- Part 1. Understanding high temperature batteries
- Part 2. Types of high temperature batteries
- Part 3. How does the design of high temperature batteries ensure their performance in extreme conditions?
- Part 4. Advantages of high temperature batteries
- Part 5. Disadvantages of high temperature batteries
- Part 6. How do high temperature batteries compare to regular lithium-ion batteries?
- Part 7. Maintenance tips for high temperature batteries
- Part 8. FAQs
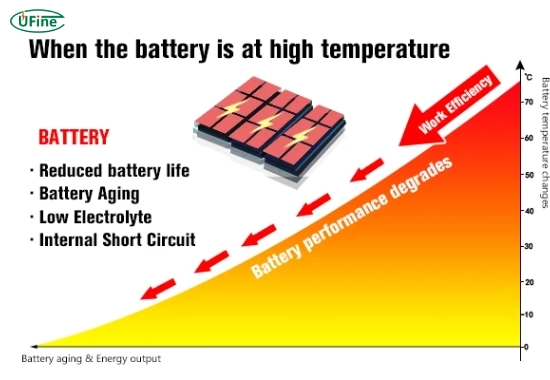
High-temperature batteries are specialized energy storage systems that operate efficiently in extreme thermal conditions. Unlike conventional batteries that may degrade or fail at elevated temperatures, high-temperature batteries can withstand and function optimally when temperatures exceed typical operational limits, often reaching up to 200°C or more. This capability makes them invaluable for various industrial and technological applications.
Part 1. Understanding high temperature batteries
High temperature batteries are engineered to provide reliable performance in harsh environments. These batteries can be categorized based on their operational temperature ranges:
- 100°C: These batteries can operate without special design modifications.
- 125°C: Requires some adjustments for optimal performance.
- 150°C to 175°C: Special designs are necessary to ensure safety and functionality.
- Above 180°C: At these temperatures, lithium becomes unsuitable for use as a cathode material, necessitating lithium alloys and additional safety measures.
The primary electrochemical systems utilized in these batteries include Lithium/Sulfur Dioxide (Li/SO2) and Lithium/Sulfur Dichloride (Li/SOCl2). These systems offer high energy density and long storage times, making them ideal for demanding applications.
Part 2. Types of high temperature batteries
High temperature batteries come in several types, each designed for specific applications and performance requirements:
- Lithium/Sulfur Dioxide (Li/SO2) Batteries: Known for their high energy density, these batteries are often used in military and aerospace applications due to their reliability in extreme conditions.
- Lithium/Sulfur Dichloride (Li/SOCl2) Batteries: These batteries are typically employed in remote sensing and telecommunications, offering long shelf life and stable performance.
- Nickel Cadmium (NiCd) Batteries: Although not as common as lithium-based solutions, NiCd batteries can perform well at elevated temperatures and are used in some industrial applications.
- Zinc Chloride Batteries: These are less common but can be effective in specific high-temperature scenarios, mainly where cost is a significant concern.
Part 3. How does the design of high temperature batteries ensure their performance in extreme conditions?
The design of high temperature batteries is key to their ability to work well in extreme environments. Several important features and materials help these batteries stay safe and effective, even at high temperatures.
1. Special Materials
High temperature batteries use materials that can handle heat. For example, the electrodes are often made from lithium alloys or thionyl chloride. These materials do not break down or lose effectiveness when exposed to high temperatures, allowing the battery to function well above 200°C.
2. Unique Electrolytes
The electrolyte is crucial for how a battery works. In high-temperature batteries, the electrolyte is often solid or specially made to stay stable at high temperatures. For instance, lithium thionyl chloride (Li/SOCl2) batteries use an electrolyte that does not break down quickly, which helps ions move efficiently even in extreme conditions.
3. Heat Management Systems
High-temperature batteries often have systems to manage heat to avoid overheating. These may include thermal barriers made from insulating materials that help spread heat and keep the battery at a safe temperature. Some materials can expand when heated, providing extra protection against fire.
4. Strong Casings
The outer casing of high temperature batteries is built to withstand harsh conditions. It is usually made from solid metals or rigid plastics that can handle changes in temperature without cracking or leaking. This strength is vital for keeping the battery safe in harsh environments like oilfields or deserts.
5. Safety Features
Safety is paramount in high temperature battery design. These batteries include features to prevent overheating and pressure buildup. For example, they may have pressure relief valves and thermal fuses that help control temperature and voltage, ensuring safe operation.
