- Part 1. What is a lithium titanate battery?
- Part 2. How does a lithium titanate battery work?
- Part 3. What are the advantages of lithium titanate batteries?
- Part 4. What are the disadvantages of lithium titanate batteries?
- Part 5. Where are lithium titanate batteries used?
- Part 6. How do lithium titanate batteries compare to other battery technologies?
- Part 7. Are there any safety concerns with lithium titanate batteries?
- Part 8. How do you maintain a lithium titanate battery?
- Part 9. FAQs
The lithium titanate battery (LTO) is a cutting-edge energy storage solution that has garnered significant attention due to its unique properties and advantages over traditional battery technologies. Understanding the intricacies of lithium titanate batteries becomes essential as the world increasingly shifts towards renewable energy and electric vehicles. This article delves into the workings, benefits, and applications of LTO technology, providing a comprehensive overview for those interested in modern energy solutions.
Part 1. What is a lithium titanate battery?
A lithium titanate battery is rechargeable and utilizes lithium titanate (Li4Ti5O12) as the anode material. This innovation sets it apart from conventional lithium-ion batteries, which typically use graphite for their anodes. The choice of lithium titanate as an anode material offers several key benefits:
- Structural Stability: Lithium titanate’s unique spinel structure provides excellent structural stability during charge and discharge cycles. This stability helps prevent the formation of dendrites, tiny, needle-like structures that can grow on the anode and lead to short circuits.
- High Rate Capability: LTO batteries can deliver high power output due to their ability to facilitate rapid ion movement. This characteristic makes them ideal for applications requiring quick bursts of energy.
- Safety Features: Lithium titanate’s chemical properties enhance safety. Unlike other lithium-ion batteries, LTO batteries are less prone to overheating and thermal runaway, making them safer options for various applications.
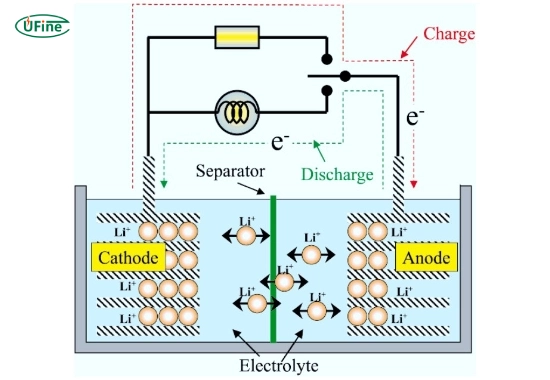
Part 2. How does a lithium titanate battery work?
The operation of a lithium titanate battery involves the movement of lithium ions between the anode and cathode during the charging and discharging processes. Here’s a more detailed look at how this works:
- Charging Process: When charging, an external power source applies a voltage across the battery terminals. This causes lithium ions from the cathode (commonly made from lithium manganese oxide) to migrate through the electrolyte and intercalate into the lithium titanate anode. The unique structure of lithium titanate allows for fast ion diffusion, enabling rapid charging times.
- Discharging Process: During discharging, the process reverses. Lithium ions move back from the anode to the cathode through the electrolyte, releasing stored energy as an electrical current. The high conductivity of the electrolyte and the anode facilitates this process, allowing for efficient energy transfer.
This mechanism enhances performance and contributes to LTO batteries’ longevity, making them suitable for applications where reliability is paramount.
Part 3. What are the advantages of lithium titanate batteries?
Lithium titanate batteries come with several notable advantages:
- Fast Charging: One of the standout features of LTO batteries is their ability to charge rapidly—often within minutes—making them ideal for applications that require quick recharging.
- Long Cycle Life: With a cycle life exceeding 10,000 charge-discharge cycles, LTO batteries significantly outlast traditional lithium-ion batteries, which typically last around 500–1,500 cycles.
- Wide Temperature Range: These batteries can operate effectively in extreme temperatures ranging from -30°C to 55°C (-22°F to 131°F), making them suitable for various environments.
- Safety: The risk of thermal runaway is considerably lower in LTO batteries compared to other types, reducing safety concerns associated with battery use.
- Environmental Impact: Lithium titanate batteries contain fewer toxic materials than many other battery types, making them more environmentally friendly.
Part 4. What are the disadvantages of lithium titanate batteries?
Despite their numerous benefits, there are some disadvantages associated with lithium titanate batteries:
- Lower Energy Density: LTO batteries generally have lower energy density than traditional lithium-ion batteries. This means they store less energy per unit weight or volume, which can be a limitation in applications where space and weight are critical factors.
- Higher Cost: Due to the materials used and their complex production methods, the manufacturing process for LTO batteries is more expensive. This higher cost can make them less attractive for specific consumer applications.
- Limited Availability: While demand grows, LTO technology is less widely available than other battery types, which may limit its adoption in some markets.
Part 5. Where are lithium titanate batteries used?
Lithium titanate batteries find applications across various sectors due to their unique properties:
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): Some EV manufacturers opt for LTO technology because it allows for fast charging capabilities and long cycle life, essential for electric mobility.
