- Part 1. What is a USB rechargeable cell?
- Part 2. USB rechargeable cell history
- Part 3. Types of rechargeable cells
- Part 4. Types of battery charging ports
- Part 5. What makes USB rechargeable cells unique?
- Part 6. USB rechargeable cell pros and cons
- Part 7. USB rechargeable cell chargers
- Part 8. USB rechargeable cell charging tips
- Part 9. Conclusion
In a world increasingly reliant on technology, the demand for portable and sustainable power sources has grown exponentially. USB rechargeable cells have emerged as a revolutionary solution, blending convenience with eco-friendliness. They eliminate the need for traditional chargers and bring a modern twist to battery technology. But what makes these cells so special? How do they work, and why should you consider them over other options? In this detailed guide, we’ll explore everything about USB rechargeable cells, from their unique features to charging tips that maximize their lifespan.
Part 1. What is a USB rechargeable cell?
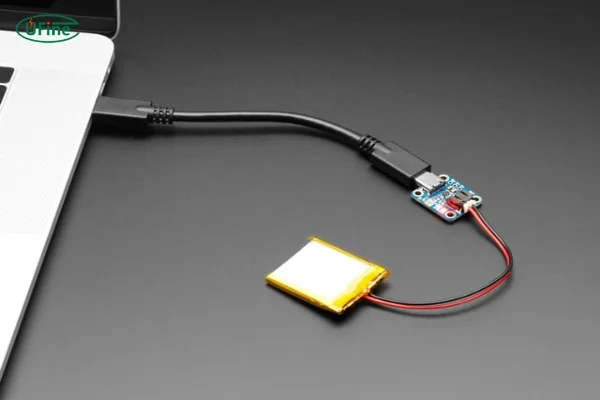
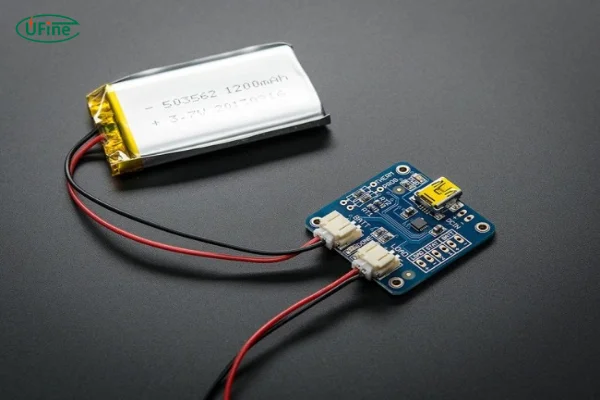
At its core, a USB rechargeable cell is a type of battery designed with convenience in mind. These batteries integrate a built-in charging circuit, allowing them to be recharged directly using a USB cable. Unlike standard rechargeable batteries that require separate charging devices, USB rechargeable cells can plug into almost any USB port, whether on a laptop, power bank, or wall adapter.
These cells are most commonly powered by lithium-ion (Li-ion) technology, known for its high energy density and longevity. What sets them apart is their versatility—they’re perfect for powering everyday devices like flashlights, toys, remote controls, and more.
Imagine never needing to hunt for a proprietary charger again or reducing your reliance on disposable batteries that harm the environment. USB rechargeable cells combine practicality with sustainability, making them an essential innovation in modern energy solutions.
Part 2. USB rechargeable cell history
The story of USB rechargeable cells begins with the convergence of two groundbreaking technologies: rechargeable batteries and USB ports. While rechargeable batteries have been around since the late 19th century, it wasn’t until the 21st century that the idea of integrating USB technology into battery design became feasible.
Who Invented the USB Rechargeable Cell?
The concept of USB rechargeable batteries was pioneered by forward-thinking engineers in the early 2010s. Among the first companies to commercialize the idea was Pale Blue, a company focused on creating innovative, eco-friendly power solutions. They introduced lithium-ion rechargeable batteries with built-in Micro-USB ports, a groundbreaking development in battery technology.
When Was It Invented?
