The lithium polymer battery, also known as a polymer lithium battery, is a chemical battery. Compared to earlier battery technologies, it possesses high energy, miniaturization, and lightweight design characteristics. Lithium polymer batteries exhibit ultra-thin properties, enabling them to meet the requirements of specific products. You can shape them into various forms and capacities, with a theoretical minimum thickness of up to 0.5mm.
Part 1. Lithium battery components
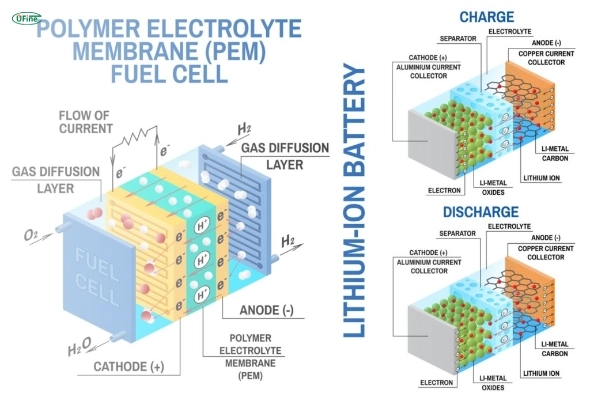
Battery Anode
The anode is the negative side of the battery. It typically consists of graphite, a form of carbon. The anode is crucial in storing and releasing lithium ions during the charge and discharge cycles.
Material:
- Typically graphite.
- You can also make it from other carbon-based materials.
Function:
- Stores lithium ions when the battery charges.
- Releases lithium ions when the battery discharges.
Battery Cathode
The cathode is the positive side of the battery. Manufacturers make it from lithium metal oxides, such as lithium cobalt oxide or lithium iron phosphate. The cathode determines the battery’s voltage and capacity.
Material:
- Common materials include lithium cobalt oxide, iron phosphate, and manganese oxide.
Function:
- Releases lithium ions during charging.
- Accepts lithium ions during discharging.
Battery Electrolyte
The electrolyte is a chemical medium that allows lithium ions to move between the anode and cathode. In lithium polymer batteries, the electrolyte is usually a solid or gel-like substance.
Material:
- Polymer gel or solid-state electrolyte.
- Contains lithium salts.
Function:
- Conducts lithium ions.
- Separates the anode and cathode to prevent short circuits.
Battery Separator
The separator is a thin, porous membrane between the anode and cathode. It prevents the electrodes from touching each other while allowing lithium ions to pass through.
Material:
- Made from a microporous polymer film.
Function:
- Prevents short circuits.
- Allows ionic movement.
Battery Current Collectors
Current collectors are thin metal foils that carry electrons to and from the electrodes. The anode current collector is usually copper, while the cathode current collector is aluminum.
Material:
- Copper for the anode.
- Aluminum for the cathode.
Function:
- Conducts electrons.
- Connects the battery to the external circuit.
Part 2. How lithium polymer batteries work?
1. Basic Operation
Lithium polymer batteries move lithium ions between the anode and cathode through the electrolyte. This process involves the following steps:
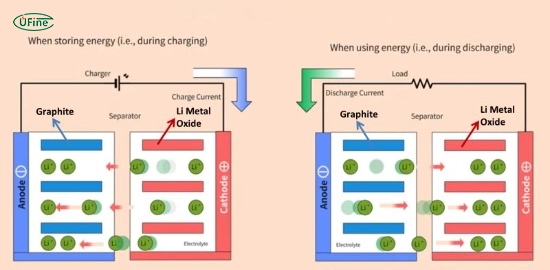
Charging:
- Lithium ions move from the cathode to the anode when the battery charges.
- Electrons flow through the external circuit to balance the charge.
Discharging:
- During discharging, lithium ions move back from the anode to the cathode.
- Electrons flow through the device that powers it, providing electrical energy.
2. Charging Process
During charging, an external power source applies a voltage to the battery. This causes lithium ions to move through the electrolyte from the cathode to the anode.
Movement of Ions:
- Lithium ions travel from the cathode to the anode.
- Electrons flow from the external circuit to the anode.
Energy Storage:
- The anode stores lithium ions.
- The battery stores electrical energy as chemical energy.
3. Discharging Process
When the battery discharges, it supplies power to a device. Lithium ions return to the cathode, and electrons flow through the external circuit, powering the device.
Movement of Ions:
- Lithium ions move from the anode to the cathode.
- Electrons flow through the device, creating a current.
Energy Release:
- The battery releases stored chemical energy as electrical energy.
- Powers devices like phones, laptops, and drones.
4. The Role of Electrolytes
The electrolyte in a LiPo battery facilitates the movement of lithium ions between the anode and cathode. It must be stable, conductive, and safe.
Properties:
- High ionic conductivity.
- Stability under different temperatures and voltages.
Function:
- Allows ion movement.
- Prevents direct contact between the anode and cathode.
