Lithium Polymer (LiPo) batteries are widely used in various applications, including drones, RC cars, electric vehicles, and consumer electronics. Their high energy density and lightweight properties make them an excellent choice for modern high-performance applications. In this guide, we will explore key specifications such as capacity, energy density, charge/discharge rate, voltage, cycle life, internal resistance, self-discharge, operating temperature range, safety features, charging efficiency, and storage recommendations.
Part 1. Capacity (Ah)
Capacity is a crucial specification for LiPo batteries, determining how much charge they can store and deliver. It is measured in ampere-hours (Ah), indicating the total charge a battery can provide under specific conditions. For instance, a 48V 200Ah LiPo battery can store 48V * 200Ah = 9.6kWh (9.6 kilowatt-hours) of energy.
Types of Capacity
-
Actual Capacity: The charge a LiPo battery can deliver under real-world conditions, influenced by temperature, discharge rate, and voltage limits.
-
Theoretical Capacity: The maximum possible charge a battery could deliver if all active material participated in the reaction.
-
Rated Capacity: The value specified by manufacturers based on controlled testing conditions.
Factors like temperature can significantly impact capacity. For example, in cold climates, smartphone LiPo batteries discharge faster due to reduced chemical activity.
For customized LiPo battery solutions tailored to your specific needs, Ufine Battery is a trusted Chinese manufacturer specializing in lithium-ion, LiPo, 18650, LiFePO4, and special-shaped batteries. We offer bespoke battery solutions in different sizes, shapes, voltages, and capacities. Contact Ufine Battery today for expert battery customization!
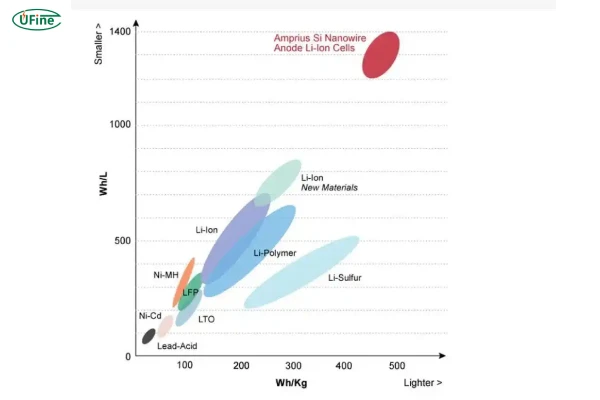
Part 2. Energy density (Wh/kg or Wh/L)
Energy density defines how much energy a LiPo battery can store relative to its weight (Wh/kg) or volume (Wh/L). It is a critical factor in applications where space and weight are limited.
Current LiPo batteries typically have an energy density of 100–200Wh/kg. However, for electric vehicles to achieve a 500km range comparable to gasoline-powered cars, battery energy density must exceed 300Wh/kg.
Unlike Moore’s Law in semiconductors, LiPo battery energy density improves slowly, creating a gap between growing power demands and battery advancements.
Part 3. Charge/discharge rate (C-Rate)
The charge and discharge rate (C-rate) indicates how fast a LiPo battery can be charged or discharged. For example:
-
A 20Ah battery rated at 0.5C can be charged or discharged at 10A.
-
A maximum discharge rate of 10C@10s means it can sustain a 200A discharge for 10 seconds.
Higher C-rates require advanced battery management to prevent overheating and degradation. LiPo batteries used in drones and RC vehicles often require high discharge rates to sustain performance.
Part 4. Voltage (V)
LiPo battery voltage is a fundamental characteristic influencing performance:
-
Open-Circuit Voltage (OCV): Voltage when the battery is idle.
-
Operating Voltage: Voltage under load conditions, typically lower than OCV due to internal resistance.
-
Charge Cutoff Voltage: Maximum allowable charge voltage.
-
Discharge Cutoff Voltage: Minimum allowable voltage before damage occurs.
Exceeding voltage limits can lead to irreversible damage, overheating, and even safety hazards like fires or explosions.
Part 5. Cycle life & depth of discharge (DoD)
Cycle life refers to how many charge-discharge cycles a LiPo battery can endure before capacity drops significantly. Depth of discharge (DoD) plays a key role:
-
Shallow Discharge (<25% DoD): Extends battery lifespan.
-
Deep Discharge (80% DoD): Common in high-performance applications but reduces longevity.
