If you’ve ever wondered how batteries work, or how they store and release energy, you’re not alone. Many people don’t realize that batteries don’t simply “hold energy”—they store it in a specific form and release it when needed. This article will explain the different types of energy stored in batteries, how they store that energy, and why understanding this is important for everyday use. Whether you’re looking to better understand your car’s battery, the one in your phone, or even larger-scale batteries used for renewable energy, you’ll find this guide helpful.
Part 1. What is energy? How to store energy?
Before delving into the specifics of battery energy, let’s first define what energy is and how it can be stored. Energy is the capacity to do work—it can take various forms, such as heat, light, or mechanical movement. Energy storage refers to the method by which energy is saved for later use.
For example, mechanical energy can be stored in a spring or a flywheel, while thermal energy is stored in substances like ice or water. Batteries, on the other hand, store electrical energy chemically. This stored electrical energy can then be released as electrical current when needed, such as when charging a phone or running an electric vehicle.
Thus, energy storage is essential because it allows us to harness and use energy at times when it isn’t directly available, such as on a cloudy day or when you’re on the go.
Part 2. What is a battery?
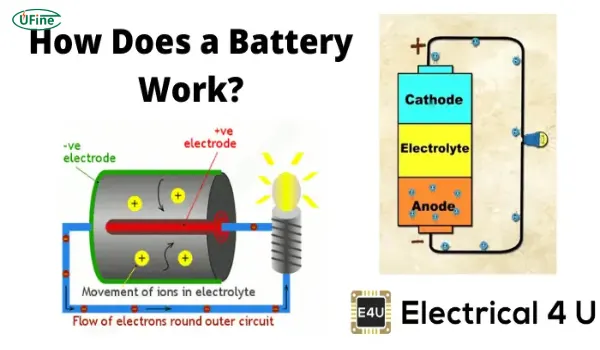
A battery is a device that stores electrical energy in chemical form. In its most basic form, it consists of one or more electrochemical cells that convert chemical energy into electrical energy when discharged. These cells contain two electrodes—a positive electrode (cathode) and a negative electrode (anode)—that are immersed in an electrolyte, which allows ions to move between them.
When a battery is connected to a device, the chemical reactions inside the battery create a flow of electrons from the negative to the positive terminal, thus producing an electric current that powers your devices.
Different batteries, however, vary in their composition, energy storage capacity, and applications. Understanding these differences will help you better choose the right battery for your needs.
If you’re in need of high-quality customized battery solutions, Ufine Battery is here to provide you with reliable and tailored batteries to suit your specific requirements.
For more information or inquiries, feel free to contact us today!
Part 3. Common battery types
Batteries come in many shapes, sizes, and types. Some of the most common types include:
- Lithium-Ion Batteries (Li-ion): These are widely used in everything from smartphones to laptops. They have a high energy density and long lifespan.
- Lead-Acid Batteries: Commonly used in cars, they store energy through a chemical reaction between lead plates and sulfuric acid.
- Nickel-Cadmium Batteries (NiCd): Known for their use in power tools, these batteries are durable but suffer from a phenomenon called the “memory effect,” which reduces their capacity over time.
- Nickel-Metal Hydride Batteries (NiMH): These batteries are more environmentally friendly than NiCd batteries and are often used in hybrid vehicles.
- LiFePO4 Batteries: A safer and more stable form of lithium battery, often used in electric vehicles and solar energy storage systems.
Each of these battery types has different energy storage capacities, efficiencies, and applications. The type of energy they store is ultimately determined by the chemistry used in their construction.
AGM VS Lithium VS Lead-Acid Battery: Comprehensive Comparison
Part 4. Why is it so important to reserve batteries?
With the growing demand for mobile devices, electric vehicles, and renewable energy storage, battery reserve capacity is more important than ever. Batteries serve as energy reserves, storing energy for later use when it is not readily available. For example, solar power systems often rely on batteries to store energy generated during the day for use at night or on cloudy days. Similarly, electric vehicles depend on batteries to store energy for transportation.
Without a reliable battery reserve, the functionality of devices, vehicles, and even power grids would be severely compromised. Therefore, understanding how energy is stored and utilized in batteries is crucial for both personal and commercial purposes.
