A tubular battery is a specialized type of lead-acid battery renowned for its unique design and superior performance. Unlike traditional flat plate batteries, they feature tubular plates that enhance their efficiency and longevity. This makes them an excellent choice for various applications, particularly in energy storage systems. This article will explore the construction, working mechanism, advantages, applications, maintenance tips, and common misconceptions associated with tubular batteries. By the end, you will have a comprehensive understanding of tubular batteries and why they might be the right choice for your energy needs.
Part 1. What is a tubular battery?
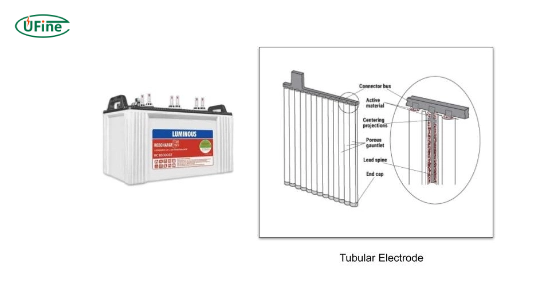
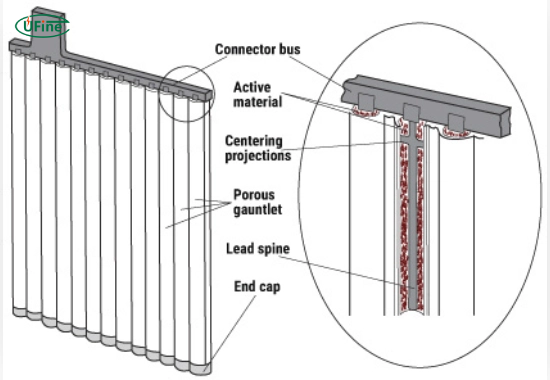
A tubular battery is defined by its distinctive construction featuring tubular plates made from lead dioxide. These plates maximize the surface area for chemical reactions, significantly improving the battery’s efficiency and performance. The electrolyte used in these batteries is typically diluted sulfuric acid, which facilitates the necessary chemical processes during charging and discharging cycles. Tubular batteries are commonly used in applications where reliable energy storage is crucial, such as renewable energy systems, telecommunications, and industrial power backup solutions.
Part 2. What are the components of a tubular battery?
A tubular battery comprises several key components that contribute to its functionality and efficiency:
- Tubular Plates: The hallmark of a tubular battery is its tubular plates made from lead dioxide. These plates are designed to maximize surface area for chemical reactions, which enhances overall efficiency.
- Electrolyte: The electrolyte in a tubular battery is typically diluted sulfuric acid. It plays a crucial role in facilitating the flow of ions between the positive and negative plates during the charging and discharging processes.
- Container: Tubular batteries are housed in robust containers made from durable materials like polypropylene or ABS plastic. These materials protect the internal components from environmental factors such as moisture and temperature fluctuations.
- Vent Caps: These caps allow gases produced during charging to escape while preventing contaminants from entering the battery, ensuring safe operation.
Part 3. How does a tubular battery work?
The operation of a tubular battery can be broken down into several stages:
- Charging: When connected to a power source, an electric current flows through the electrolyte, causing chemical reactions at the plates. Lead dioxide at the positive plate reacts with hydrogen ions from the electrolyte, converting it into lead sulfate.
- Discharging: When the battery is connected to a load, the stored chemical energy is converted back into electrical energy. The lead sulfate reverts to lead dioxide and lead at the respective plates, releasing electrons that power connected devices.
- Cycle Repetition: This process can be repeated multiple times, allowing for extensive use without significant degradation if appropriately maintained.
Part 4. What are the advantages of tubular batteries?
Tubular batteries offer several benefits that make them an attractive option for various applications:
- Longer Lifespan: Due to their robust design and construction, tubular batteries typically range from 5 to 12 years, significantly longer than conventional flat plate batteries.
- Higher Efficiency: The larger surface area of tubular plates allows for more efficient chemical reactions, resulting in better performance and higher energy output.
- Low Maintenance: Many modern tubular batteries are designed to be low-maintenance, requiring minimal intervention over their lifespan.
- Deep Discharge Capability: Tubular batteries can handle deep discharges better than traditional batteries, making them suitable for applications where complete discharge is common.
Part 5. Where are tubular batteries commonly used?
Tubular batteries find application in various sectors due to their reliability and efficiency:
- Renewable Energy Systems: They are often used in solar power systems where energy storage is crucial for maintaining power supply during non-sunny periods.
- Telecommunications: Tubular batteries provide backup power for telecom towers and data centers, ensuring uninterrupted service even during outages.
- Industrial Applications: Many industries rely on tubular batteries for uninterrupted power supply in critical operations such as manufacturing and emergency systems.
- Inverter Systems: They are widely used in inverter setups for homes and businesses to store energy for later use during outages or peak demand times.
Part 6. How do you maintain a tubular battery?
Proper maintenance is essential for maximizing the lifespan and performance of a tubular battery:
- Regular Inspection: Check terminals and connections for signs of corrosion or damage. Keeping terminals clean can prevent performance issues.
- Electrolyte Levels: Ensure that electrolyte levels are adequate; top up with distilled water if necessary to maintain optimal performance.
- Cleaning: Clean the battery terminals to prevent buildup that can affect performance. Mix baking soda and water to neutralize any acid spills during cleaning.
