NiMH batteries, which stand for Nickel Metal Hydride, are rechargeable batteries. They use a special metal that can absorb hydrogen. These batteries can store more energy than nickel-cadmium batteries. This article talks about how NiMH batteries work, their good and not-so-good sides, and where we use them. It also compares them to another kind of battery called Lithium-ion.
Part 1. Nickel metal hydride battery
Composition
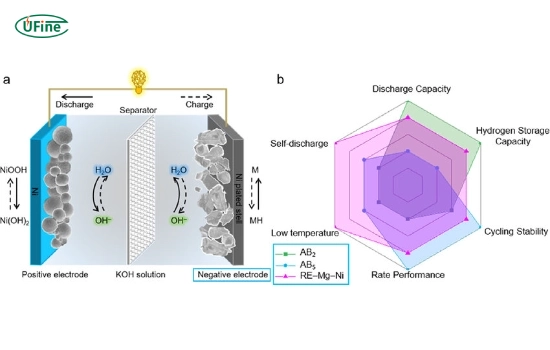
NiMH batteries house a positive electrode composed of nickel oxyhydroxide (NiOOH) and a negative electrode incorporating a hydrogen-absorbing alloy, often made of a mixture of rare earth metals, nickel, and other elements like titanium or zirconium. This combination facilitates the reversible electrochemical reactions crucial for energy storage and discharge.
Electrolyte
The electrolyte within NiMH batteries is typically an alkaline potassium hydroxide (KOH) solution, aiding in the conduction of ions between the electrodes during charging and discharging cycles. This electrolytic medium plays a vital role in sustaining the battery’s functionality.
Voltage and capacity
NiMH batteries commonly operate at a nominal voltage of 1.2 volts per cell, slightly lower than other rechargeable batteries like Lithium-ion. However, they compensate with a commendable capacity, often ranging from 1000mAh to 3000mAh or higher, depending on the size and design.
Charging rate and dimensions
These batteries exhibit variable charging rates, typically ranging from C/10 to C/3, where ‘C’ denotes the battery’s capacity in ampere-hours. For instance, a 2000mAh NiMH battery can be charged at rates between 200mA (C/10) to 667mA (C/3). Sizes of NiMH batteries vary widely, from AAA and AA cells to larger formats like C and D cells, each with differing capacities and physical dimensions to suit various applications.
Self-discharge characteristics
NiMH batteries, while offering high energy density, do experience a higher self-discharge rate compared to some other rechargeable batteries. They can lose approximately 1-5% of their charge per day when idle, impacting their suitability for long-term storage without regular recharging.
Part 2. Advantages and disadvantages of nickel metal hydride batteries
Advantages of nickel metal hydride batteries
1. Energy density and capacity
NiMH batteries boast a commendable energy density, surpassing traditional nickel-cadmium batteries. Their capacity ranges from approximately 1000mAh to 3000mAh or higher, providing reliable and sustained power for various devices.
2. Rechargeability and cycle life
These batteries excel in longevity, enduring hundreds to thousands of charge-discharge cycles. Their rechargeability and ability to retain capacity over multiple cycles make them a cost-effective and sustainable option for numerous consumer electronics and portable gadgets.
3. Environmental friendliness
Comprising fewer harmful materials compared to certain battery types, NiMH batteries present an environmentally friendly choice. The absence of toxic cadmium reduces environmental impact during disposal or recycling, aligning with eco-conscious practices.
4. Enhanced safety features
Relative to some battery chemistries, NiMH batteries possess a safer profile, exhibiting stability and lower risk of thermal runaway or fire hazards. This safety factor contributes to their suitability in various applications where reliability is crucial.
5. Cost-effectiveness
NiMH batteries are known for their cost efficiency. With the capability to be recharged hundreds to thousands of times before significant capacity loss, they offer a long-term economical power solution, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
Disadvantages of nickel metal hydride batteries
1. High self-discharge rate
A notable drawback of NiMH batteries is their relatively high self-discharge rate. They can lose around 1-5% of their charge per day when idle, affecting their shelf life and necessitating regular recharging.
2. Memory effect and voltage sag
While less prone than nickel-cadmium batteries, NiMH cells can still suffer from memory effect issues if not fully discharged before recharging. Moreover, they might exhibit voltage sag under heavy loads, impacting performance in devices requiring consistent power output.
3. Sensitivity to temperature extremes
Extreme temperatures adversely affect NiMH battery performance. High temperatures accelerate self-discharge and degrade the battery, while low temperatures reduce efficiency and capacity, limiting functionality in extreme environmental conditions.
4. Limited fast charging capability
NiMH batteries have slower charging rates compared to newer technologies. Their limited ability for rapid charging requires longer charging times, affecting convenience in fast-paced scenarios.
5. Reduced voltage output
Compared to some newer battery chemistries, NiMH batteries exhibit lower voltage outputs, affecting their compatibility with devices requiring higher voltage levels for optimal performance.
Part 3. What are nickel metal hydride batteries used for?
NiMH batteries have found applications across various industries and consumer devices, catering to diverse power needs.
Consumer electronics
NiMH batteries find extensive use in various consumer electronics such as digital cameras, handheld gaming devices, portable music players, and remote controls. Their ability to provide consistent power output suits these devices, ensuring prolonged usage without frequent recharges.
Power tools
These batteries are commonly employed in power tools like cordless drills, electric screwdrivers, and other cordless devices due to their ability to deliver sufficient power and endure multiple recharge cycles, catering to the demands of professional and DIY enthusiasts.