Part 5. What type of energy is a battery?
The type of energy stored in a battery is chemical energy, which is converted into electrical energy when the battery is discharged. Essentially, batteries act as energy converters—they take energy from a chemical reaction and release it in a useful form (electrical energy) to power devices.
Chemical Energy in Batteries
The chemical energy in a battery is stored in the electrochemical cells inside the battery. The process begins when the battery is charged. During charging, electrons move from the positive electrode to the negative electrode, storing energy in the process. When the battery is used, these electrons flow from the negative to the positive electrode, generating an electrical current.
Electrical Energy Output
When a battery is connected to a device, such as your phone or car, it releases the stored chemical energy as electrical energy. The energy is then used to power the device. Therefore, the type of energy a battery provides is electrical energy that has been chemically stored.
Part 6. How batteries store and release energy?
Batteries store energy through chemical reactions that occur inside the battery. When charging, energy is supplied externally (usually via a charger), which causes the positive and negative electrodes inside the battery to undergo a chemical transformation. This transformation results in the storage of energy. When the battery is used, the reverse chemical reactions take place, releasing energy in the form of electricity.
The rate at which energy is stored or released is determined by the charge rate and the discharge rate of the battery, respectively. These rates depend on factors such as the battery’s size, chemistry, and design.
Part 7. What energy conversions occur in batteries?
Batteries convert chemical energy into electrical energy. The process begins when the battery is charged, and energy is stored through chemical reactions. When the battery is discharged, these chemical reactions reverse, converting the stored chemical energy back into electrical energy. Essentially, batteries are energy conversion devices that provide electrical power when needed.
Moreover, the efficiency of this energy conversion depends on the battery’s design and the materials used. For example, lithium-ion batteries offer higher energy conversion efficiency compared to older lead-acid batteries, which is why they are commonly used in mobile devices and electric cars.
Part 8. Indicators for measuring battery energy
To determine how much energy a battery has stored, we use several key indicators:
- Voltage: Measured in volts (V), this indicates the potential difference between the battery’s positive and negative terminals.
- Capacity: Measured in ampere-hours (Ah) or milliampere-hours (mAh), this tells you how much charge the battery can store.
- Energy Density: This refers to the amount of energy stored in a given volume or mass of the battery.
- State of Charge (SOC): The SOC indicates how much energy remains in the battery relative to its maximum capacity.
Part 9. FAQs
-
What type of energy does a battery store?
Batteries store chemical energy, which is converted into electrical energy when the battery is discharged. -
Can a battery store other types of energy?
No, batteries primarily store chemical energy. However, some types of batteries may be designed to store energy from renewable sources, such as solar energy, for later use. -
How do I know if a battery is storing energy correctly?
You can check a battery’s voltage and capacity using a multimeter. If the battery has the correct voltage and charge capacity, it is storing energy correctly. -
Why are some batteries more efficient than others?
The efficiency of a battery depends on its chemistry and design. For example, lithium-ion batteries have a higher energy density and efficiency than lead-acid batteries. -
How can I increase a battery’s lifespan?
To increase a battery’s lifespan, avoid overcharging, use the appropriate charger, and keep the battery at a moderate temperature. Proper maintenance also includes regular discharges and charges.
Related Tags:
More Articles

How to Choose the Best Floor Scrubber Battery for Commercial Cleaning?
Selecting the ideal floor scrubber battery ensures a long runtime, rapid charging, and minimal maintenance for efficient commercial cleaning operations.
Battery for Blower vs Battery for Leaf Vacuum: Which One Should You Choose?
Battery for blower vs leaf vacuum—learn the key differences in power, fit, and runtime to choose the right battery for your outdoor tool needs.
How to Choose the Right Battery for Blower?
Choosing the right blower battery? Consider voltage, capacity, chemistry & usage. This guide helps match the best battery for peak performance.
How to Choose the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries?
Choosing the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries? Discover key factors such as size, material, and safety for optimal protection and performance.
7 Critical Elements on a Lithium Battery Shipping Label
What must be on a lithium battery shipping label? Learn 7 key elements to ensure safety, legal compliance, and correct handling across all transport modes.