Quick Answer: A fully charged 12V AGM battery typically reads 12.6–12.8V at rest (open-circuit). During charging, absorption voltage is 14.4–14.8V, and float voltage is 13.5–13.8V. Proper monitoring ensures long life and avoids damage.
Key Takeaways:
- Open-Circuit Voltage (OCV) shows the battery’s true charge state.
- Absorption and float voltages prevent overcharging while keeping batteries ready.
- Temperature, charging current, and capacity affect voltage behavior.
- Voltage charts help quickly gauge state-of-charge (SOC).
- Using an AGM-specific charger and performing regular maintenance prolongs battery life.
Part 1. Learn AGM battery voltage
AGM batteries are a type of lead-acid battery that utilizes a unique construction method. Instead of using liquid electrolyte, they employ a fiberglass mat that absorbs the electrolyte, creating a sealed and spill-proof design. This construction method offers several advantages, including:
- Increased Safety: The sealed design eliminates the risk of spills and leaks, making them safer for various applications. This is particularly important in enclosed spaces or environments where spills could pose a hazard.
- Improved Performance: The absorbent glass mat allows for greater electrolyte contact with the lead plates, leading to higher efficiency and faster charging. This means AGM batteries can deliver more power and charge up quicker compared to traditional lead-acid batteries.
- Enhanced Durability: The sealed design and robust construction make AGM batteries more resistant to vibration and shock, making them ideal for mobile applications. This makes them a reliable choice for vehicles, marine applications, and other environments where they might experience rough handling.
The voltage of an AGM battery is a key indicator of its state of charge. It represents the electrical potential difference between the battery’s positive and negative terminals. A fully charged AGM battery typically has a voltage of 12.6 to 12.8 volts, indicating that it is ready to deliver maximum power. As the battery discharges, its voltage gradually decreases, reflecting the depletion of stored energy. This voltage drop is a natural process, but it’s important to monitor it to understand how much power remains in the battery.
AGM VS Lithium VS Lead-Acid Battery: Comprehensive Comparison
Part 2. AGM battery voltage types
| Voltage Type | Typical Value (12V AGM) | Purpose / Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Open-Circuit Voltage (OCV) | 12.6–12.8V | Shows SOC at rest |
| Charged Voltage | 14.4–14.8V | Maximum voltage during charging |
| Float Voltage | 13.5–13.8V | Maintains full charge over time |
| Absorption Voltage | 14.4–14.8V | Final stage of charging to top-off battery |
| Termination Voltage | 14.4–14.8V | Voltage where charger stops charging |
| Discharge Voltage | ~10.5V | Considered fully discharged |
While the overall voltage of an AGM battery is a crucial indicator, there are different types of voltage measurements that provide a more detailed picture of the battery’s state and performance:
- Open Circuit Voltage (OCV): This is the voltage you measure when the battery isn’t connected to anything. It’s a good indicator of the battery’s overall state of charge, with a fully charged AGM battery typically having an OCV of around 12.6 to 12.8 volts. However, it’s important to note that OCV can be influenced by factors like temperature and battery age.
- Charged Voltage: This is the voltage the battery reaches when it’s fully charged. It’s typically around 14.4 to 14.8 volts, depending on the charger and temperature. This voltage is crucial for ensuring that the battery is fully charged and ready to deliver its full capacity.
- Float Voltage: This is the voltage used to maintain a fully charged battery over time. It’s typically around 13.5 to 13.8 volts. Float voltage is used in applications where the battery needs to be kept at a constant state of charge, like in solar systems or backup power systems.
- Absorption Voltage: This is the voltage used to charge the battery to its full capacity. It’s typically around 14.4 to 14.8 volts. Absorption voltage is used during the final stages of charging to ensure that the battery is fully charged.
- Termination Voltage: This is the voltage at which the charger stops charging the battery. It’s typically around 14.4 to 14.8 volts. Termination voltage is important for preventing overcharging, which can damage the battery.