Smartphones provide a practical example: Initially, a phone may require charging once per day, but after hundreds of cycles, battery degradation results in more frequent charges.
Cycle Life vs. Calendar Life
-
Cycle Life: Number of charge/discharge cycles until 20% capacity loss.
-
Calendar Life: Total usable lifespan considering idle storage, temperature fluctuations, and usage patterns.
Manufacturers often specify cycle life but not calendar life due to its complexity. For accurate estimations, real-world testing is necessary.
Part 6. Internal resistance (Ω)
Internal resistance affects how efficiently a LiPo battery delivers power. It consists of:
-
Ohmic Resistance: Arises from electrode materials, electrolytes, and connectors.
-
Polarization Resistance: Includes electrochemical and concentration polarization.
Higher internal resistance leads to greater power loss, heat generation, and reduced lifespan. Low-resistance LiPo batteries perform better in high-drain applications.
Part 7. Self-discharge rate
Even when not in use, LiPo batteries gradually lose charge. Self-discharge is measured as a percentage of lost capacity per month. Minimizing self-discharge is crucial for longevity, especially in stored batteries.
Over-discharge from prolonged storage can cause irreversible damage. Therefore, periodic recharging is recommended for long-term storage.
Part 8. Operating temperature range
LiPo batteries have an optimal temperature range, typically -20°C to 60°C. Performance varies based on environmental conditions:
-
High Temperatures: Increase degradation and risk of thermal runaway.
-
Low Temperatures: Reduce capacity and discharge efficiency.
Storing LiPo batteries outside recommended temperature limits can permanently degrade performance. Proper thermal management is essential, especially in electric vehicles and aerospace applications.
Part 9. Safety features
Modern LiPo batteries include safety mechanisms such as:
-
Overcharge Protection to prevent voltage exceeding safe limits.
-
Short-Circuit Protection to avoid electrical faults.
-
Thermal Cutoff to shut down in extreme heat conditions.
Part 10. Charging efficiency
Efficient charging ensures long battery life. LiPo batteries typically charge best with dedicated balance chargers that prevent overcharging and ensure even cell distribution.
Part 11. Storage recommendations
Proper storage extends battery life. For long-term storage, LiPo batteries should be kept at 40-60% charge in a cool, dry place. Avoid storing them fully charged or completely discharged.
Part 12. FAQs
What is the best way to extend the lifespan of a LiPo battery?
To maximize lifespan, avoid deep discharges, use a balance charger, store at 40-60% charge, and keep within the recommended temperature range.
Can LiPo batteries explode or catch fire?
Yes, if overcharged, punctured, or exposed to extreme temperatures. Always follow safety guidelines and use quality chargers with overcharge protection.
How do I properly dispose of a LiPo battery?
Never throw a LiPo battery in regular trash. Fully discharge it in saltwater (if safe) and take it to a certified e-waste or battery recycling facility.
What is the difference between soft-case and hard-case LiPo batteries?
Soft-case LiPo batteries are lighter and used in drones and RC planes, while hard-case ones offer better physical protection, ideal for RC cars and rugged applications.
Can I charge my LiPo battery with any charger?
No, always use a LiPo-specific balance charger to prevent overcharging, undercharging, or unbalanced cells, which can reduce lifespan or cause safety hazards.
Why do LiPo batteries have multiple cells (e.g., 3S, 4S, etc.)?
Each cell provides a nominal voltage of 3.7V. A 3S LiPo has three cells (11.1V), and a 4S has four cells (14.8V). More cells mean higher voltage and power.
Related Tags:
More Articles

How to Choose the Best Floor Scrubber Battery for Commercial Cleaning?
Selecting the ideal floor scrubber battery ensures a long runtime, rapid charging, and minimal maintenance for efficient commercial cleaning operations.
Battery for Blower vs Battery for Leaf Vacuum: Which One Should You Choose?
Battery for blower vs leaf vacuum—learn the key differences in power, fit, and runtime to choose the right battery for your outdoor tool needs.
How to Choose the Right Battery for Blower?
Choosing the right blower battery? Consider voltage, capacity, chemistry & usage. This guide helps match the best battery for peak performance.
How to Choose the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries?
Choosing the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries? Discover key factors such as size, material, and safety for optimal protection and performance.
7 Critical Elements on a Lithium Battery Shipping Label
What must be on a lithium battery shipping label? Learn 7 key elements to ensure safety, legal compliance, and correct handling across all transport modes.