The first USB rechargeable cells entered the consumer market around 2013-2015. This period marked the initial integration of USB charging circuits directly into battery housings, eliminating the need for separate chargers. The innovation quickly gained traction due to the growing ubiquity of USB ports and the rising demand for portable and sustainable energy solutions.
Historical Evolution of USB Rechargeable Cells
-
Early Rechargeable Batteries (1859-1900s):
Rechargeable batteries, such as lead-acid and nickel-cadmium, were developed in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. These early versions were bulky and limited to industrial use. -
The Rise of Lithium-Ion Technology (1990s):
Lithium-ion batteries revolutionized the rechargeable battery market with their high energy density and lightweight design. This technology laid the foundation for USB rechargeable cells. -
USB Port Standardization (1996-2000s):
The adoption of USB as a universal charging and data transfer standard created the infrastructure necessary for USB rechargeable batteries to thrive. -
Integration of USB Charging (2013-2015):
The first USB rechargeable cells were introduced, featuring built-in charging circuits compatible with Micro-USB ports. These batteries were designed for convenience and compatibility with widespread USB infrastructure. -
Advancements in USB-C Technology (2018-Present):
With the rise of USB-C, USB rechargeable cells have become even more efficient. The integration of USB-C ports allows faster charging and broader compatibility with modern devices.
The Future of USB Rechargeable Cells
As USB technology continues to evolve, the potential for USB rechargeable cells grows. Innovations like higher-capacity lithium-ion chemistry, faster charging speeds, and even wireless charging integration are on the horizon. With their unique blend of convenience, sustainability, and adaptability, USB rechargeable cells are set to play a key role in the future of energy storage.
Part 3. Types of rechargeable cells
Rechargeable batteries are available in several types, each suited to specific uses. Here’s a breakdown:
Nickel-Cadmium (NiCd)
- Advantages: Durable and capable of handling high discharge rates.
- Disadvantages: Prone to memory effect (loss of capacity over time) and environmentally unfriendly due to toxic cadmium.
Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH)
- Advantages: Higher capacity than NiCd and less prone to memory effect.
- Disadvantages: Shorter lifespan and self-discharge when not in use.
Lithium-Ion (Li-ion)
- Advantages: Lightweight, high energy density, and long lifespan.
- Disadvantages: More expensive and sensitive to extreme temperatures.
Lithium-Polymer (LiPo)
- Advantages: Thin, flexible, and ideal for compact devices.
- Disadvantages: More expensive and requires careful handling to prevent damage.
Most USB rechargeable cells rely on Li-ion technology, offering the perfect balance between performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
NiMH Battery vs Li-Ion Battery vs NiCad Battery: How are they different?
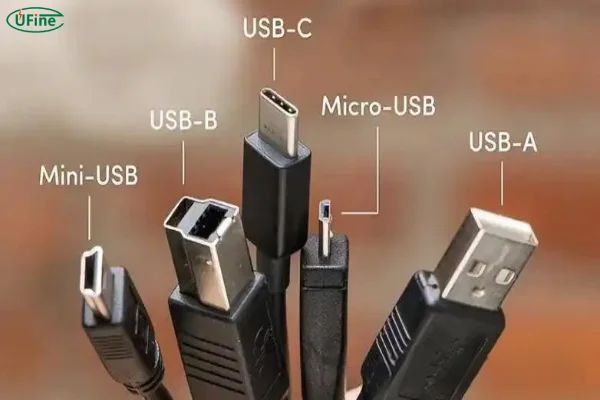
Part 4. Types of battery charging ports
USB rechargeable cells utilize different types of charging ports, which determine their compatibility and charging speed.
Micro-USB
- Common in older devices and budget-friendly products.
- Offers slower charging speeds compared to newer standards.
USB-C
- Modern, fast, and reversible, making it easier to plug in.
- Supports higher power delivery, enabling quicker charging.
Mini-USB
- Rarely used today; found in older gadgets.
- Bulkier and less efficient compared to newer port types.
Lightning (Apple)
- Proprietary to Apple devices, not typically used in USB rechargeable cells.
Most USB rechargeable cells favor Micro-USB or USB-C ports for their wide compatibility and ease of use. USB-C, in particular, is becoming the preferred choice due to its superior charging capabilities.
