LiFePO4 batteries have garnered attention and significance for their distinct chemistry and applications across various industries. Their unique composition and characteristics make them a compelling choice for a multitude of energy storage needs.
The article delving into their construction, advantages, limitations, and diverse applications provides a comprehensive understanding of their role in the energy storage ecosystem.
Part 1. What is a LiFePO4 battery?
LiFePO4 batteries, short for Lithium Iron Phosphate batteries, represent a subset of rechargeable lithium-ion battery types. They are recognized for their unique composition, employing iron phosphate as the cathode material. This characteristic sets them apart from other lithium-ion batteries and contributes to their distinct performance and safety features.
Part 2. What are the advantages of LiFePO4?
Wide operating temperature range
LiFePO4 batteries exhibit exceptional performance across temperatures ranging from -20°C to 60°C (or -4°F to 140°F). This wider range allows for usage in diverse environmental conditions, making them ideal for various applications, including outdoor and automotive sectors.
Extended lifespan
LiFePO4 batteries boast a notably longer lifespan compared to conventional lead-acid batteries or standard lithium-ion batteries. Typically, they can endure around 2000 to 7000 charge-discharge cycles, depending on the specific application and depth of discharge. This extended lifecycle makes them a preferred choice for long-term energy storage solutions and electric vehicle applications.
Enhanced safety performance
The inherent chemical stability of LiFePO4 batteries significantly reduces the risk of thermal runaway or combustion, even under harsh conditions. Their solid stability, combined with advanced battery management systems, provides enhanced safety levels, crucial in high-demanding environments such as aerospace and medical equipment.
Low self-discharge rates
LiFePO4 batteries have impressively low self-discharge rates, retaining a charge over extended periods when not in use. This attribute makes them well-suited for backup power systems, renewable energy storage applications, and other scenarios requiring intermittent power availability.
Environmental friendliness
LiFePO4 batteries are an environmentally friendly energy storage solution. They contain non-toxic and abundant materials, making them more sustainable and recyclable compared to other battery chemistries. Reduced reliance on toxic materials contributes positively to environmental conservation efforts.
Compatibility with rapid charging
These batteries support rapid charging capabilities, efficiently accommodating higher charge rates without compromising safety or lifespan, making them suitable for applications requiring quick recharge cycles.
Part 3. What are the disadvantages of LiFePO4?
Slightly lower voltage
In comparison to other lithium-ion chemistries, LiFePO4 batteries have a lower nominal voltage, usually around 3.2 to 3.3 volts per cell. While this isn’t a significant issue, it might require specific considerations in some applications requiring higher voltages.
Reduced specific power
LiFePO4 batteries may have limitations in delivering high power outputs compared to some other lithium-ion batteries. This characteristic might not be suitable for applications that necessitate extremely high power discharge rates.
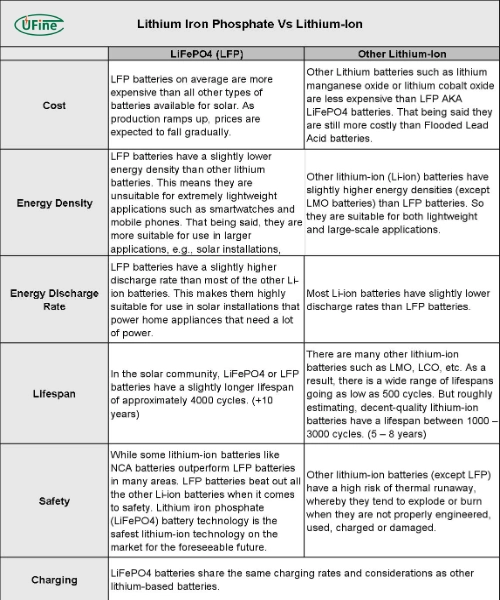
Part 4. LiFePO4 battery VS. other lithium-ion batteries
The comparison between LiFePO4 batteries and other lithium-ion batteries reveals distinct differences in chemistry, performance, and safety. LiFePO4 batteries, characterized by Lithium Iron Phosphate chemistry, offer heightened safety with lower volatility and an extended cycle life of over 2000 cycles. However, they exhibit a moderate energy density and relatively slower charging and discharging rates, suitable for applications prioritizing safety and longevity over high power demands.
