- Part 1. What is battery charging?
- Part 2. Types of batteries and their charging methods
- Part 3. The importance of proper charging techniques
- Part 4. How does pulse charging help in reviving older batteries?
- Part 5. What role does temperature play in the charging process of lithium-ion batteries?
- Part 6. FAQs
Have you ever wondered what a battery charge means? In simple terms, battery charge refers to storing electrical energy in a battery for later use. Understanding how batteries work and charge is essential in our technology-driven world. From smartphones to electric vehicles, batteries power many devices we rely on daily. This article will cover everything you need to know about battery charging, including the different types of batteries, charging methods, and tips for effective charging.
Part 1. What is battery charging?
Battery charging adds electrical energy to a battery, allowing it to store energy for future use. A device known as a battery charger facilitates this process. Connecting your device to a charger supplies an electrical current that reverses the chemical reactions when the battery discharges.
How does battery charging work?
To understand how battery charging works, let’s look at the essential components involved:
- Electrodes: Every battery has two electrodes—an anode (negative) and a cathode (positive). During discharge, electrons flow from the anode to the cathode through an external circuit.
- Electrolyte: This medium allows ions to move between the electrodes during charging and discharging.
- Charger: The charger provides the voltage and current to replenish the battery’s energy.
When you plug in your device, the charger sends a direct current (DC) into the battery. This current pushes electrons back into the anode, restoring the chemical compounds that store energy. The battery then becomes charged and ready for use.
How do different types of battery chargers compare in terms of efficiency?
Battery chargers vary widely in their design and efficiency. Here are some common types:
- Standard Chargers: These chargers provide a fixed voltage and current. They are simple but often less efficient because they must adjust based on the battery’s needs.
- Smart Chargers: These chargers can detect a battery’s state of charge and adjust their output accordingly. They are more efficient because they reduce energy waste and prevent overcharging.
- Fast Chargers: These chargers deliver higher currents to charge batteries quickly. While convenient, they can generate heat, which may affect battery life if used excessively.
- Solar Chargers: These eco-friendly chargers convert sunlight into electricity. Their efficiency depends on sunlight availability but can be very effective in sunny conditions.
Choosing the right charger can significantly impact your battery’s efficiency and lifespan.
Part 2. Types of batteries and their charging methods
Different batteries have unique characteristics and require specific charging methods for optimal performance. Here are some common types:
Lead-acid batteries
Lead-acid batteries are often used in vehicles and backup power systems. They typically follow a three-stage charging process:
- Bulk Charge: The charger supplies a constant current until the battery reaches 80% capacity.
- Absorption Charge: The voltage is constant while the current gradually decreases until around 90-95% capacity.
- Float Charge: The charger maintains a lower voltage to keep the battery fully charged without overcharging.
This method ensures that charging lead-acid batteries efficiently extends their lifespan.
Lithium-ion batteries
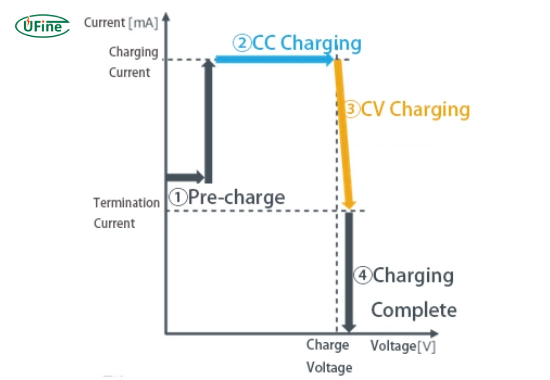
Lithium-ion batteries are popular in portable electronics and electric vehicles due to their high energy density. They usually employ a Constant Current/Constant Voltage (CC/CV) method:
- Constant Current: The charger initially supplies a steady current until the voltage reaches a predetermined level.
- Constant Voltage: The charger then maintains a constant voltage while gradually reducing the current until the battery is fully charged.
This method helps prevent overheating and ensures efficient energy storage.
Nickel-based batteries
Older devices commonly use nickel-cadmium (NiCd) and nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries. You can charge them using:
- Trickle Charging: A low current is continuously supplied to maintain the charge.
- Fast Charging: A higher current is used for quicker recharging but requires careful monitoring to prevent overheating.
Understanding these different types of batteries and their charging methods can help you choose the right one for your needs.