Medical devices
NiMH batteries play a crucial role in medical devices such as portable oxygen concentrators, infusion pumps, and various monitoring devices. Their reliability, rechargeability, and energy density make them ideal for sustaining power in critical healthcare equipment.
Hybrid vehicles
Some hybrid vehicles integrate NiMH batteries into their power systems. While newer technologies like Lithium-ion are becoming more prevalent, NiMH batteries have historically been utilized in hybrid cars for their ability to store and deliver power efficiently.
Emergency lighting and backup power
NiMH batteries serve as a reliable source of backup power in emergency lighting systems, uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), and backup generators. Their ability to retain charge and deliver power when needed makes them suitable for critical backup applications.
Renewable energy storage
In smaller-scale renewable energy systems like solar-powered installations or wind energy storage units, NiMH batteries offer a cost-effective and dependable means of storing surplus energy for later use, contributing to sustainable power solutions.
Flashlights and portable devices
NiMH batteries power flashlights, camping lanterns, and other portable devices due to their rechargeability and ability to sustain power output, making them ideal for outdoor activities and emergency kits.
Electric bicycles and scooters
Some electric bicycles and scooters utilize NiMH batteries for their power supply. While newer technologies are becoming prevalent, NiMH batteries have historically provided a reliable power source for these applications.
Part 4. Lithium-ion vs. nickel metal hydride battery
Similarities
1. Rechargeability
Both Li-ion and NiMH batteries are rechargeable, allowing for multiple charge-discharge cycles, making them cost-effective and sustainable alternatives to disposable batteries.
2. Applications
Both types find extensive use in consumer electronics, power tools, electric vehicles, and various portable devices due to their ability to provide consistent power output.
3. Eco-friendliness
Compared to traditional disposable batteries, both Li-ion and NiMH batteries are more environmentally friendly as they can be reused, reducing the environmental impact of battery disposal.
What Are Lithium Polymer Batteries?
Differences
1. Energy density
Li-ion batteries typically exhibit higher energy density compared to NiMH batteries. This means Li-ion batteries can store more energy per unit weight or volume, providing longer battery life in smaller and lighter packages.
2. Self-discharge rate
NiMH batteries have a higher self-discharge rate compared to Li-ion batteries. NiMH batteries can lose charge even when not in use, impacting their shelf life, whereas Li-ion batteries hold their charge better over time.
3. Memory effect
NiMH batteries are more susceptible to the memory effect, a phenomenon where batteries lose their maximum energy capacity if not fully discharged before recharging. Li-ion batteries, on the other hand, are virtually free from this issue.
4. Charging speed
Li-ion batteries generally offer faster charging times compared to NiMH batteries. They can be charged more rapidly, which is advantageous for quick charging needs in various electronic devices.
5. Voltage output
NiMH batteries typically have a lower voltage output compared to Li-ion batteries. This difference in voltage output might impact the compatibility and performance of devices requiring specific voltage levels.
6. Cost and availability
Li-ion batteries can be more expensive to manufacture than NiMH batteries, impacting their cost. Additionally, the availability of Li-ion batteries might be more limited compared to NiMH batteries in certain markets or applications.
Part 5. FAQs
-
Are NiMH batteries better than lithium batteries?
It depends on the specific application. NiMH batteries are known for their lower energy density but have advantages in terms of cost and environmental impact. Lithium batteries, particularly lithium-ion, offer higher energy density, longer life cycles, and lighter weight, making them preferable for certain high-energy applications. -
Is NiMH safer than lithium?
In general, NiMH batteries have a reputation for being safer in terms of reduced risk of fire or explosion compared to some variations of lithium batteries, like lithium-polymer (LiPo) batteries. However, proper handling, charging, and storage practices are crucial for all battery types to ensure safety. -
Which is better, lithium-ion, or nickel metal hydride?
Lithium-ion batteries generally offer higher energy density, longer lifespan, and lighter weight compared to NiMH batteries. However, NiMH batteries are more cost-effective and have a better environmental impact due to their recyclability. -
How long do NiMH batteries last?
The lifespan of NiMH batteries is typically around 2 to 3 years or about 500 to 1000 charge cycles, depending on usage patterns and charging practices. -
Can I replace NiMH batteries with lithium?
It’s not straightforward to replace NiMH batteries with lithium batteries without considering differences in voltage, size, and application requirements. Lithium batteries might have different voltage characteristics and require device modifications to function properly.
Related Tags:
More Articles

White Stuff on Battery Terminals: A Step-by-Step Cleaning and Maintenance Guide
White stuff on battery terminals is corrosion. Learn how to clean it safely, prevent damage, and keep your battery running strong with simple steps.
Understanding How Glass Mat Batteries Work: Technology, Benefits, and Limitations
Glass mat batteries power cars, RVs, and solar systems. Learn how they work, their benefits, and what to consider before choosing one.
A Buyer’s Guide for AA Size Lithium Battery
Discover the power of AA size lithium batteries—types, voltage, capacity, and more! Learn how to choose the best one for your needs. Read now!
Li-Ion Battery Prices – Where to Buy Cheap & Safe
Discover li-ion cell prices, key market factors, and how to find affordable custom batteries from top suppliers like Ufine Battery.
How Long Does a 2200mAh Battery Last?
Discover everything about 2200mAh batteries—types, charging time, lifespan, and whether it’s enough for your device.