Solar energy is revolutionizing how we power our lives, and thin film solar cells are at the forefront of this transformation. But what exactly are they, and why are they gaining so much attention? This article explores everything you need to know about thin film solar cells, from how they work to their benefits, applications, and more. Whether you’re a homeowner considering solar energy or someone curious about renewable technologies, this guide will give you all the essential details in a clear, conversational style.
Part 1. What is a thin film solar cell?
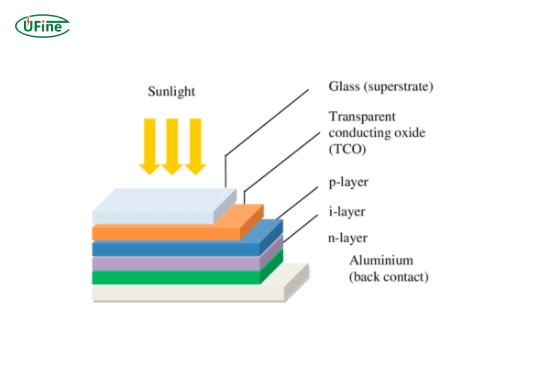
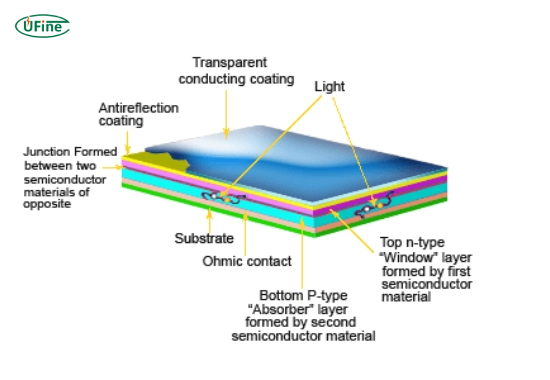
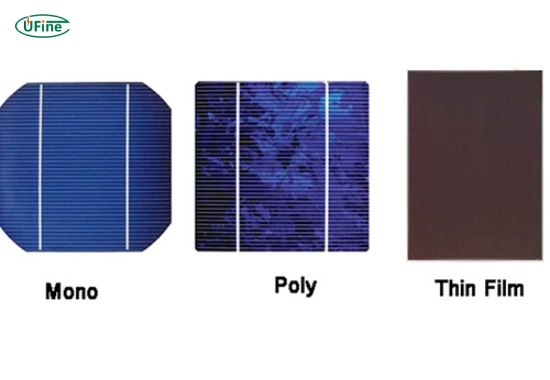
A thin-film solar cell is a photovoltaic device that converts sunlight into electricity. Unlike traditional silicon-based solar panels, thin-film solar cells are made by depositing one or more layers of photovoltaic material onto a substrate. These layers are incredibly thin—often just a few micrometers thick—hence the name “thin film.”
This lightweight, flexible design makes thin-film solar cells a versatile option for many applications, particularly where traditional solar panels may not be practical.
Part 2. How does a thin film solar cell work?
Thin film solar cells work on the same basic principle as other solar cells: they convert sunlight into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown:
- Absorption of sunlight: The thin film layer absorbs sunlight, which excites electrons in the material.
- Generation of electric charge: The excited electrons create an electric current as they move through the material.
- Electricity output: The electric charge is collected and directed to an external circuit, providing usable electricity.
The key difference is in the materials used and the manufacturing process, which allows thin-film solar cells to be more flexible and lightweight than traditional solar panels.
Part 3. What materials are used in thin film solar cells?
Thin film solar cells are made using various materials, each with advantages and applications. The most common types include:
- Amorphous Silicon (a-Si): A non-crystalline silicon that is cheap and easy to produce.
- Cadmium Telluride (CdTe): Known for its high efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
- Copper Indium Gallium Selenide (CIGS): Offers high efficiency and flexibility, making it suitable for curved or irregular surfaces.
- Organic Photovoltaics (OPVs): Made from organic compounds, these are lightweight and can be manufactured using eco-friendly processes.
Each material has strengths, making thin film solar cells adaptable to various applications.
