appropriate battery port for your device or system involves several factors, including power requirements, size constraints, and environmental conditions. Here are some tips to help you choose the right one:
- Power requirements: High-power devices like drones or electric vehicles need connectors that can handle high currents. Anderson Powerpole connectors or XT60 connectors are ideal for these applications.
- Size constraints: More miniature DC barrel connectors or USB ports are more practical for compact devices.
- Durability: If your device is used outdoors or in rugged environments, opt for more robust connectors like SAE or XT60.
Part 4. Battery ports in electric vehicles
Electric vehicles (EVs) have specific charging requirements, so selecting the proper battery port is critical. There are different types of EV charging ports:
- Level 1 charging port: A standard 120V outlet. It’s slow but can be convenient for home charging.
- Level 2 charging port: A 240V outlet offering faster charging speeds.
- DC fast charging port: The fastest charging option in commercial EV chargers.
Each of these ports has its benefits, with Level 2 and DC fast charging ports providing much quicker charging times than Level 1 ports.
Part 5. Battery ports in solar power systems
Battery ports are essential for connecting solar panels, charge controllers, and batteries for solar energy systems. The MC4 connector is the most commonly used in solar setups because it is waterproof, durable, and can handle high-voltage output.
MC4 connectors: These connectors are designed to handle the high-voltage output from solar panels, ensuring a secure connection.
Anderson Powerpole: For larger solar setups, Anderson Powerpole connectors handle higher currents.
Part 6. Key factors to consider when selecting a battery port
Several key factors influence the selection of the best battery port for your needs. Consider the following when making your decision:
- Voltage and current requirements: Ensure the port supports your device’s appropriate voltage and current. Higher-power applications need more robust connectors, such as XT60 or Anderson Powerpole.
- Environmental conditions: If the port is exposed to rain, dirt, or other harsh elements, opt for weather-resistant or waterproof options like MC4 connectors.
- Compatibility: Make sure the port and battery are used to fit your device. This includes checking for connector compatibility and the type of cable required.
Part 7. Battery port maintenance
Maintaining battery ports is vital to ensuring their longevity and functionality. Here are some tips to help you keep them:
- Check for corrosion: Corrosion on the connectors can affect your system’s performance. Regularly inspect and clean the ports.
- Ensure tight connections: Loose connections can cause power loss or damage to the device. Always check that the port and cable are correctly connected.
- Use anti-corrosion sprays: These can help prevent rust and corrosion, especially in outdoor or marine environments.
Part 8. Common problems with battery ports
Despite their durability, battery ports can experience problems over time. Some common issues include:
- Loose connections: This may cause inconsistent power supply and system malfunction.
- Corrosion: Exposure to moisture or dirt can result in corrosion, reducing the effectiveness of the connection.
- Damaged pins or connectors: Wear and tear can cause connectors to become bent or damaged, leading to poor connections.
Part 9. Future trends in battery port technology
As technology evolves, battery port designs are becoming more efficient and user-friendly. Some trends include:
- Wireless charging: Soon, wireless battery ports may eliminate the need for physical connectors, offering a more convenient and universal solution.
- Faster charging options: With the increasing demand for faster power delivery, expect the development of battery ports that support even quicker charging speeds without compromising safety.
Artikel Terkait: 10 Frequently Asked Questions about Battery Terminals
Part 10. FAQs
-
What is the most common type of battery port?
The most common battery port is the USB port, especially in consumer electronics. For higher power applications, Anderson Powerpole or XT60 connectors are often used. -
How do I know which battery port is correct for my device?
Consider your device’s power requirements, size constraints, and durability. High-power devices need robust connectors like Anderson Powerpole or XT60 connectors. In contrast, low-power devices can use USB or DC barrel connectors. -
Can I use a high-current battery port for a low-power device?
Yes, you can use a high-current battery port for a low-power device. Still, it might be unnecessarily large for the application. It’s better to match the port to your device’s power requirements. -
Are there any battery ports designed for outdoor use?
Yes, connectors like MC4 and XT60 are designed to handle outdoor environments and high power. These connectors are often used in solar setups and rugged outdoor equipment. -
How do I maintain battery ports?
Regularly inspect the connectors for corrosion, ensure the connections are tight, and clean the ports to remove dirt or grime. Using anti-corrosion spray can also help protect the connectors in harsh environments.
Related Tags:
More Articles

How to Improve Battery Performance Using a Voltage Regulator Lithium?
Learn how lithium voltage regulators improve battery performance, extend lifespan, and optimize efficiency in devices and systems.
What Is an Oxide Battery and How Does It Differ from Other Types of Batteries?
Oxide batteries are a unique technology with potential for various uses. Learn about their functions, advantages, and how they differ from other types.
Is a Tesla with LFP Batteries Right for You?
Learn why Tesla's LFP battery is a smart choice for electric vehicles. See how it offers efficiency and reliability. Dive into the details!
The Truth About 12V 200Ah LiFePO4 Battery Lifespan
Wondering how long a 12V 200Ah LiFePO4 battery lasts? Discover its lifespan and tips to extend it. Learn more today.
What Is a Battery Port and How Does It Impact Battery Performance?
Battery ports are crucial for device performance. Learn how they work and impact battery life to optimize your devices and extend battery efficiency.