- Temperature Monitoring: Store and operate the battery in environments with moderate temperatures (ideally between 20°C and 25°C) to avoid overheating or freezing conditions that could damage the battery.
Part 7. What are common misconceptions about tubular batteries?
Several misconceptions surround tubular batteries that can mislead potential users:
- They Are Maintenance-Free: While many modern designs require less maintenance than older models, they still need periodic electrolyte levels and terminal conditions checks.
- They Are Too Expensive: Although initial costs may be higher than conventional batteries, their longevity and efficiency often result in lower overall costs over time due to reduced replacement frequency.
- They Are Only Suitable for Large Applications: Tubular batteries come in various sizes and capacities, making them suitable for small-scale (home solar systems) and large-scale (industrial power backup) applications.
Part 8. How do tubular batteries compare to other types of batteries?
When evaluating different types of batteries, it’s essential to consider their unique characteristics based on real data:
Lifespan:
- Tubular Batteries typically last between 5 to 12 years.
- Flat Plate Batteries usually last around 3 to 5 years.
- Lithium-ion batteries can last up to 15 years or more with proper care.
Maintenance Requirements:
- Tubular Batteries require low maintenance but need periodic checks.
- Flat Plate Batteries require moderate maintenance.
- Lithium-ion batteries are generally low-maintenance, with no need for regular electrolyte checks.
Efficiency Ratings:
- Tubular Batteries have an efficiency rating of around 80%–85%.
- Flat Plate Batteries typically have an efficiency rating of about 70%–75%.
- Lithium-ion batteries boast high efficiency ratings of around 90%–95%.
Cost Considerations:
- Tubular Batteries have moderate upfront costs but offer long-term savings.
- Flat Plate Batteries are generally cheaper initially but may require more frequent replacements.
- Lithium-ion batteries have higher initial costs but can provide significant savings over time due to their longevity.
Here’s a comparison table summarizing these features:
| Feature | Tubular Battery | Flat Plate Battery | Lithium-Ion Battery |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lifespan | 5 to 12 years | 3 to 5 years | Up to 15+ years |
| Maintenance | Low | Moderate | Low |
| Efficiency | 80%–85% | 70%–75% | 90%–95% |
| Cost | Moderate | Lower | Higher |
| Deep Discharge Tolerance | Excellent | Poor | Good |
Part 9. Are there any safety concerns with tubular batteries?
While generally safe when used correctly, there are some safety considerations:
- Acid Spills: Handle with care as sulfuric acid can cause burns; ensure proper containment during use and storage.
- Gas Emission: During charging, gases like hydrogen may be emitted; ensure adequate ventilation in enclosed spaces to prevent buildup that could lead to explosions or fires.
- Overcharging Risks: Overcharging can lead to overheating or damage; use appropriate chargers with built-in protections against overcharging scenarios.
Part 10. What should you consider when buying a tubular battery?
When purchasing a tubular battery, keep these factors in mind:
- Capacity Needs: Assess your energy storage requirements based on your application (e.g., home use vs. industrial use) to choose an appropriately sized battery that meets your needs.
- Brand Reputation: Opt for reputable brands known for the quality and reliability of their products; check reviews and ratings before deciding.
- Warranty Period: Look for warranties that indicate confidence in the product’s longevity and performance; more extended warranties often signify better quality assurance from manufacturers.
- Cost vs. Value: Consider not just the upfront cost but also long-term value based on lifespan, efficiency ratings, and maintenance needs; this will help you make an informed decision that balances initial investment with future savings.
Part 11. FAQs
-
What is the average lifespan of a tubular battery?
The average lifespan ranges from 5 to 12 years, depending on usage conditions and maintenance practices. -
Can I use a tubular battery with solar panels?
Yes! Tubular batteries are ideal for solar energy systems due to their deep discharge capabilities and longevity. They are perfect for storing solar energy generated during sunny days at night or during cloudy periods. -
How do I know when my tubular battery needs replacing?
Signs include reduced capacity (shorter usage time), visible corrosion on terminals or casing, or physical damage such as bulging or leaks indicating potential failure. -
Are tubular batteries environmentally friendly?
While they contain lead and sulfuric acid, proper recycling processes exist that minimize environmental impact when disposed of correctly; many manufacturers also offer take-back programs for old batteries. -
Can I install a tubular battery myself?
While professional installation may be recommended to ensure safety and optimal performance, improper installation can lead to safety hazards or reduced efficiency.
Related Tags:
More Articles

How to Choose the Right Electric Fence Battery?
Choosing the right electric fence battery is key to security. This guide helps you pick a reliable farm, garden, or animal power source.
What Are Lithium Pouch Cells?
Explore how lithium pouch cells work, their structure, advantages, and uses. Learn from a trusted supplier like Ufine Battery for custom lithium solutions.
The Evolution of Ring Battery Pack Technology in Lithium Battery Manufacturing
Ring battery packs are reshaping lithium battery tech. Discover their evolution, key uses, and why they matter for the future of energy storage.
Lithium vs Lithium Salt: What’s the Difference?
Lithium is a pure metal, while lithium salts are stable battery compounds. Learn their key roles and differences in battery manufacturing.
What You Need to Know About AA 3.6V Lithium Battery
Learn all about AA 3.6V lithium batteries—voltage, size, capacity, uses, and the best replacements. Discover why they’re powerful, and highly reliable.