- Grid Energy Storage: LTO batteries are ideal for stabilizing power grids by storing excess energy generated from renewable sources like wind and solar power. Their rapid discharge capabilities help balance supply and demand effectively.
- Public Transport: Buses and trams benefit from quick recharging times during short stops at stations or terminals.
- Consumer Electronics: Certain high-performance gadgets utilize LTO technology for rapid charging, enhancing user experience in laptops and smartphones.
Part 6. How do lithium titanate batteries compare to other battery technologies?
When comparing lithium titanate batteries with other popular battery technologies like traditional lithium-ion and lead-acid batteries, several vital differences emerge:
Lithium Titanate vs. Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries are widely used due to their high energy density and efficiency; however, they have limitations in terms of safety and cycle life compared to LTO technology. Here’s how they stack up:
- Energy Density: Lithium-ion batteries have higher energy density than LTOs.
- Cycle Life: LTOs offer significantly longer cycle life.
- Charge Time: LTOs can be charged much faster than typical lithium-ion cells.
- Safety: LTOs are generally safer due to the lower risk of thermal runaway.
Lithium Titanate vs. Lead-Acid Batteries
Lead-acid batteries have been around for decades but face challenges in terms of efficiency and lifespan:
- Energy Density: Lithium titanate has a higher energy density than lead acid.
- Cycle Life: LTOs significantly outperform lead-acid in cycle life.
- Charge Time: Lead-acid requires longer charging times compared to LTOs.
- Weight: Lithium titanate is lighter than lead-acid options.
Here’s a simple table summarizing these comparisons:
| Feature | Lithium Titanate | Lithium-Ion | Lead-Acid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | Low | High | Medium |
| Cycle Life | Very High | Medium | Low |
| Charge Time | Fast | Moderate | Slow |
| Safety | High | Moderate | Low |
| Weight | Light | Moderate | Heavy |
This comparison highlights that while each battery type has strengths and weaknesses, lithium titanate stands out regarding safety and longevity.
Part 7. Are there any safety concerns with lithium titanate batteries?
While generally considered safe due to their thermal stability and lower risk of combustion compared to other technologies, users should still be aware of potential safety considerations:
- Overcharging Risks: Like all rechargeable batteries, overcharging can lead to degradation over time or potential failure if not appropriately managed.
- Physical Damage: Any battery can pose risks if physically damaged; thus, proper handling and storage are essential.
In summary, when used correctly within specified parameters, LTO batteries present minimal safety concerns compared to other battery technologies.
Part 8. How do you maintain a lithium titanate battery?
Proper maintenance can significantly extend the lifespan and performance of a lithium titanate battery:
- Avoid Extreme Temperatures: Store and operate within recommended temperature ranges to prevent damage or performance degradation.
- Regular Charging Cycles: Charge your battery regularly rather than allowing it to drain completely; this helps maintain optimal performance levels over time.
- Monitor Health Indicators: If your device has health monitoring features or software available, monitor them for any signs indicating degradation or issues developing within the battery system.
Part 9. FAQs
-
What is the lifespan of a lithium titanate battery?
Lithium titanate batteries can last over 10,000 cycles under optimal conditions, significantly outlasting traditional lithium-ion options. -
Can I use a lithium titanate battery in my electric vehicle?
Yes! Many electric vehicles utilize lithium titanate technology due to its fast charging capabilities and long cycle life. -
Are there any environmental concerns with using lithium titanate batteries?
Lithium titanate batteries have a lower environmental impact than other types because they contain fewer toxic materials and are more recyclable. -
How do I know if my device uses a lithium titanate battery?
Check your device’s specifications or consult the manufacturer’s documentation; they typically indicate the type of battery used. -
What makes lithium titanate better than traditional lead-acid batteries?
Lithium titanate offers faster charging times, longer cycle life, better efficiency at extreme temperatures, and better safety than lead-acid alternatives.
Related Tags:
More Articles

How Long Do Rechargeable AA Batteries Last?
How long do rechargeable AA batteries last? Compare NiMH and lithium AA lifespan, recharge cycles, key factors, and performance vs alkaline batteries.
12V STD vs 12V AGM: Meaning, Differences, and Which Is Better
Understand what STD and AGM batteries mean, their key differences, and which 12V battery fits your needs best in 2026.
Battery Reconditioning Explained: A Comprehensive Guide
Learn what battery reconditioning is, how it works, how long it takes, and when reconditioning chargers are used for lead-acid and lithium-ion batteries.
Recommended 10 Best Batteries For Smoke Detectors
Compare the best batteries for smoke detectors in 2026. See which 9V lithium and alkaline batteries last longest and perform best in smoke alarms.
Triple A Battery Voltage: Everything You Need to Know
How many volts is a AAA battery? See a clear AAA battery voltage chart, compare alkaline, lithium and NiMH cells, and learn how voltage affects device use.