- Discharge Voltage: This is the voltage at which the battery is considered discharged. It’s typically around 10.5 volts. Discharge voltage is important for determining when the battery needs to be recharged to prevent deep discharges, which can shorten the battery’s lifespan.
The charged voltage of an AGM battery is a critical parameter for ensuring its optimal performance and longevity. It represents the maximum voltage the battery can achieve when fully charged, and it is essential for maximizing the battery’s capacity and minimizing its internal resistance.
A fully charged AGM battery will typically have a voltage of 12.6 to 12.8 volts, depending on the battery’s capacity, temperature, and age. Maintaining a charged voltage within this range ensures that the battery is ready to deliver its full power and minimizes the risk of premature degradation.
Part 3. AGM battery voltage charts
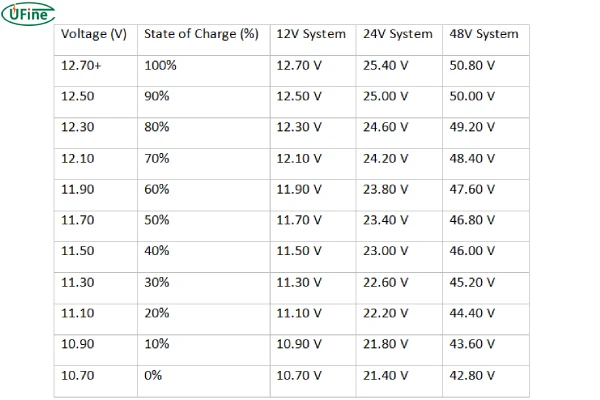
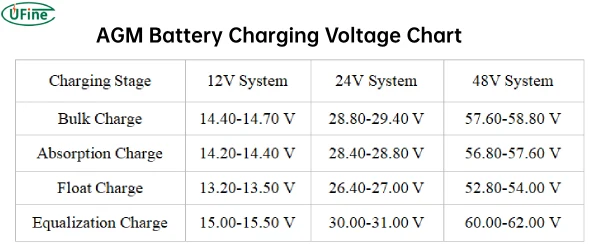
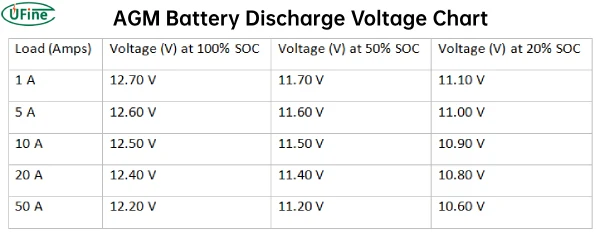
Voltage charts are helpful tools for understanding the relationship between AGM battery voltage and its state of charge.
These charts typically show voltage levels at different states of charge, from fully charged to deeply discharged.
They provide a visual representation of the battery’s voltage behavior and can help you determine the battery’s state of charge based on its voltage reading.
AGM Battery voltage chart for State of Charge (SOC)
AGM Battery Discharge Voltage Chart
AGM Battery Charging Voltage Chart
Part 4. What is the charged voltage of an AGM battery?
The charged voltage of an AGM battery is the voltage it reaches when it’s fully charged. It’s the maximum voltage the battery can hold. This voltage is typically around 14.4 to 14.8 volts. It’s important to note that the charged voltage can vary slightly depending on the battery’s capacity, temperature, and age.
Part 5. Factors influencing charged voltage
Several factors can influence the charged voltage of an AGM battery:
- Battery Capacity: Larger capacity batteries tend to have slightly higher charged voltages than smaller capacity batteries. This is because they have more lead plates and electrolyte, which can store more energy. The increased storage capacity allows for a higher electrical potential difference, resulting in a slightly higher charged voltage.
- Charging Current: The charging current used to charge the battery can also affect its charged voltage. Higher charging currents can lead to slightly higher charged voltages, but it’s important to note that excessive charging currents can damage the battery. This is because high currents can generate heat, which can accelerate the breakdown of the battery’s internal components.