5. Cycle Life
LiPo batteries go through many charge and discharge cycles during their life. Each cycle affects the battery’s capacity and efficiency.
Life:
- Typically 300 to 500 cycles.
- It can vary based on usage and conditions.
Efficiency:
- Maintains high energy efficiency.
- Gradual decrease in capacity over time.
6. Safety Features
LiPo batteries are designed with safety features to prevent accidents. These include protection circuits, thermal sensors, and robust casings.
Protection Circuits:
- Prevent overcharging and over-discharging.
- Protect against short circuits.
Thermal Management:
- Sensors monitor temperature.
- Shut down the battery if it overheats.
Casing and Packaging:
- Robust and flexible casing.
- Protects from physical damage.
Part 3. Lithium polymer battery advantages
1. High Energy Density
The operating voltage of a single battery is as high as 3.6V to 3.8V, which is much higher than the 1 and 2V voltage of nickel-metal hydride and nickel-cadmium batteries. Its capacity density is significant, and its capacity density is 1.5 to 2.5 times that of nickel-metal hydride batteries or nickel-cadmium batteries or higher. The polymer lithium battery is 10 to 15% higher than the steel shell battery of the same size and 5 to 10% higher than the aluminum shell battery, which has become the first choice for color screen mobile phones and MMS mobile phones. Most color screen and MMS mobile phones on the market also use polymer cells.
2. Good Discharge Characteristics
Polymer lithium batteries use colloidal electrolytes; compared with liquid electrolytes, colloidal electrolytes have stable discharge characteristics and higher discharge platforms. Therefore, its self-discharge is small, and its capacity loss is also tiny after being placed for a long time.
3. Long Life
The cycle life of the polymer battery can reach more than 500 times in everyday use.
4. No Memory Effect
The battery has no memory effect and does not have to empty the remaining power before charging, which is convenient to use.
5. Good Safety Performance
The polymer lithium battery uses aluminum-plastic flexible packaging in the structure, which is different from the metal shell of the liquid battery. Once there is a security risk, the liquid battery is prone to explosion, and the polymer battery will only bulge at most.
6. Small Thickness
Manufacturers assemble lithium-polymer batteries so thin that they can fit into credit cards. Ordinary liquid lithium battery uses the first custom shell and then plug the positive and negative electrode material method; the thickness is less than 3.6mm, and there is a technical bottleneck; the polymer battery cell does not have this problem, and the thickness can be less than 1mm, in line with the current mobile phone demand direction.
7. Light Weight
Lithium polymer batteries Batteries using polymer electrolytes do not need a metal shell as a protective outer packaging. The weight of the polymer battery is 40% lighter than the steel shell lithium battery of the exact capacity specification and 20% lighter than the aluminum shell battery.
8. Low Internal Resistance
The internal resistance of the polymer lithium battery cell is smaller than that of the general liquid battery cell. The internal resistance of the domestic polymer battery cell can even be below 35, which significantly reduces the battery power consumption, extends the standby time of the mobile phone, and can fully reach the level of international standards. This polymer lithium battery, which supports large discharge currents, is an ideal choice for remote control models and has become the most promising alternative to Ni-MH batteries.
9. Shapes Can be Customized
Polymer lithium battery manufacturers are not limited to the standard form factor. They can be made to the correct size economically. The battery can increase or reduce the thickness of the cell according to the needs of customers, develop new cell models, the price is low, the mold opening cycle is short, and some can even be tailored according to the shape of the mobile phone to make full use of the battery shell space and improve the battery capacity.
10. The Protection Board Design is Simple
Due to the use of polymer materials, the polymer lithium battery cell does not catch fire or explode; it inherently provides sufficient safety. Manufacturers can consider omitting PTC and fuse in the protection line design of the polymer battery, thereby reducing battery costs.
Part 4. Lithium polymer battery disadvantages
Lithium polymer batteries, while advantageous in many respects, also present several drawbacks that need consideration:
1. Limited Lifespan
LiPo batteries degrade over time, lasting between 300 to 500 charge cycles. This means they need replacement more frequently compared to some other battery types.
2. Sensitivity to Overcharging and Over-discharging
These batteries are susceptible to overcharging, leading to overheating and, in extreme cases, swelling or even explosion. Over-discharging can also cause irreversible damage, reducing battery performance and lifespan.
3. Risk of Swelling and Puncture
LiPo batteries are prone to swelling if subjected to physical damage or incorrect charging practices. Swelling indicates internal damage and can lead to safety hazards like puncture, which may result in fire or leakage of hazardous materials.
4. Higher Cost
The production of LiPo batteries involves advanced manufacturing processes and materials, making them more expensive than traditional battery types. This higher cost can be a barrier to widespread adoption in some applications.
Part 5. What are lithium-polymer batteries used for?
Lithium-polymer (LiPo) batteries serve crucial roles across different industries due to their specific advantages:
Consumer Electronics
Manufacturers integrate LiPo batteries into smartphones, tablets, laptops, and wearable devices for their lightweight design and high energy density, ensuring prolonged usage without added bulk.