Part 4. What are the advantages of thin film solar cells?
Thin film solar cells have numerous advantages, making them a popular choice in modern solar technology. Here are some of the key benefits:
- Lightweight: The thin layers reduce the overall weight, making transportation and installation easier.
- Flexibility: Thin film solar cells can be installed on curved or irregular surfaces, unlike rigid traditional panels.
- Affordable manufacturing: The production process is less energy-intensive, which helps lower costs.
- Better performance in low light: Thin film solar cells are more efficient in dim conditions, such as cloudy weather or indoor lighting.
- Aesthetic appeal: Their sleek, thin design can blend seamlessly into buildings and other structures.
These features make thin film solar cells an excellent choice for residential and commercial applications.
Part 5. What are the disadvantages of thin film solar cells?
While thin film solar cells have many benefits, they also have some drawbacks. Here are the main challenges:
- Lower efficiency: Compared to traditional silicon panels, thin film solar cells often have lower energy conversion efficiency.
- Shorter lifespan: They typically have a shorter operational lifespan, requiring replacement sooner.
- Use of rare materials: Some thin film technologies rely on rare or toxic materials, like cadmium, which raises environmental concerns.
- Higher installation costs for specific applications: While the cells are cheaper, the need for specialized installation techniques can sometimes increase costs.
By weighing these pros and cons, you can determine if thin film solar cells are the right choice for your energy needs.
Part 6. What are the applications of thin film solar cells?
Thin film solar cells are incredibly versatile, and their unique properties allow them to be used in a variety of applications:
- Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV): Thin film solar cells can be integrated into windows, walls, and roofs, providing clean energy while maintaining aesthetic appeal.
- Portable solar devices: Their lightweight and flexible nature makes them ideal for powering portable electronics like smartphones, laptops, and camping gear.
- Agriculture: Thin film solar cells can be used in greenhouses, as they allow some sunlight to pass through while generating electricity.
- Transportation: They are being explored in electric cars, trains, and solar-powered aircraft.
- Off-grid systems: Perfect for remote areas without access to traditional power grids, such as rural villages or isolated research stations.
These diverse applications showcase the potential of thin film solar cells to transform the energy landscape.
Part 7. How do thin film solar cells compare to traditional solar panels?
When comparing thin-film solar cells to traditional solar panels, several factors must be considered, including efficiency, cost, weight, flexibility, and durability. Both technologies serve different purposes and excel in specific applications. Below is a detailed description of the differences to help you make an informed choice.
Efficiency
Traditional solar panels, primarily made of crystalline silicon, are more efficient at converting sunlight into electricity. Their efficiency typically ranges from 15% to 22%. On the other hand, thin-film solar cells have lower efficiency, usually 10% to 12%, although some advanced thin-film technologies like CIGS or perovskite cells can reach efficiencies of 13% to 18%.
Thickness and Weight
Thin-film solar cells are much thinner and lighter than traditional panels. While traditional panels are rigid and heavy due to their thick silicon wafers, thin-film panels are made by depositing micrometer-thin photovoltaic layers onto lightweight substrates. This makes them ideal for applications where weight and flexibility are crucial, such as portable solar devices or curved surfaces.
Cost
Thin film solar cells are generally cheaper due to their more straightforward production process and lower material requirements. However, their lower efficiency means that more surface area is needed to generate the same amount of power, which can increase installation costs in specific scenarios.
While traditional panels are more expensive to produce, they often have a better return on investment over time due to their higher efficiency and longer lifespan.
Lifespan and Durability
Traditional solar panels have a longer lifespan, typically 20–25 years, with minimal efficiency loss. Thin-film solar cells, on the other hand, generally last 10–20 years and may degrade faster, especially in harsh weather conditions.
Flexibility and Installation
Thin film solar cells are flexible and can be installed on uneven or curved surfaces, making them suitable for unique use cases. Traditional panels are rigid and limited to flat installations on rooftops or ground-mounted systems.