- Temperature: Temperature plays a significant role in charging an AGM battery. Higher temperatures can lead to faster charging but can also increase the risk of overcharging and damage. Lower temperatures can slow down the charging process and reduce the battery’s capacity. This is why it’s important to charge AGM batteries in a moderate temperature range to ensure optimal charging and prevent damage.
Part 6. Charging AGM batteries properly
Charging an AGM battery properly is crucial for maximizing its lifespan and ensuring its optimal performance. Here are some key points to keep in mind:
- Use a Suitable Charger: Use a charger specifically designed for AGM batteries. These chargers are designed to deliver the correct voltage and current for optimal charging and prevent overcharging. Using a charger that is not specifically designed for AGM batteries can lead to overcharging or undercharging, which can damage the battery.
- Follow Charging Instructions: Consult the manufacturer’s instructions for your specific AGM battery. They will provide guidance on the appropriate charging current, voltage, and time. These instructions will vary depending on the battery’s capacity and other factors.
- Avoid Overcharging: Overcharging can damage an AGM battery by accelerating the breakdown of the lead plates and electrolyte. Make sure your charger has a built-in overcharge protection feature. Overcharging can lead to excessive heat generation, which can damage the battery’s internal components.
- Monitor Battery Temperature: Monitor the battery’s temperature during charging, especially in hot or cold environments. Excessive heat or cold can affect the charging process and potentially damage the battery. It’s best to charge AGM batteries in a moderate temperature range to ensure optimal charging and prevent damage.
- Regular Maintenance: Regularly check the battery’s terminals for corrosion and clean them as needed. Also, inspect the battery’s case for any signs of damage or leaks. Regular maintenance can help extend the battery’s lifespan and prevent premature failure.
Common Applications & Charging Strategies
| Application | Charging Strategy | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| RV / Marine | Absorption 14.4–14.8V, float 13.6V | High vibration; AGM-specific charger recommended |
| Solar / Backup UPS | Float 13.5–13.8V | Keep battery topped off; avoid deep discharges |
| Automotive Start | Bulk 14.4–14.8V | Must handle high cranking currents |
Tip: For high-cycle or high-drain use, consider comparing AGM vs Lithium for cost and lifespan.
Part 7. FAQs
What is the fully charged voltage of an AGM battery?
12.6–12.8V at rest (OCV), 14.4–14.8V during charging.
Why is float voltage lower than absorption voltage?
Float voltage maintains SOC without overcharging, preserving battery life.
Can I use a standard lead-acid charger for AGM batteries?
Not recommended. AGM-specific chargers ensure correct voltage and prevent damage.
How does temperature affect AGM charging?
High temperatures can overcharge; low temperatures reduce effective capacity. Charge in moderate temperatures.
How do I know when an AGM battery needs replacing?
Signs include inability to hold charge, voltage drops under load, visible bulges, or electrolyte leakage.
Related Tags:
More Articles
Capacitor vs Battery: What is the Difference?
Capacitor vs battery explained in detail. Learn the difference between capacitor and battery in energy storage, charging speed, lifespan, and real applications.
18650 Battery vs AA: Which Is Better for Your Device?
Compare 18650 vs AA batteries in capacity, voltage, rechargeability, and applications. Learn which battery type fits high-drain or everyday devices.
What is the Difference Between Battery Cell, Battery Control Module, and Battery Pack?
Compare battery cells, modules, and packs. Learn functions, design differences, control modules, and selection tips for EV, ESS, and industrial use.
How to Prevent LiPo Battery Explosion?
Can LiPo batteries explode or catch fire? Learn key causes of LiPo battery fires and proven charging, storage, and handling tips to reduce explosion risk.
Aluminium Ion Battery vs Lithium-Ion: A Detailed Comparison
Compare aluminium ion battery vs lithium-ion battery in energy density, charging speed, safety, cost, and uses. A practical guide for engineers and buyers.