- Part 1. What is a VRB battery?
- Part 2. What is a lithium-ion battery?
- Part 3. What are the differences between VRB and lithium-ion batteries?
- Part 4. Which battery is better for renewable energy storage?
- Part 5. Environmental impact of VRB vs. lithium-ion batteries
- Part 6. Applications of VRB and lithium-ion batteries
- Part 7. Advantages of VRB batteries
- Part 8. Advantages of lithium-ion batteries
- Part 9. Challenges of using VRB batteries
- Part 10. FAQs
Batteries have become a cornerstone of modern energy storage as the world moves toward more sustainable energy solutions. Among the many battery technologies available today, Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries (VRB) and Lithium-Ion Batteries stand out as two of the most important. But what exactly is a VRB battery, and how does it compare to lithium-ion batteries? This article will explore these two technologies’ unique features, benefits, and drawbacks.
Part 1. What is a VRB battery?
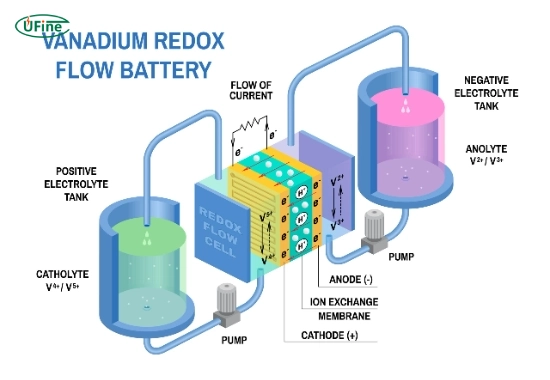
A Vanadium Redox Flow Battery (VRB), also known as a Vanadium Flow Battery, is a rechargeable battery that stores and releases energy using vanadium ions in different oxidation states. Unlike traditional batteries that store energy in solid electrodes, VRBs store energy in liquid electrolytes, which flow through the system during charge and discharge cycles.
How does a VRB battery work?
VRB batteries consist of two tanks filled with liquid electrolytes: one with a positive electrolyte and the other with a negative electrolyte. A pump moves these liquids through a cell stack containing a membrane, where the electrochemical reaction occurs. During charging, electricity causes vanadium ions in the electrolytes to change their oxidation states, storing energy. When discharging, the system reverses the process, releasing the stored energy.
Key features of VRB batteries
- Long lifespan: VRBs can last 10–20 years with minimal degradation.
- Scalability: The energy capacity of a VRB can be increased simply by adding more electrolyte solutions.
- Safety: VRBs are non-flammable and operate at room temperature, making them safer than many other battery types.
Part 2. What is a lithium-ion battery?
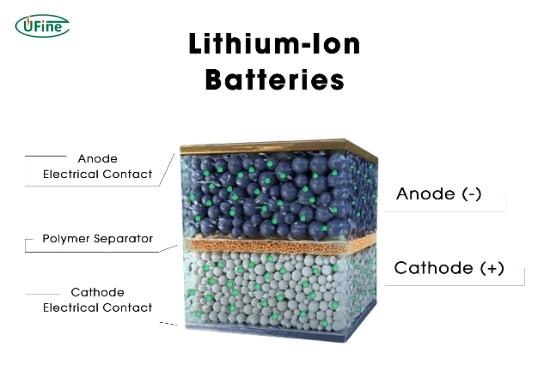
A lithium-ion battery is a widely used rechargeable battery that stores energy in solid electrodes of lithium compounds. People commonly use these batteries in smartphones, laptops, electric vehicles, and renewable energy systems.
How does a lithium-ion battery work?
Lithium-ion batteries transfer lithium ions between a positive electrode (cathode) and a negative electrode (anode) through an electrolyte. Lithium ions move from the cathode to the anode, storing energy during charging. During discharging, the ions move back to the cathode, releasing energy.
Key features of lithium-ion batteries
- High energy density: Lithium-ion batteries can store much energy in a small space.
- Fast charging: These batteries can be charged more quickly than other technologies.
- Wide application: Lithium-ion batteries are versatile and used in everything from small electronics to large-scale energy storage.
Vanadium in Lithium Batteries: How It Contributes to Power Efficiency and Longevity
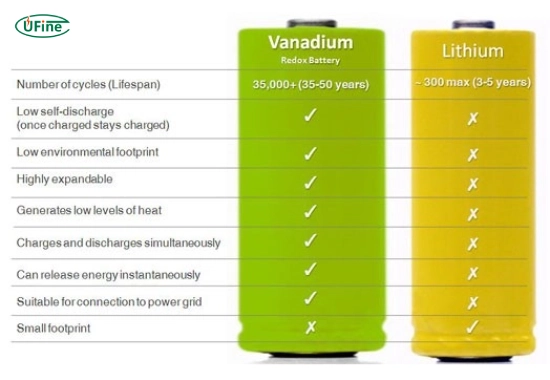
Part 3. What are the differences between VRB and lithium-ion batteries?