Performance in Low Light
Thin film solar cells perform better in low-light conditions, such as cloudy weather or shaded areas, than traditional panels. This makes them a good option for regions with inconsistent sunlight.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Thin Film Solar Cells | Traditional Solar Panels |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | 10%–12% (up to 18% for advanced types) | 15%–22% |
| Thickness | Very thin (micrometers) | Thick (200–300 micrometers) |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavy |
| Cost | Lower manufacturing cost, but more area needed | Higher upfront cost, better ROI |
| Lifespan | 10–20 years | 20–25 years |
| Durability | Less durable; prone to faster degradation | Highly durable, withstands harsh weather |
| Flexibility | Flexible; suitable for curved or uneven surfaces | Rigid; limited to flat installations |
| Performance in low light | Better performance in low light conditions | Not as efficient in low light |
| Applications | Portable devices, curved surfaces, BIPV | Rooftop, ground-mounted solar farms |
Real-World Example
Suppose you have a standard residential rooftop and want to maximize energy output. Traditional solar panels are likely the better choice due to their higher efficiency and durability. However, thin film solar cells would be ideal if you want to integrate solar into a curved building façade or need a lightweight solution for portable power.
Understanding these differences lets you choose the solar technology that best meets your needs and project requirements.
Part 8. What is the future of thin film solar cells?
The future of thin film solar cells looks promising as technology advances. Researchers are working to improve their efficiency and durability while reducing environmental impacts. Some key trends include:
- Perovskite thin-film solar cells offer high efficiency and low-cost manufacturing and are poised to revolutionize the industry.
- Self-healing materials: Scientists are exploring materials that can repair themselves, extending the lifespan of solar cells.
- Wider adoption: As costs continue to decrease, thin film solar cells are expected to become more accessible to consumers and businesses.
With these developments, thin film solar cells will likely play a significant role in the global transition to renewable energy.
Part 9. Why choose thin film solar cells?
If you’re looking for a lightweight, flexible, and aesthetically appealing solar solution, thin-film solar cells are an excellent choice. They may not match the efficiency of traditional panels, but their unique properties make them ideal for specialized applications.
From powering portable gadgets to integrating into building designs, thin film solar cells offer a glimpse into the future of renewable energy. Understanding their advantages and limitations lets you decide whether they fit your needs.
Artikel Terkait: Solar Batteries and Rechargeable Batteries: Are They the Same?
Part 10. FAQs
-
Are thin film solar cells better than traditional solar panels?
It depends on the application. Thin film solar cells are better for lightweight, flexible, or aesthetic installations. At the same time, traditional panels offer higher efficiency for residential or commercial roofs. -
How long do thin film solar cells last?
On average, thin-film solar cells last 10–20 years, shorter than the lifespan of traditional solar panels (20–25 years). -
Can thin film solar cells work indoors?
Yes, thin film solar cells can generate electricity from low light, making them suitable for indoor applications or cloudy conditions. -
Are thin film solar cells environmentally friendly?
While they reduce carbon emissions, some thin film technologies use toxic or rare materials, which can raise environmental concerns. However, advancements are being made to address these issues. -
How much do thin film solar cells cost?
Thin film solar cells are generally cheaper than traditional panels, but installation costs may vary depending on the application.
Related Tags:
More Articles

How to Choose the Best Floor Scrubber Battery for Commercial Cleaning?
Selecting the ideal floor scrubber battery ensures a long runtime, rapid charging, and minimal maintenance for efficient commercial cleaning operations.
Battery for Blower vs Battery for Leaf Vacuum: Which One Should You Choose?
Battery for blower vs leaf vacuum—learn the key differences in power, fit, and runtime to choose the right battery for your outdoor tool needs.
How to Choose the Right Battery for Blower?
Choosing the right blower battery? Consider voltage, capacity, chemistry & usage. This guide helps match the best battery for peak performance.
How to Choose the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries?
Choosing the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries? Discover key factors such as size, material, and safety for optimal protection and performance.
7 Critical Elements on a Lithium Battery Shipping Label
What must be on a lithium battery shipping label? Learn 7 key elements to ensure safety, legal compliance, and correct handling across all transport modes.