In contrast, other lithium-ion batteries, composed of various chemistries like Lithium Cobalt Oxide or Lithium Manganese Oxide, deliver higher energy densities and faster charge/discharge rates but often at the expense of reduced cycle life and lower inherent safety.
|
Parameter |
LiFePO4 Battery |
Other Lithium-Ion Batteries |
|
Chemistry |
Lithium Iron Phosphate |
Various combinations (e.g., Lithium Cobalt Oxide, Lithium Manganese Oxide) |
|
Energy Density |
Moderate |
High |
|
Safety |
High (Less volatile) |
Moderate to High |
|
Cycle Life |
Long (>2000 cycles) |
Varies (Generally lower) |
|
Cost |
Relatively Higher |
Varies |
|
Operating Temp. |
Wide (-20°C to 60°C) |
Varies |
|
Specific Power |
Lower |
Higher |
|
Charging & Discharging |
Slower charge and discharge rates are typically limited to lower C-rates |
Faster charge and discharge rates, capable of higher C-rates |
Part 5. What is the LiFePO4 battery used for?
LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate) batteries find widespread applications across diverse industries owing to their unique characteristics, making them suitable for various devices and systems.
Electric vehicles (EVs)
LiFePO4 batteries serve as a reliable power source in electric vehicles due to their safety, longevity, and stable performance. Their ability to withstand high charge-discharge cycles makes them an ideal choice for EV manufacturers aiming for durable and secure energy storage solutions.
Renewable energy storage
In the renewable energy sector, LiFePO4 batteries play a crucial role in storing energy from solar panels and wind turbines. Their high cycle life and safety features make them a preferred choice for stationary energy storage applications in residential and commercial settings.
Portable electronics
The application of LiFePO4 batteries extends to portable electronic devices such as power banks, laptops, and tablets. While they might offer slightly lower energy density compared to other lithium-ion batteries, their enhanced safety and longevity make them a reliable power source for these devices.
Marine and RV systems
LiFePO4 batteries are gaining popularity in marine and recreational vehicle (RV) systems due to their robustness and ability to sustain deep charge-discharge cycles. Their safety and ability to endure extreme conditions make them suitable for demanding marine and off-grid applications.
Medical devices and tools
In the medical industry, LiFePO4 batteries are utilized in various equipment and tools due to their stable performance and reduced risk of thermal runaway. These batteries ensure reliable power sources for critical medical devices.
Telecommunication infrastructure
LiFePO4 batteries are also employed in telecommunication infrastructure for backup power due to their long cycle life and stable performance under varying environmental conditions.
Part 6. FAQs
-
What is the difference between a lithium battery and a LiFePO4 battery?
The primary difference lies in their chemical composition. Lithium batteries typically encompass various lithium-based chemistries like lithium-ion or lithium-polymer, while LiFePO4 batteries specifically use lithium-iron phosphate chemistry known for enhanced safety and longevity. -
What is the problem with the LiFePO4 battery?
LiFePO4 batteries generally have a lower energy density compared to some other lithium-ion chemistries. While they offer enhanced safety and stability, they might have a slightly lower specific energy and be less compact. -
Can I charge a LiFePO4 battery with a lithium-ion charger?
It’s not recommended to charge a LiFePO4 battery with a lithium-ion charger due to differences in voltage and charging profiles. Using a charger specifically designed for LiFePO4 batteries ensures safe and efficient charging. -
How do you charge a LiFePO4 battery?
During charging, LiFePO4 batteries are typically charged in two stages: constant current (CC) and constant voltage (CV). The CC stage involves charging at a consistent current rate (usually 0.3C to 1C) until reaching a predefined voltage level, followed by the CV stage where the voltage is maintained while the current gradually decreases until the battery is fully charged.
Related Tags:
More Articles
10000mAh Battery Explained: How Long It Lasts, How It Works
A full guide on 10000mAh li-ion batteries, voltage, usage time, and tips. Discover how a 10000mAh battery works, how long it lasts, and how to choose.
10440 Battery Guide: Size, Voltage, Capacity, Uses & More
Understand 10440 batteries better—size, voltage, safety, and how they compare to AAA. Find the best fit for your high-performance devices.
White Stuff on Battery Terminals: A Step-by-Step Cleaning and Maintenance Guide
White stuff on battery terminals is corrosion. Learn how to clean it safely, prevent damage, and keep your battery running strong with simple steps.
Understanding How Glass Mat Batteries Work: Technology, Benefits, and Limitations
Glass mat batteries power cars, RVs, and solar systems. Learn how they work, their benefits, and what to consider before choosing one.
A Buyer’s Guide for AA Size Lithium Battery
Discover the power of AA size lithium batteries—types, voltage, capacity, and more! Learn how to choose the best one for your needs. Read now!