Part 3. The importance of proper charging techniques
Using appropriate charging techniques is essential for maximizing battery life and performance. Here are key reasons why proper charging matters:
Preventing overcharging
Overcharging can lead to excessive heat buildup, damaging internal components and reducing lifespan. Smart chargers monitor voltage and current levels to prevent overcharging, ensuring your device remains safe while charging.
Enhancing efficiency
Efficient charging methods help reduce energy waste during the process, ensuring that more supplied energy goes into storing usable power rather than being lost as heat or other forms of energy loss.
Extending lifespan
Batteries charged correctly tend to last longer than those subjected to improper techniques or excessive cycling. Following manufacturer guidelines for charging can significantly improve longevity.
Part 4. How does pulse charging help in reviving older batteries?
Pulse charging is an innovative technique that sends short bursts of electrical energy into a battery rather than a continuous flow. This method has several advantages:
- Reviving older batteries: Pulse charging can help restore capacity in older or degraded batteries by breaking down sulfate crystals that form on lead-acid battery plates over time.
- Reducing heat generation: Since pulse charging delivers energy in short bursts, it generates less heat than traditional continuous charging methods, reducing stress on battery components.
- Improving efficiency: This technique can enhance overall efficiency by allowing better ion movement within the electrolyte solution, improving performance during discharge cycles.
Pulse charging can be particularly beneficial for users looking to extend the life of older lead-acid batteries or improve their performance without replacing them entirely.
Part 5. What role does temperature play in the charging process of lithium-ion batteries?
Temperature significantly affects lithium-ion battery performance during both the charging and discharging processes:
- Optimal temperature range: Lithium-ion batteries perform best when charged between 20°C (68°F) and 25°C (77°F). Charging outside this range can lead to issues such as reduced capacity or even thermal runaway.
- Cold temperatures: Charging lithium-ion batteries at low temperatures can slow down chemical reactions within the cells, resulting in longer charge times and reduced capacity. In extreme cases, it may even cause lithium plating on electrodes, permanently damaging the battery.
- High temperatures: Conversely, high temperatures during charging can accelerate chemical reactions and increase risks such as overheating or thermal runaway. This can lead to swelling or even fires in severe cases.
Maintaining an appropriate temperature during charging is crucial for ensuring safety and extending lithium-ion battery life.
Part 6. FAQs
-
What happens if I use the wrong charger?
Using an incompatible charger can lead to overheating, reduced performance, or even permanent damage to your battery due to incorrect voltage or current levels. -
How long does it take to charge a battery?
Charging times vary depending on battery type and charger specifications, but they generally range from one hour for fast chargers to several hours for standard chargers, depending on capacity and state of charge. -
Can I charge my device while using it?
Yes, most devices allow simultaneous usage while charging; however, this may slow down the charging process due to increased power consumption from running applications or features simultaneously. -
Is it safe to leave my device plugged in all day?
For most modern devices equipped with smart chargers, leaving them plugged in poses minimal risk as they automatically stop drawing power once fully charged; however, it’s still good practice to unplug when not needed for extended periods. -
How can I tell if my battery is fully charged?
Most devices indicate full charge status through visual cues such as LED lights or on-screen notifications once they reach full capacity; checking these indicators helps ensure optimal usage without unnecessary wear on your device’s components.
Related Tags:
More Articles
What is the Difference Between Silver Zinc Battery vs. Lithium-ion Rechargeable?
Compare silver zinc and lithium-ion rechargeable batteries: energy density, cycle life, safety, cost, and uses in drones, medical devices, EVs, and electronics.
What are Watts and Watt Hours in Battery?
Understand watt vs watt-hour in batteries: key differences, how to calculate capacity, and why they matter. Includes free comparison table.
Best 10 Blood Pressure Monitor Battery Review: Finding the Most Reliable
Are you looking for a reliable Blood Pressure Monitor battery? Here is a complete guide with the top 10 best blood pressure monitor batteries.
Bluetooth Headphone Battery Guide: All You Need to Know
Maximize headphone battery life with expert tips! Learn how to charge, check, troubleshoot, and choose the best bluetooth headphone battery in 2025.
LiFePO4 Battery VS. Lithium-ion Polymer Battery: Which One Is Best?
Comprehensive comparison of LiFePO4 vs Lithium Ion Polymer batteries: energy density, safety, lifespan, cost. Find out which battery suits your needs in 2025.