Portable Electronics
They power drones, portable power banks, and handheld gadgets, providing efficient and compact energy solutions for outdoor activities and on-the-go charging needs.
Medical Devices
LiPo batteries are essential in medical equipment such as pacemakers and hearing aids, offering reliable and long-lasting power to support vital health functions.
Electric Vehicles
From electric cars to e-bikes and scooters, LiPo batteries enable efficient energy storage and delivery, facilitating the shift toward sustainable transportation solutions.
Renewable Energy Storage
When integrated into solar and wind energy systems, LiPo batteries store excess energy for later use, optimizing the efficiency and reliability of renewable energy sources.
RC Hobby and Toys
Enthusiasts rely on LiPo batteries to power radio-controlled vehicles, drones, and toys, benefiting from their high discharge rates and lightweight properties for enhanced performance.
Military and Aerospace Applications
LiPo batteries are utilized in satellites, spacecraft, and military equipment for their robustness and ability to function reliably in extreme environmental conditions, ensuring mission success and operational safety.
Industrial Applications
They support portable tools, industrial equipment, and backup power systems, providing durable and high-power-density solutions for diverse industrial operations.
Part 6. What is the difference between lithium-polymer and lithium battery?
Lithium-polymer (LiPo) batteries and lithium-ion batteries have distinct characteristics that cater to different needs and applications:
Battery Structure:
- Lithium-ion (Li-ion) Batteries Typically use a rigid metal casing to house electrodes and electrolytes. Manufacturers commonly produce them in cylindrical or prismatic shapes.
- Lithium-polymer (LiPo) Batteries: Utilize a flexible polymer pouch to contain the electrodes and electrolytes. This flexible packaging allows for a thinner and lighter battery design.
Energy Density:
- Li-ion Batteries Generally have a higher energy density compared to LiPo batteries, providing more energy storage capacity per unit volume or weight.
- LiPo Batteries: While slightly lower in energy density than Li-ion, they offer more flexibility in shape and size, making them suitable for applications where the form factor is crucial.
Safety and Handling:
- Li-ion Batteries are typically considered safer in terms of puncture resistance and thermal stability due to their rigid casing and well-established manufacturing processes.
- LiPo Batteries: Require careful handling to avoid physical damage to the pouch, which can lead to swelling or even fire if mishandled or improperly charged.
Cost and Manufacturing:
- Li-ion Batteries are generally more cost-effective to manufacture in large quantities due to established production lines and economies of scale.
- LiPo Batteries can be more expensive due to specialized pouch materials and assembly processes. However, costs are decreasing with technological advancements.
Part 7. FAQs
-
Are lithium-polymer batteries rechargeable?
You can recharge lithium polymer batteries, but we recommend using a standard charger and fully charging the battery to 100%. Do not use an uncertified charger or casually connect to the power supply to charge to avoid damage to the battery. -
Can I charge a lithium polymer battery with a lithium-ion charger?
No, charging a lithium polymer battery with a charger designed for lithium-ion batteries is unsafe. Lithium polymer batteries require a different charging profile and voltage, and using the wrong charger can lead to overheating, swelling, or even fire hazards. -
How do I know if my lithium polymer battery is swelling?
You can detect swelling in a lithium polymer battery by visually inspecting it for bulging or puffiness. A swollen battery may feel larger or thicker than usual and could have altered its shape. If you suspect swelling, discontinue use immediately and cautiously handle the battery to prevent potential safety risks. -
What is the life of lithium polymer batteries?
Under the international unified standard, the battery’s life does not express time but rather the number of cycles. This means the battery undergoes a complete discharge once, with typical lithium batteries lasting between 500 and 800 cycles. -
Are lithium-polymer batteries bad for the environment?
Lithium-polymer batteries contain materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which can be harmful to the environment if not correctly disposed of or recycled. It’s important to recycle them through proper channels to minimize environmental impact.
Related Tags:
More Articles

What You Need to Know About AA 3.6V Lithium Battery
Learn all about AA 3.6V lithium batteries—voltage, size, capacity, uses, and the best replacements. Discover why they’re powerful, and highly reliable.
What Are Lithium Salts and Why They Matter in Battery Electrolytes
Lithium salts in electrolytes are key to battery performance, powering everything from phones to EVs and shaping the future of clean energy.
Lithium AAA Battery Guide: Power, Performance & Chargers
Explore lithium AAA batteries—voltage, capacity, weight, top brands, and more. Learn how to choose the best battery for your device and why it really matters.
How to Calculate Watts, Volts, and Amps (With Simple Formulas and Examples)
Learn how to calculate watts, volts, and amps for lithium batteries with simple formulas and examples, ideal for EVs, solar, and energy systems.
Comprehensive Analysis of U.S. Tariffs on Chinese Lithium Batteries
U.S. tariffs on Chinese lithium batteries in 2025 impact costs, supply chains, and EV, energy storage, and electronics industries globally.