Part 5. What makes USB rechargeable cells unique?
USB rechargeable cells offer several features that set them apart from other rechargeable options.
Built-in Charging Circuitry
Traditional rechargeable batteries require a separate charger, often specific to the battery type. USB rechargeable cells eliminate this hassle, incorporating the charging mechanism directly into the battery.
Universal Compatibility
Whether you’re at home, in the office, or on the road, you can charge these batteries anywhere with a USB port. This universality means fewer accessories to carry and greater convenience.
Sustainability
By reducing reliance on disposable batteries, USB rechargeable cells minimize electronic waste, making them an eco-friendly choice.
Portability
Their compact design and ability to charge on the go make them ideal for travelers, outdoor enthusiasts, and emergency kits.
These features make USB rechargeable cells a practical and forward-thinking solution for modern energy needs.
Part 6. USB rechargeable cell pros and cons
Pros:
- Convenience: Charge directly using USB cables—no need for additional chargers.
- Cost-Effective: Save money over time by avoiding disposable batteries.
- Eco-Friendly: Reduces waste and supports sustainability.
- Versatility: Works with a wide range of devices.
- Portability: Easy to carry and charge anywhere.
Cons:
- Initial Cost: Slightly more expensive than traditional rechargeable batteries.
- Charging Speed Variability: Dependent on the port type (e.g., USB-C is faster than Micro-USB).
- Capacity Limitations: May not match the energy capacity of some non-USB rechargeable batteries.
Understanding these advantages and disadvantages can help you make an informed decision about whether USB rechargeable cells are the right choice for your needs.
Part 7. USB rechargeable cell chargers
While USB rechargeable cells are designed to work with standard USB ports, the type of charger you use can affect their performance and longevity.
Recommended Chargers:
- USB Wall Adapters: Provide fast and reliable charging.
- Power Banks: Great for on-the-go charging, especially during travel.
- Laptop/PC USB Ports: Convenient for desk use, though typically slower.
Tips for Choosing a Charger:
- Look for adapters with appropriate voltage and amperage to match the cell’s specifications.
- Avoid low-quality chargers, as they may cause overheating or damage.
Part 8. USB rechargeable cell charging tips
To maximize the performance and lifespan of your USB rechargeable cells, follow these essential tips:
- Use the Right Charger: Stick to chargers with recommended power output.
- Avoid Overcharging: Disconnect the battery once it’s fully charged to prevent damage.
- Charge Before Fully Depleting: Lithium-ion cells last longer when charged before they completely run out.
- Store Properly: Keep batteries in a cool, dry place when not in use. Avoid exposing them to extreme heat or cold.
- Inspect Regularly: Check for physical damage or wear to avoid potential safety risks.
By adopting these practices, you’ll ensure your USB rechargeable cells deliver reliable performance for years to come.
Part 9. Conclusion
USB rechargeable cells are more than just a modern convenience—they represent a step forward in sustainable energy solutions. By understanding their unique features, benefits, and proper usage, you can make the most of this innovative technology. Whether you’re looking to reduce waste, save money, or enjoy the convenience of charging anywhere, USB rechargeable cells are an investment worth considering.
Related Tags:
More Articles

What are Watts and Watt Hours in Battery?
Understand watt vs watt-hour in batteries, how to calculate battery watt hours, and what Wh means for car batteries, devices, and energy storage.
A Complete Guide to the Best Batteries for Flashlights
Compare the best batteries for flashlights, including AA, AAA, 18650, 21700, CR123A. See which battery offers the best brightness, runtime, and reliability.
How Long Do Rechargeable AA Batteries Last?
How long do rechargeable AA batteries last? Compare NiMH and lithium AA lifespan, recharge cycles, key factors, and performance vs alkaline batteries.
How Much Current Can a 9V Battery Really Supply?
Discover how many amps a 9V battery can supply, its actual current output, discharge rate, and capacity for alkaline, lithium, and rechargeable 9V batteries.
12V STD vs 12V AGM: Meaning, Differences, and Which Is Better
Understand what STD and AGM batteries mean, their key differences, and which 12V battery fits your needs best in 2026.