6. Vibration Resistance
High temperature batteries must also resist vibrations, especially in drilling or military applications. The design includes shock-absorbing materials and secure mounting systems to protect the battery’s internal parts from damage due to movement.
Part 4. Advantages of high temperature batteries
High temperature batteries offer several notable advantages:
- Enhanced Energy Density: They provide higher energy density than traditional batteries, allowing longer operation times without frequent recharging.
- Extended Lifespan: These batteries typically have longer lifespans due to their ability to operate efficiently in extreme conditions.
- Low Maintenance Requirements: They require fewer maintenance requirements than standard batteries, which offers convenience for users in demanding environments.
Part 5. Disadvantages of high temperature batteries
Despite their benefits, high temperature batteries also come with certain drawbacks:
- Higher Costs: The advanced materials and technologies used in their construction make high temperature batteries more expensive than conventional options.
- Special Care Needs: They require specific handling and maintenance protocols to ensure longevity and performance stability.
Part 6. How do high temperature batteries compare to regular lithium-ion batteries?
High temperature batteries differ significantly from regular lithium-ion batteries in several key aspects:
- Temperature Tolerance: While standard lithium-ion batteries typically operate optimally between 0°C and 60°C, high temperature batteries can function effectively at much higher temperatures, often exceeding 200°C.
- Material Composition: High temperature batteries utilize specialized materials that maintain stability under extreme heat, whereas regular lithium-ion batteries may degrade or become unsafe when exposed to similar conditions.
- Application Suitability: High temperature batteries are specifically designed for demanding applications such as military equipment and industrial processes, while standard lithium-ion batteries are more commonly used in consumer electronics and electric vehicles.
Part 7. Maintenance tips for high temperature batteries
To maximize the lifespan and performance of high temperature batteries, follow these maintenance tips:
- Regular Cleaning: To prevent corrosion, keep the battery terminals clean from dust and debris.
- Proper Storage Conditions: When not in use, store batteries in a cool, dry place to avoid unnecessary stress on the materials.
- Correct Charging Practices: Use appropriate charging equipment for high temperature batteries to prevent damage.
Part 8. FAQs
-
What are the main types of high temperature batteries?
The main types include Lithium/Sulfur Dioxide (Li/SO2), Lithium/Sulfur Dichloride (Li/SOCl2), Nickel Cadmium (NiCd), and Zinc Chloride batteries. -
How do high temperature batteries perform compared to regular lithium-ion batteries?
High temperature batteries can operate effectively at temperatures exceeding 200°C, while regular lithium-ion batteries typically function best between 0°C and 60°C. -
What industries primarily use high temperature batteries?
Industries such as military, telecommunications, oil extraction, and renewable energy applications benefit significantly from high temperature battery technology due to its reliability under extreme conditions. -
Are there any safety concerns associated with high temperature batteries?
When properly designed and maintained, high-temperature batteries incorporate safety features that mitigate risks associated with overheating and other hazards. However, due to their specialized nature, they require careful handling. -
Can I use standard chargers with high temperature batteries?
No, using chargers specifically designed for high temperature batteries is essential to ensure safe and efficient charging practices.
Related Tags:
More Articles
What is the Difference Between Silver Zinc Battery vs. Lithium-ion Rechargeable?
Compare silver zinc and lithium-ion rechargeable batteries: energy density, cycle life, safety, cost, and uses in drones, medical devices, EVs, and electronics.
What are Watts and Watt Hours in Battery?
Understand watt vs watt-hour in batteries: key differences, how to calculate capacity, and why they matter. Includes free comparison table.
Best 10 Blood Pressure Monitor Battery Review: Finding the Most Reliable
Are you looking for a reliable Blood Pressure Monitor battery? Here is a complete guide with the top 10 best blood pressure monitor batteries.
Bluetooth Headphone Battery Guide: All You Need to Know
Maximize headphone battery life with expert tips! Learn how to charge, check, troubleshoot, and choose the best bluetooth headphone battery in 2025.
LiFePO4 Battery VS. Lithium-ion Polymer Battery: Which One Is Best?
Comprehensive comparison of LiFePO4 vs Lithium Ion Polymer batteries: energy density, safety, lifespan, cost. Find out which battery suits your needs in 2025.