While VRB and lithium-ion batteries are energy storage solutions, they fundamentally differ in design, performance, and applications. Here’s a breakdown:
1. Energy storage mechanism
- VRB: Stores energy in liquid electrolytes.
- Lithium-ion: Stores energy in solid electrodes.
2. Lifespan
- VRB: Can last 10–20 years with almost no degradation.
- Lithium-ion: Typically lasts 5–10 years, with performance gradually degrading over time.
3. Scalability
- VRB: Highly scalable by increasing the size of electrolyte tanks.
- Lithium-ion: Limited scalability due to the fixed capacity of cells.
4. Energy density
- VRB: Lower energy density, making it less compact.
- Lithium-ion: High energy density, ideal for portable applications.
5. Safety
- VRB: Non-flammable and operates at room temperature.
- Lithium-ion: Risk of overheating and thermal runaway, which can cause fires.
6. Cost
- VRB: Higher upfront cost but lower operating costs over time.
- Lithium-ion: Lower initial cost but higher maintenance and replacement costs.
Part 4. Which battery is better for renewable energy storage?
When it comes to renewable energy storage, both VRB and lithium-ion batteries have distinct advantages:
VRB batteries are ideal for large-scale applications, such as storing energy from solar farms or wind turbines. Their long lifespan and scalability make them cost-effective for grid-level energy storage.
Due to their compact size and high energy density, lithium-ion batteries are better suited for smaller-scale applications, such as home solar systems or electric vehicles.
Part 5. Environmental impact of VRB vs. lithium-ion batteries
VRB batteries
- Eco-friendly materials: Vanadium is a recyclable and abundant resource, making VRBs more sustainable.
- Long lifespan: Fewer replacements reduce waste over time.
Lithium-ion batteries
- Mining concerns: Lithium and cobalt mining can have significant environmental and ethical implications.
- Recycling challenges: Lithium-ion batteries are more complicated to recycle due to their complex chemistry.
Part 6. Applications of VRB and lithium-ion batteries
VRB applications
- Grid-scale energy storage
- Backup power for industrial facilities
- Integration with renewable energy sources
Lithium-ion applications
- Electric vehicles
- Consumer electronics (smartphones, laptops, etc.)
- Residential energy storage systems
Part 7. Advantages of VRB batteries
- No degradation: VRBs do not lose capacity over time, unlike lithium-ion batteries.
- Safety: The non-flammable nature of VRBs makes them safer for large-scale use.
- Sustainability: Recyclable materials reduce environmental impact.
Part 8. Advantages of lithium-ion batteries
- Compact size: High energy density allows for lightweight and portable designs.
- Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of applications.
- Cost-effective for small systems: Lower upfront costs for smaller setups.
Part 9. Challenges of using VRB batteries
- High upfront cost: The initial investment for a VRB system can be significant.
- Low energy density: VRBs require more physical space compared to lithium-ion batteries.
- Complexity: Pumping systems and liquid storage add to the system’s complexity.
Part 10. FAQs
-
What is the main difference between VRB and lithium-ion batteries?
The main difference lies in their energy storage mechanism: VRBs use liquid electrolytes, while lithium-ion batteries use solid electrodes. -
Which battery lasts longer, VRB or lithium-ion?
VRBs last longer, with a lifespan of 10–20 years, compared to 5–10 years for lithium-ion batteries. -
Are VRB batteries safer than lithium-ion batteries?
Yes, VRBs are non-flammable and operate at room temperature, making them safer than lithium-ion batteries, which can overheat and catch fire. -
Why are VRB batteries more expensive than lithium-ion batteries?
The higher cost of VRBs is due to the materials and complexity of the system. However, their long lifespan and scalability can offset these costs over time. -
Which battery is better for renewable energy storage?
VRBs are better for large-scale renewable energy storage, while lithium-ion batteries are ideal for smaller, portable applications.
Related Tags:
More Articles
Capacitor vs Battery: What is the Difference?
Capacitor vs battery explained in detail. Learn the difference between capacitor and battery in energy storage, charging speed, lifespan, and real applications.
18650 Battery vs AA: Which Is Better for Your Device?
Compare 18650 vs AA batteries in capacity, voltage, rechargeability, and applications. Learn which battery type fits high-drain or everyday devices.
What is the Difference Between Battery Cell, Battery Control Module, and Battery Pack?
Compare battery cells, modules, and packs. Learn functions, design differences, control modules, and selection tips for EV, ESS, and industrial use.
How to Prevent LiPo Battery Explosion?
Can LiPo batteries explode or catch fire? Learn key causes of LiPo battery fires and proven charging, storage, and handling tips to reduce explosion risk.
Aluminium Ion Battery vs Lithium-Ion: A Detailed Comparison
Compare aluminium ion battery vs lithium-ion battery in energy density, charging speed, safety, cost, and uses. A practical guide for engineers and buyers.